Important Facts For Prelims
Indigenous TnpB-Based Gene Editing Technology
- 24 Nov 2025
- 6 min read
Why in News?
Indian scientists at ICAR’s Central Rice Research Institute (CRRI), Cuttack, have developed a new indigenous genome-editing technology using TnpB proteins, offering a compact, low-cost and IP-free alternative to the globally patented CRISPR-Cas systems.
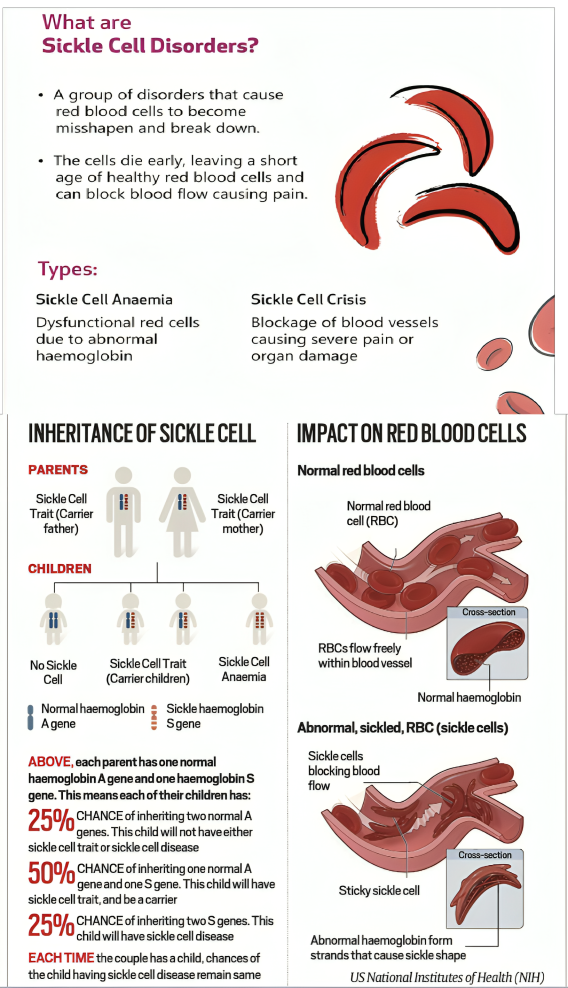
- In another development, CSIR–Institute of Genomics & Integrative Biology (IGIB) has developed “BIRSA 101”, India’s first indigenous CRISPR-based gene therapy for Sickle Cell Disease, marking a major scientific breakthrough.
What is India’s Indigenous TnpB-Based Genome Editing Tool?
- About: It uses TnpB (Transposon-associated proteins) instead of CRISPR-Cas9 or Cas12a, functioning as a miniature molecular scissor that enables precise Deoxy-Ribonucleic Acid (DNA) cuts and edits in plants.
- Because TnpB is extremely small (about 408 amino acids compared with 1,000–1,400 for Cas9 and around 1,300 for Cas12a) it can be delivered into plant cells far more easily, often without the complex tissue-culture steps required for bulkier Cas proteins.
- Significance: TnpB-Based Genome Editing Tool reduces dependence on foreign CRISPR patents held by global institutions like Broad Institute and Corteva.
- It enables affordable, commercial genome-edited (GE) crops without paying high licensing fees.
- It supports Atmanirbhar Bharat in agri-biotechnology and boosts India’s capacity for next-generation GE crops and addresses concerns that GE tools are controlled by foreign multinationals, giving India full technological sovereignty.
What is BIRSA 101?
- About: BIRSA 101 works as a precise gene-editing therapy that directly corrects the mutation responsible for Sickle Cell Disease.
- The therapy is named “BIRSA 101” in honour of Bhagwan Birsa Munda, the tribal freedom fighter. The name is a symbolic tribute to recognise the high burden of Sickle Cell Disease among India’s tribal communities.
- BIRSA 101 uses the engineered enFnCas9 (enhanced Francisella novicida Cas9) CRISPR platform developed by IGIB.
- Significance: It offers a low-cost alternative to global therapies such as Casgevy, priced at USD 2.2 million.
- The technology transferred to the Serum Institute of India to ensure large-scale, low-cost, and accessible deployment.
- BIRSA 1010 represents a major step toward the goal of a Sickle Cell–Free India by 2047.
- It strengthens India’s leadership in Atmanirbhar Bharat, genomic medicine, and affordable advanced therapeutics.
What is Genome Editing?
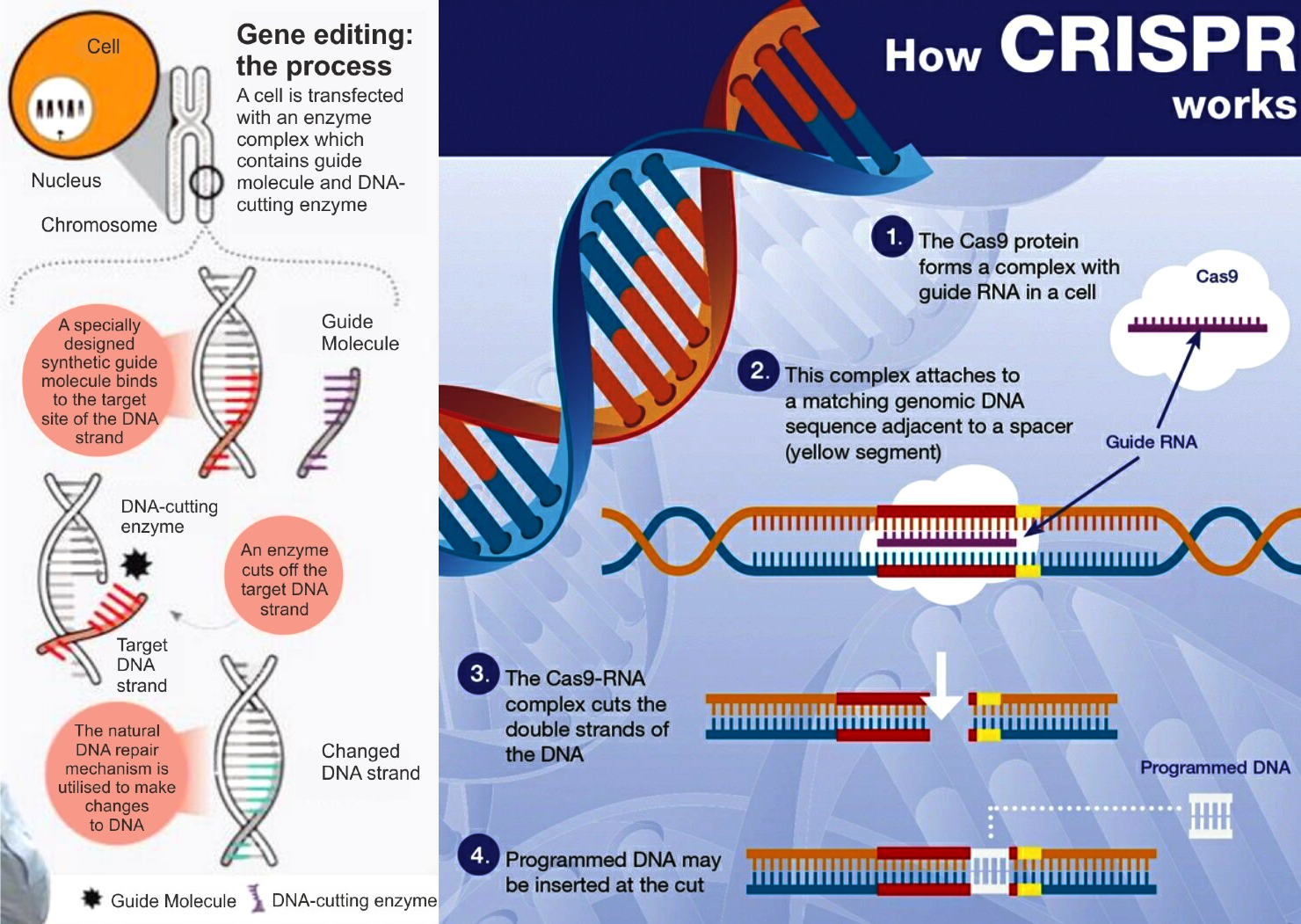
- About: Genome editing is a set of techniques like CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats), that allow scientists to precisely cut, alter, or replace specific DNA sequences within an organism’s genome.
- It creates targeted mutations in genes already present in the organism, without adding foreign DNA.
- CRISPR: It is a powerful gene-editing tool. It uses a guide RNA to locate a specific sequence in the genome and directs a Cas enzyme (usually Cas9 or Cas12a) to that spot.
- The Cas enzyme acts as a molecular scissor, cutting the DNA at the targeted point after which the cell repairs the break.
- Cas9 is widely used for simple cuts, while Cas12a offers higher precision and works with different guide RNA structures.
- This repair process allows scientists to switch off a gene, fix a mutation, or insert a new DNA sequence with high accuracy.
- Applications
- Medicine: Correcting genetic diseases, developing gene therapies (e.g., sickle cell disease).
- Agriculture: Creating climate-resilient, high-yield, disease-resistant crops.
- Research: Helps in understanding gene functions and developing new biological tools.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is India’s indigenous TnpB-based genome-editing tool?
It is a compact, IP-free genome editor developed by Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) - Central Rice Research Institute (CRRI) using TnpB proteins, enabling precise DNA edits in plants without costly CRISPR patents.
2. Why is TnpB considered better for plant genome editing?
TnpB is extremely small (408 amino acids), making it easier to deliver into plant cells and reducing the need for complex tissue-culture steps required for Cas9/Cas12a.
3. What is BIRSA 101 and who developed it?
BIRSA 101 is India’s first indigenous CRISPR-based gene therapy for Sickle Cell Disease, developed by Council of Scientific & Industrial Research-Institute of Genomics and Integrative Biology (CSIR–IGIB) using the engineered enFnCas9 platform.
4. Why is BIRSA 101 important for India’s tribal communities?
Sickle Cell Disease has a high prevalence among tribal populations, and BIRSA 101 offers a potential one-time curative therapy at low cost.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. What is Cas9 protein that is often mentioned in news? (2019)
(a) A molecular scissors used in targeted gene editing
(b) A biosensor used in the accurate detection of pathogens in patients
(c) A gene that makes plants pest-resistant
(d) A herbicidal substance synthesized in genetically modified crops
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of society? (2021)