Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Rajasthan’s Potential in Rare Earth Mineral Production
Why in News?
Surveys by the Geological Survey of India (GSI) and Atomic Minerals Directorate (AMD) have revealed large reserves of rare earth minerals in Bhati Kheda, Siwana tehsil, Balotra, Rajasthan.
- With ongoing surveys and advancements in technology and infrastructure, Rajasthan is poised to become a major global supplier in the rare earth market.
Key Points
About Rare Earth Reserves in Rajasthan
- India’s First Hard Rock Rare Mineral Block: Bhati Kheda in Balotra holds significant reserves of rare earth minerals, confirming the presence of 17 high-demand elements critical for modern technologies.
- It is set to become the country's first block to contain rare earth minerals in hard rock granite, a more challenging form for mineral extraction.
- The G2 level survey confirms the large reserves of these minerals, making it a significant find.
- It is set to become the country's first block to contain rare earth minerals in hard rock granite, a more challenging form for mineral extraction.
- Survey and Mining Process: The GSI and AMD have conducted extensive surveys in Balotra and Jalore districts, with the survey in Bhati Kheda nearing completion.
- The central government will soon auction mining leases for these rare minerals, opening up opportunities for both private companies and state agencies.
- As there are no wildlife sanctuaries or similar protected areas nearby, there are minimal environmental or local-level challenges expected in Bhati Kheda.
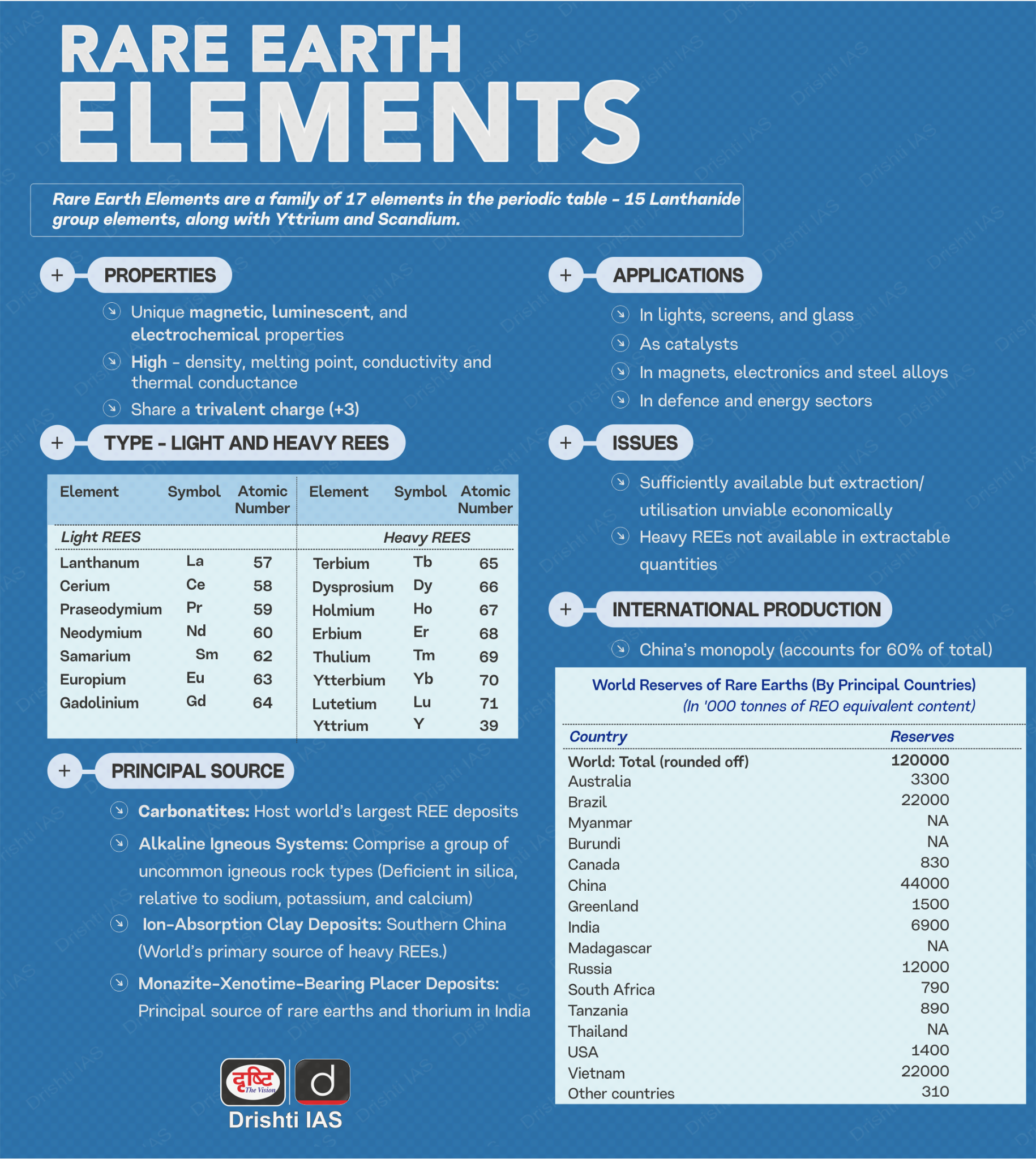
About Rare Earth Minerals
- Rare earth minerals are minerals that contain one or more rare earth elements (REEs) as a major metal constituent.
