Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
UP Announces Firecracker Ban in NCR Districts
Why in News?
The Uttar Pradesh government has declared a complete ban on the manufacturing, storage, sale, and use of firecrackers in the National Capital Region (NCR) districts of the state.
Key Points
- Coverage: The ban applies to eight districts under the Delhi-NCR region, including Meerut, Ghaziabad, Gautam Budh Nagar, Bulandshahr, Hapur, Baghpat, Shamli, and Muzaffarnagar.
- Legal Framework: The ban is implemented ahead of the festive season, including Dussehra and Diwali, in compliance with a Supreme Court directive to reduce pollution levels in the NCR.
- The violation will invite imprisonment for up to five years and a fine of up to Rs 1 lakh, or both under Section 15 of the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
- Section 15 empowers the Central Government to instruct any authority or officer to act for environmental protection.
- For repeat offenses, an additional fine of Rs 5,000 per day will be imposed until compliance is achieved.
- The violation will invite imprisonment for up to five years and a fine of up to Rs 1 lakh, or both under Section 15 of the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
- Objectives of the Ban:
- Air Pollution Control: The ban is aimed at addressing the annual surge in air pollution during the festive season, particularly caused by the use of firecrackers.
- Public Health Protection: The measure seeks to protect public health from the harmful effects of air pollution, especially during the high-pollution months.
Environment (Protection) Act, 1986
- The EPA, 1986, was passed by the Parliament in the wake of the Bhopal Gas Tragedy, highlighting the urgent need for a comprehensive law to protect the environment and public health.
- EPA enacted under Article 253 of the Constitution (empowers the Parliament to enact laws for implementing international agreements) to fulfill international commitments made at the 1972 Stockholm Conference.
- The Act empowers the Central Government to prevent, control, and respond to environmental pollution. It allows the Centre to set standards, regulate emissions, shut down polluting industries, and control essential services.
- Article 48A directs the State to protect the environment, forests, and wildlife, while Article 51A makes it the duty of every citizen of India to protect and improve the natural environment.
National Current Affairs Switch to Hindi
World Water Week 2025
Why in News?
World Water Week, a leading global conference on water-related issues, was held in Stockholm, Sweden, from 24th - 28th August 2025.
- During the event, the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) was recognized as a global inspiration for river revival and community-driven efforts.
Key Points
- About: Established in 1991, this event is organized by the Stockholm International Water Institute (SIWI) and provides a critical platform for the exchange of knowledge, solutions, and commitments related to water management.
- The 2025 edition, marking its 35th year, focused on the theme ‘Water for Climate Action’, highlighting the role of water in tackling climate change and achieving sustainable development.
- India’s Role: During World Water Week 2025, NMCG was part of the session ‘River Cities Reimagined: Climate-Smart and Basin-Centric Urban Development’, which highlighted the role of river-centric urban development in ensuring climate-resilient cities.
- The session highlighted the benefits of sustainable urban planning and the need for basin-centric approaches that consider the entire river ecosystem.
- The session was led by NMCG, the National Institute of Urban Affairs (NIUA), and Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ).
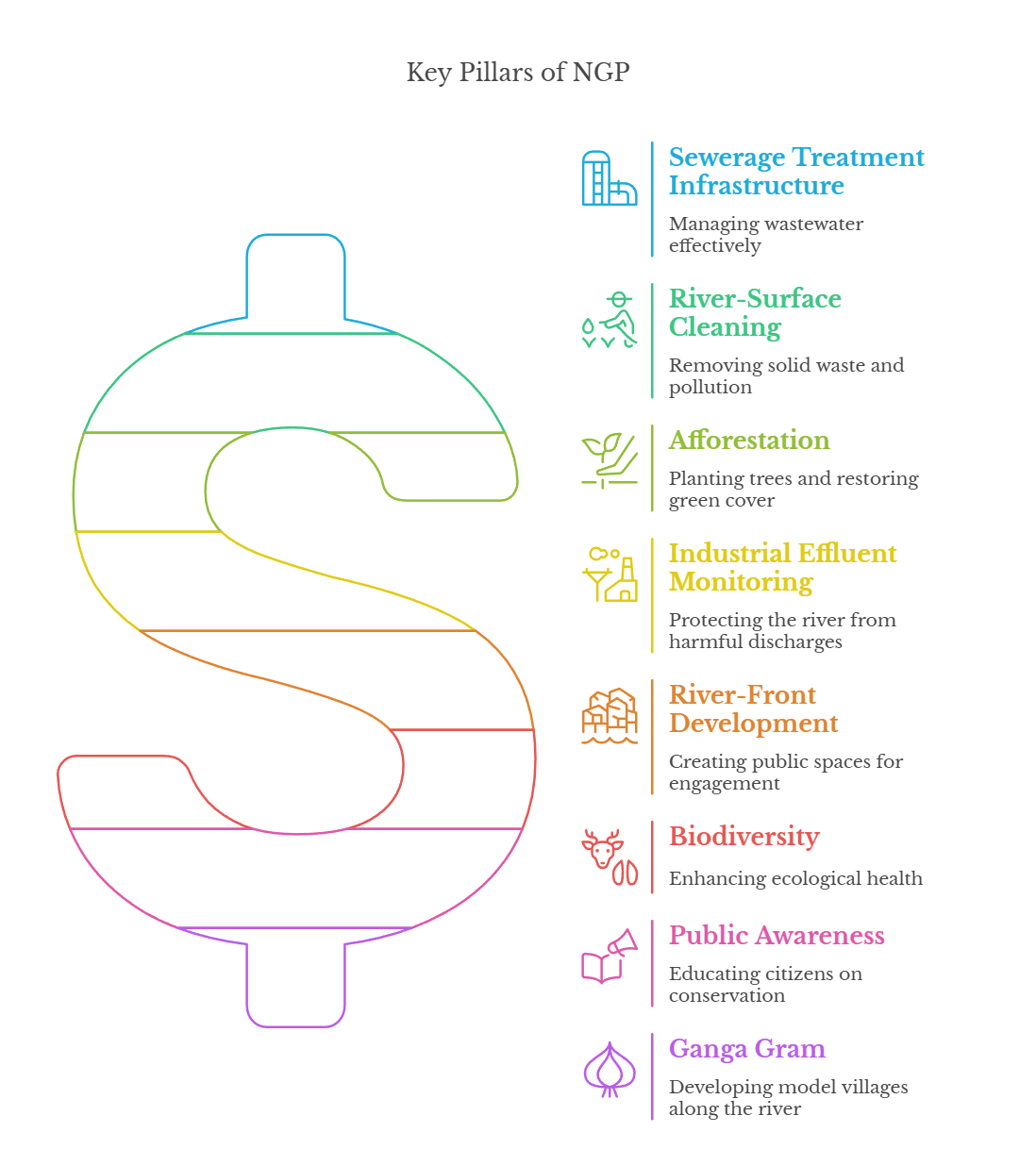
Namami Gange Mission
- About: It is a flagship programme for the rejuvenation of the Ganga River and its tributaries by reducing pollution, improving water quality, and restoring the river’s ecosystem.
