Important Facts For Prelims
Growth of India’s Biotechnology Sector
- 10 Mar 2025
- 6 min read
Why in News?
At the “Emerging Innovations in Biochemistry and Biotechnology” conference, the Union Minister of Science & Technology highlighted the evolution of India’s biotechnology sector and biotechnology potential of the Himalayan region, especially J&K.
How has India’s Biotechnology Sector Evolved, and What is its Potential?
- About: It is the use of biological systems, organisms, or their components to create products and technologies that benefit agriculture, medicine, industry, and sustainability.
- Evolution:
- Foundational Phase (Pre-1986): Focus on fermentation-based industries (alcohol, antibiotics), composting, biofertilizers.
- Modern biotechnology started with the establishment of the Department of Biotechnology.
- Growth Phase (1990s–2000s): Key achievements included India’s first test-tube baby (1978), plant tissue culture, and diagnostic kits.
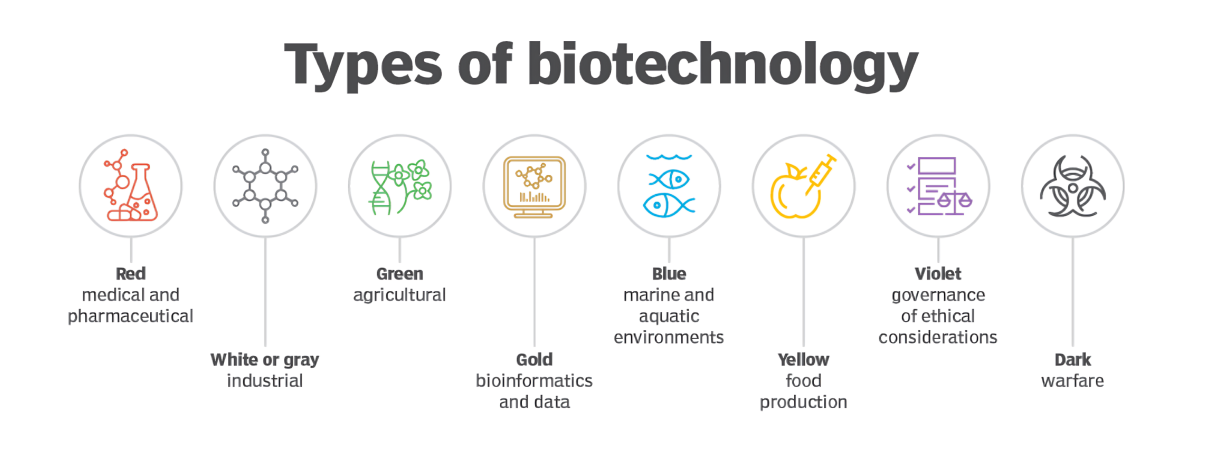
- Diversification (2000s–2010s): Expansion into red (medical), green (agriculture), white (industrial), and blue (marine) biotech.
- Industry Maturity (2010s–Present): Biotech recognized as a sunrise sector, with 3% global market share.
- Foundational Phase (Pre-1986): Focus on fermentation-based industries (alcohol, antibiotics), composting, biofertilizers.
- Growth & Potential: India's bioeconomy grew over 10 times in a decade (2014-24), rising from USD 10 billion in 2014 to USD 130 billion in 2024.
- Achievements: Development of the world’s first Human Papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine.
- Discovery of ‘Nafithromycin,’ a groundbreaking indigenous antibiotic.
- First successful gene therapy experiment for Hemophilia.
- Potential of India’s Biotechnology Sector:
- Healthcare & Biopharma:
- Expansion in biosimilars and gene therapy.
- Expected to become a global hub for affordable vaccines and therapeutics.
- Agricultural Biotechnology:
- Development of climate-resilient crops, biofertilizers, and precision farming.
- Key to ensuring food security and improving farm productivity.
- Environmental Sustainability:
- Application of bioremediation, waste-to-energy technologies, and green manufacturing.
- Economic and Employment Impact:
- Expected to generate millions of high-skilled jobs.
- Potential to add USD 300 billion by 2030.
- Healthcare & Biopharma:
- Achievements: Development of the world’s first Human Papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine.
- Biotechnology Potential of Himalayan region: Rich flora and medicinal plant diversity offer potential for pharmaceutical and herbal industries.
- Medicinal Plants: E.g., Artemisia annua is used for treatment of malaria and Rheum emodi is used for treating low digestion, and constipation.
- Aromatic Plants: Saussurea lappa is used in perfume making.
- Government initiatives like Aroma Mission, Floriculture Revolution (commercial flower farming) support this.
- Microbial Diversity: Microorganisms in harsh cold environments support biotechnology applications like enzyme production, biofuels, and industrial bioprocesses.
- Hot springs in Manikaran and Yumthang host thermophilic bacteria like Bacillus and Thermus species, which can produce thermostable enzymes for industrial use.
- Types:
- Government’s Key Initiatives: BioE3 Policy, Anusandhan National Research Foundation (NRF), Bio-RIDE Scheme (2014: 50 biotech startups, 2025: 9,000).
- Progress in Global Innovation: India improved its ranking from 80th in 2014 to 39th in the Global Innovation Index 2024.
- India ranks 3rd in the Asia-Pacific and 12th globally in biomanufacturing.
- Over 5,352 Indian researchers now feature in the world’s top 2% of scientists.
Aroma Mission (Lavender Revolution)
- About: Started in J&K, it boosts India's aroma industry by promoting aromatic crops and essential oil production.
- Focus: Cultivation of lemongrass, lavender, vetiver, palmarosa etc for fragrant oils used in cosmetics, aromatherapy, and food flavoring.
- Nodal Agency: CSIR-Central Institute of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants (CSIR-CIMAP), Lucknow.
- Potential Impact: Over 2000 tonnes of oils worth Rs 300 crores yearly, 60 lakh rural jobs, and Rs 60,000–70,000 per hectare annual farmer income.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Mycorrhizal biotechnology has been used in rehabilitating degraded sites because mycorrhiza enables the plants to (2013)
- resist drought and increase absorptive area
- tolerate extremes of pH
- resist disease infestation
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q. At present, scientists can determine the arrangement or relative positions of genes or DNA sequences on a chromosome. How does this knowledge benefit us? (2011)
- It is possible to know the pedigree of livestock.
- It is possible to understand the causes of all human diseases.
- It is possible to develop disease-resistant animal breeds.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)