- Rare earth elements refer specifically to 17 metallic elements: the 15 lanthanides on the periodic table, plus scandium and yttrium.
- These elements are used heavily in high-tech electronics, magnets, renewable energy technologies, and defense.
- Critical Minerals: Critical minerals are those that are essential for a nation’s economic development, technological advancement, or national security, and whose supply may be vulnerable to disruption due to concentrated extraction or processing in a small number of locations, geopolitical risks, or scarcity.
- The specific list of critical minerals can change over time depending on technological and economic needs.
- India has identified 30 critical minerals, including Antimony, Beryllium, Bismuth, Cobalt, and Germanium.
- China dominates the global processing of several critical minerals, including rare earths, controlling an estimated 80–90% of processing capacity.
- India is heavily dependent on imports for critical minerals, particularly from China.
- India's Initiatives for Achieving Self-Reliance on Critical Minerals:
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Uttar Pradesh Partners with UNDP for Improved Disaster Resilience
Why in News?
A Memorandum of Association (MoA) was signed between the Relief Commissioner’s Office of Uttar Pradesh and the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) to work collaboratively on making disaster management in the state more effective and scientific.
Key Points
About Memorandum of Association (MoA)
- Objective:
- It aims at implementing disaster risk reduction programmes, strengthening the state’s institutional capacity, and developing a multi-level disaster management system based on a technical approach.
- This comprehensive disaster management program will empower the state with a robust disaster risk reduction framework and enhance preparedness for potential disasters.
- It will introduce disaster risk reduction measures across the state, aiming to create a more inclusive, accountable, and effective disaster management system.
- Program Highlights:
- Creation of disaster management plans for all 75 districts of Uttar Pradesh and 15 key state departments.
- Detailed risk assessments and vulnerability studies for 20 major cities, along with the creation of urban disaster management plans for these cities.
- Preparation of detailed project reports for 10 state departments.
- Technical Improvements:
- Strengthening and integrating the state’s disaster information system through workshops, ICT tool provision, and the establishment of a Project Management Unit (PMU) at the Relief Commissioner’s Office to ensure effective coordination.
- Budget and Implementation:
- The Uttar Pradesh government has approved a budget of Rs 19.99 crore for the next three years to execute the program in phases.
- The implementation will be guided by technical proposals from UNDP, with the program aligned with the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) recommendations.
About United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)
- About:
- The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) is the UN's global development network, advocating for change and connecting countries to knowledge, experience, and resources to help people build a better life.
- Formation and Headquarters:
- The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) was officially established in 1965 by the UN General Assembly.
- UNDP was formed by merging the United Nations Expanded Programme of Technical Assistance (1949) and the United Nations Special Fund (1958).
- It has its headquarters in New York City, but works primarily through its offices in about 170 countries and territories.
- Global Presence and Approach:
- It works on the ground in some 170 countries and territories, supporting their own solutions to development challenges and developing national and local capacities that will help them achieve human development and the Sustainable Development Goals.
- Focus Areas:
- Its work is concentrated on three main focus areas:
- Sustainable development
- Democratic governance and peacebuilding
- Climate and disaster resilience
- Its work is concentrated on three main focus areas:
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Uttarakhand Creates New Record on Harela Festival
Why in News?
Uttarakhand created a new record by planting over 8.13 lakh saplings across the state on the occasion of the Harela festival, with the Chief Minister launching the campaign by planting a Rudraksh sapling.
Key Points
About Harela Festival
- Overview: It is the traditional festival of Uttarakhand and marks the beginning of the monsoon season and the sowing cycle in the Hindu month of Shravan.
- Widely observed in the Kumaon region and parts of Garhwal, it is both a religious and agrarian festival, rooted in reverence for nature and agriculture.
- Agricultural Significance: Households across the state prepare for the occasion by sowing seeds such as barley, maize, and mustard ten days in advance. These sprout into green shoots called harela, which are symbolically cut and placed on the heads of family members as a blessing for prosperity and good health.
- Religious and Cultural Observance: The festival also commemorates the divine marriage of Lord Shiva and Goddess Parvati, with many homes and temples setting up clay idols for ritual worship. Devotees offer prayers for a good harvest, environmental harmony, and community well-being.
- Celebrations and Events: Traditional folk songs, dances, and local fairs are celebrated in towns and villages, including events like the Harela Mela in Almora and Nainital.
- Children participate in bamboo-stilt games called Gedi, while elders uphold age-old customs to commemorate the festival.
- Significance in Modern Times: Celebrated primarily by Hindu communities in the hills, it serves as a reminder of the deep bond between humans and nature.
- With its blend of agricultural, religious, and ecological themes, the festival has grown in significance over the years, both as a cultural tradition and a public environmental movement.
About Plantation Drive
- The "Celebrate Harela, Repay the Debt of Mother Earth" plantation campaign saw the planting of over 8.13 lakh saplings across 13 districts, marking the largest plantation effort in the state during a single festival, aligned with the Prime Minister’s "Ek Ped Maa Ke Naam" initiative.
- The plantation effort involved active participation from the local administration, forest department, NGOs, women’s groups, and youth, spreading across villages, towns, cities, schools, and Anganwadi centers.
About Prime Minister’s "Ek Ped Maa Ke Naam" Initiative
- Launch: On World Environment Day (5 June 2024), the Prime Minister launched the 'Ek Ped Maa Ke Naam' campaign, combining environmental responsibility with a tribute to mothers.
- The campaign was inaugurated with the planting of a Peepal tree at Buddha Jayanti Park in Delhi.
- Symbolic Gesture of Tree Planting: The campaign encourages individuals to plant a tree in the name of their mother, symbolizing a heartfelt tribute to mothers' nurturing roles while contributing to environmental preservation. Trees are vital for sustenance, protection, and future generations, much like mothers.
- Contribution to Sustainable Development: The initiative aligns with India's broader quest for sustainable development, emphasizing the need for both individual actions and collective efforts in promoting environmental conservation and creating lasting legacies for future generations.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
NAMASTE Day
Why in News?
On the occasion of the 'National Action for Mechanized Sanitation Ecosystem (NAMASTE) Day', (16th July), Union Minister of State for Social Justice and Empowerment, inaugurated the helpline (14473) for waste pickers and distributed PPE kits and Ayushman cards to Sewer and Septic Tank Workers (SSWs) and Waste Pickers, in Lucknow.
Key Points
About NAMASTE Scheme
- About: The NAMASTE scheme is a human-centric initiative by the government to ensure that no Safai Karamchari has to engage in hazardous manual work such as cleaning sewers and septic tanks.
- The scheme aims to improve the working conditions of Sewer and Septic Tank Workers (SSWs) and promote their well-being through various support measures.
- Implementation and Duration: Launched jointly by the Union Ministries of Social Justice and Empowerment and Housing and Urban Affairs, the scheme is being implemented by the National Safai Karamcharis Finance and Development Corporation (NSKFDC).
- The scheme, with a budget of Rs 349.73 crore, will run from FY 2023-24 to 2025-26, covering all 4800+ ULBs and replacing the previous Self-Employment Scheme for Rehabilitation of Manual Scavengers (SRMS).
- Key Entitlements for Sewer and Septic Tank Workers (SSWs): The scheme offers various entitlements for SSWs to ensure their safety, well-being, and sustainable livelihood:
- SSWs are being profiled through a digital application.
- Provision of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) kits to ensure safety during work.
- Ensuring access to necessary safety tools and resources.
- Providing training to enhance workers' safety and skills.
- Ensuring comprehensive health insurance for SSWs.
- The scheme aims to create livelihood opportunities for SSWs through:
- Providing access to vehicles and machines related to sanitation at subsidized rates.
- Encouraging SSWs to start their own sanitation businesses, supported by capacity-building initiatives.
About Manual Scavenging
- Manual scavenging is defined as “the removal of human excrement from public streets and dry latrines, cleaning septic tanks, gutters and sewers”.
- A manual scavenger is anyone employed to manually clean, carry, or handle human excreta from insanitary latrines, open drains, pits, or railway tracks, before it fully decomposes, as per the Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act (PEMSR), 2013.