- Implementation: Under the Hybrid Annuity Model (HAM), a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) by the winning bidder handles STP development, operation, and maintenance.
- 40% of costs are paid post-construction, 60% over the project’s lifespan.
India Water Week (IWW)
- The Ministry of Jal Shakti, Government of India, conceptualized and launched India Water Week in 2012, and it is now organized biannually.
- It is aimed at addressing critical challenges pertaining to water management and fostering innovation in water-related technologies and practices.
- IWW has evolved into a crucial platform in global water diplomacy, facilitating dialogue, innovation, and knowledge exchange on critical water-related challenges.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Eradication of Vilayati Babool
Why in News?
The Panchayati Raj Minister of Rajasthan directed officials from the Panchayati Raj and Forest Department to conduct a study and issue guidelines for the complete removal of Vilayati Babool (Prosopis Juliflora), including its roots.
Vilayati Babool (Prosopis juliflora)
- About: Locally known as Vilayati Kikar or Gando Baval, it is an invasive alien plant species native to Mexico, South America, and the Caribbean, now prevalent in India's arid and semi-arid regions.
- Impact:
- The rapid spread of Prosopis Juliflora hampers vegetation growth and depletes soil fertility, reducing agricultural productivity.
- Its expansion destroys pasturelands, creating difficulties for livestock grazing and facilitating the spread of more plants.
Invasive Alien Species
- About: Invasive Alien Species are non-native organisms (plants, animals, fungi, or even microbes) introduced beyond their natural range, forming self-sustaining populations.
- They outcompete native species, disrupt ecosystems, and cause significant ecological, economic, and social impacts.
- According to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), IAS are species that can “arrive, survive, and thrive”, often outcompeting native species for resources.
- In India, the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 defines IAS as non-native species that threaten wildlife or habitats.
- Other Invasive Alien Species in India: Animal species like African catfish, Nile tilapia, red-bellied piranha, alligator gar, Red-eared Slider (a North American turtle) and plants like Lantana and Water Hyacinth are among the most widespread invasive species in India.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
AI-Powered UP Skill Gap Dashboard
Why in News?
The Uttar Pradesh Skill Development Mission (UPSDM) has launched an innovative tool called the AI-powered UP Skill Gap Dashboard to enhance employability across the state.
Key Points
- About: The initiative marks the first time AI is being used to assess district-wise skill needs in Uttar Pradesh, aiding in the creation of livelihood opportunities at the local level.
- Features:
- AI and Data Analytics Integration: The dashboard employs advanced machine learning algorithms and data analytics to analyze district-specific sectors and employment data.
- It receives district-wise data for major sectors and industries, as well as trade-specific demands from training partners.
- District-Specific Skill Assessment: The dashboard helps identify skill gaps in various districts, providing a comprehensive skill assessment.
- It recommends the necessary training based on the sector-specific growth and employment needs in each district.
- AI and Data Analytics Integration: The dashboard employs advanced machine learning algorithms and data analytics to analyze district-specific sectors and employment data.
- Benefits:
- District-Level Skill Development: The dashboard offers a scientific analysis of skill needs across districts, indicating areas that require trained manpower.
- It helps in better allocation of training targets based on local requirements, improving employability within each district.
- Reduction of Attrition: By ensuring that training is aligned with local job markets, the dashboard helps reduce attrition due to candidates seeking jobs outside their home districts.
- Involvement of Industries as Training Partners: For the first time, industries have been involved as training partners in the skill development process.
- More than 45 industries are now actively contributing to industry-specific training efforts.
- Training Partner Evaluation: Training partners are evaluated based on their past performance in training and placement.
- The top-performing partners are allocated training targets, ensuring that high-quality training is provided to candidates.
- AI-Powered Insights for Training Target Allocation: The dashboard uses real-time data scraping and primary research to project sector-wise training targets.
- It maps the top industries, job roles, and skill gaps in each district, ensuring accurate and up-to-date information for training programs.
- Integration: The system integrates with a Large Language Model-powered chatbot to provide interactive support for UPSDM.
- The AI-based tool offers real-time assistance, guiding users through the process and answering queries related to training and employment.
- District-Level Skill Development: The dashboard offers a scientific analysis of skill needs across districts, indicating areas that require trained manpower.





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan