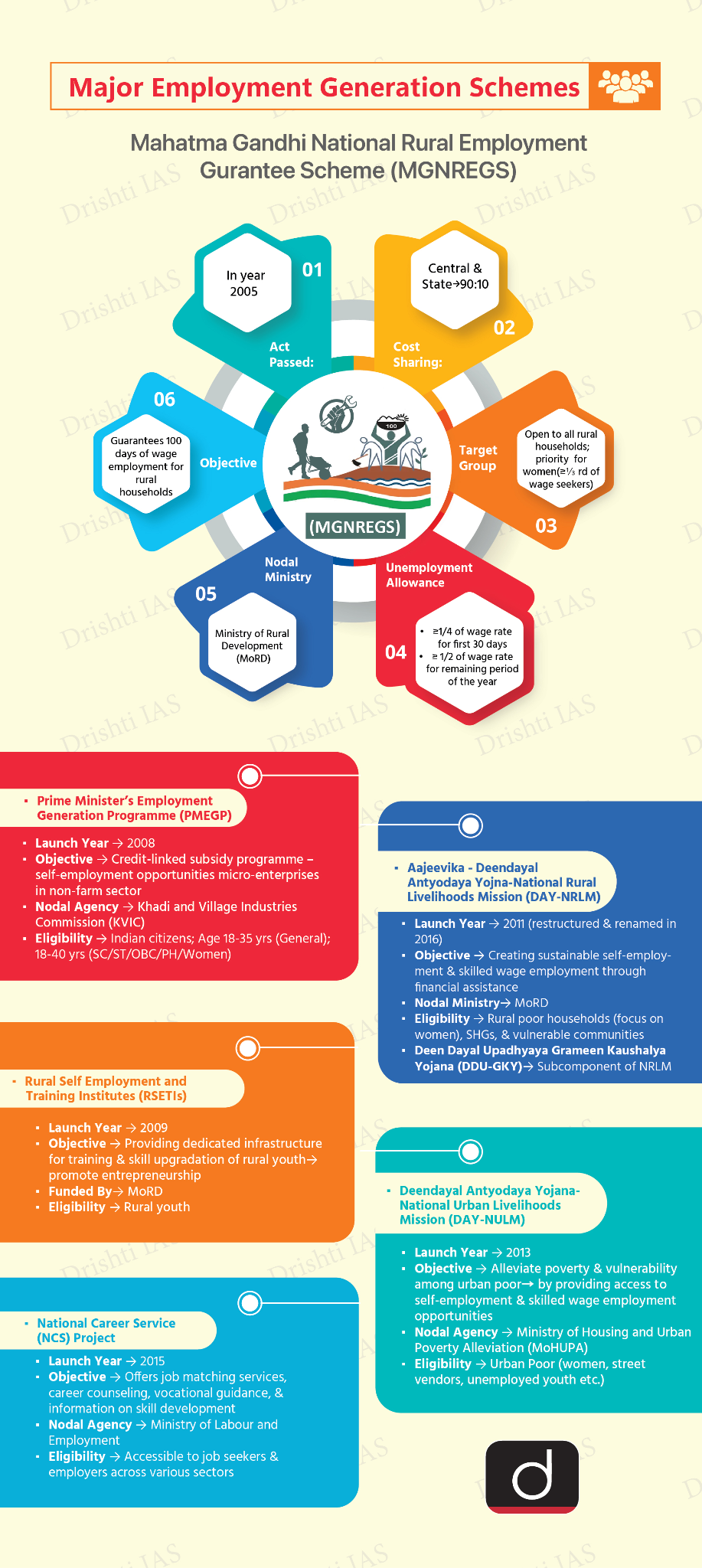
Facts for UPSC Mains
Employment Linked Incentive Scheme
- 02 Jul 2025
- 5 min read
Why in News?
The Union Cabinet approved the Employment Linked Incentive (ELI) Scheme, announced in the Union Budget 2024–25 as part of a broader Rs 2 lakh crore youth employment package.
- The ELI Scheme has a budget outlay of around Rs 1 lakh crore and will be implemented from August 2025 to 31st July 2027.
What is the Employment Linked Incentive Scheme?
- Key Components:
- Part A: Incentives for First-Time Employees
- It targets 1.92 crore first-time Employees’ Provident Fund Organization (EPFO)-registered employees, offering a one-month EPF wage (up to Rs 15,000), paid in two installments (after 6 and 12 months of service), with the latter contingent on completing a financial literacy programme.
- A portion will be deposited in a fixed savings account to promote long-term saving habits.
- It targets 1.92 crore first-time Employees’ Provident Fund Organization (EPFO)-registered employees, offering a one-month EPF wage (up to Rs 15,000), paid in two installments (after 6 and 12 months of service), with the latter contingent on completing a financial literacy programme.
- Part B: Support to Employers
- Employers hiring additional workers (salary ≤ Rs 1 lakh) will get up to Rs 3,000/month for 2 years.
- EPFO-registered firms must hire 2 additional employees (for firms with <50 employees) and 5 additional employees (for firms with ≥50 employees), with minimum 6 months’ retention.
- Aims to boost employment across sectors, especially manufacturing, targeting creation of 2.6 crore jobs.
- Part A: Incentives for First-Time Employees
- Incentive Payment Mechanism: All payments to the First Time Employees under Part A of the Scheme will be made through DBT (Direct Benefit Transfer) mode using Aadhar Bridge Payment System (ABPS).
- Payments to the Employers under Part B will be made directly into their Permanent Account Number-linked Accounts.
- Significance:
- Boost Private Sector Hiring: Encourages recruitment by reducing hiring costs through incentives, particularly for first-time jobseekers.
- Youth Employment Focus: Targets fresh graduates and new entrants with wage support and social security coverage.
- Job Retention and Upskilling: Incentives linked to retention and financial literacy promote workforce stability.
- Promote Formalisation: Through EPFO-linked payments, it supports transition from informal to formal employment.
Reduce Inequality: Prioritises economically disadvantaged youth, supporting inclusion and mobility.
Job Growth in India
- India's labour market witnessed strong momentum in FY 2023-24, with 4.67 crore new jobs added across the economy. Growth has been observed across both formal and informal sectors.
- Informal Sector:
- 10.01% employment growth recorded (23–24 Year over Year (YoY)), as per the Annual Survey of Unincorporated Sector Enterprises (ASUSE) by the Ministry of Statistics.
- The "Other Services" sector (transport, accommodation and food services, information and communication, health, education, real estate, etc.) contributed significantly, employing over 12 crore workers, up by more than 1 crore from the previous year.
- Formal Sector (first half of 2024-25):
- Employees’ Provident Fund (EPF) enrollments rose by 2.3%, reaching 6.1 million.
- Employees’ State Insurance Corporation (ESIC) enrollments grew 5.2% to 9.3 million.
- National Pension System (NPS) enrollments increased 6.8%, indicating growth in higher-quality job opportunities.
- These indicators point to improving job quality and expanding social security coverage, as also acknowledged in the latest Monthly Economic Review by the Finance Ministry.
|
Drishti Mains Question: How does the Employment Linked Incentive Scheme address youth unemployment and informality in India’s labour market? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana is aimed at (2016)
(a) bringing the small entrepreneurs into formal financial system
(b) providing loans to poor farmers for cultivating particular crops
(c) providing pensions to old and destitute persons
(d) funding the voluntary organizations involved in the promotion of skill development and employment generation
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. Most of the unemployment in India is structural in nature. Examine the methodology adopted to compute unemployment in the country and suggest improvements. (2023)