- India prohibited the practice under the PEMSR Act, 2013, which acknowledges manual scavenging as a "dehumanizing practice" and aims to address the historical injustices endured by manual scavengers.
- Government Initiatives and Schemes:
Haryana Switch to Hindi
2,000-year-old Buddhist Site Found in Haryana
Why in News?
A team from the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kanpur has discovered signs of ancient Buddhist stupas and structural remains buried beneath the soil in the Yamunanagar district of Haryana.
Key Points
About the Research Findings
- Discovery of Ancient Structures: Signs of ancient structures, including circular formations, walls, and chamber-like rooms, were detected approximately 6 to 7 feet beneath the surface using advanced Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) technology.
- This points to the possibility of a 2,000-year-old Buddhist site.
- Survey and Location: Initiated by the Haryana State Department of Archaeology, the survey aimed to uncover historical remains in areas like Topra Kalan and surrounding villages, where old bricks are occasionally found, indicating potential archaeological significance.
- Evidence of a Buddhist Stupa: GPR readings revealed semi-circular structures, leading researchers to hypothesize the presence of an ancient stupa.
- Archaeological officials have corroborated this hypothesis, confirming the likely discovery of a stupa.
- Significance: These findings may date back to the Buddhist era or even the Mahabharata period, according to local oral traditions.
- They provide crucial insights into ancient trade routes, religious networks, and cultural exchanges in the subcontinent.
- If further excavations reveal similar structures, it could demonstrate the widespread influence of this ancient culture.
About Other Prominent Buddhist Sites in India
- Bihar: Bodh Gaya is the location where Siddhartha Gautama attained enlightenment under the Bodhi tree.
- Mahabodhi Temple, a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 2002, marks the spot where Buddha achieved enlightenment.
- In Vaishali (Bihar), Buddha declared his imminent Parinirvana and preached his final sermon.
- Nalanda University in Nalanda was a famous ancient center of learning, where Buddhist scholars from across the world gathered.
- Uttar Pradesh: At Sarnath, Buddha delivered his first sermon to his disciples, outlining the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path.
- Dhamek Stupa in Sarnath marks the site of Buddha’s first sermon.
- Kushinagar is the place where Buddha passed away and attained Parinirvana (final nirvana).
- Ramabhar Stupa in Kushinagar is believed to be the place where Buddha was cremated.
- Himachal Pradesh: Dharamshala, especially McLeod Ganj, is home to the Tibetan Government-in-Exile and the Dalai Lama. It is a hub for Tibetan Buddhists.
- Maharashtra: Ellora Caves are a UNESCO World Heritage site, featuring rock-cut temples and sculptures of Buddhist, Hindu, and Jain traditions.
- The Ajanta Caves are famous for ancient Buddhist monasteries and beautiful murals depicting Buddha’s life.
- Madhya Pradesh: Sanchi Stupa is a UNESCO World Heritage site, known for its Buddhist stupas, monasteries, and pillars.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
University of Southampton Opens India Campus in Gurugram
Why in News?
The Union Minister of Education, along with the Chief Minister of Haryana, inaugurated the India campus of the University of Southampton in Gurugram, Haryana.
Key Points
About Campus of University of Southampton
- Significant Milestone in India’s Education Sector: The University of Southampton—a QS Top 100 global institution and founding member of the UK’s Russell Group becomes the first foreign university to operationalize a campus in India under the University Grants Commission’s (Setting up and Operation of Campuses of Foreign Higher Educational Institutions in India) Regulations, 2023.
- The inauguration of the University’s campus in Gurugram marks a key moment in India's higher education sector, celebrating five years of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- Internationalization of Education under NEP 2020: The Union Minister highlighted that this event strengthens the education pillar of India-UK cooperation, aligning with the India-UK Roadmap 2030.
- Campus Offerings and Programmes: The Gurugram campus will offer globally recognized undergraduate and postgraduate programs, allowing students the opportunity to spend up to one year at the University’s campuses in the UK or Malaysia.
Note:
- India is also expanding its global presence, with IIT Madras opening a campus in Zanzibar and IIT Delhi establishing one in Abu Dhabi.
About UGC (FHEI) Regulations, 2023
- The UGC (FHEI) Regulations, 2023, paved the way for foreign universities, ranked among the world's top 500, to establish branch campuses in India.
- The move aligns with the National Education Policy(NEP), 2020, envisioning a legislative framework for top global universities in India.
- The NEP 2020 provided that selected universities, e.g., those from among the top 100 universities in the world, will be facilitated to operate in India.
- University Grants Commission (UGC):
- UGC is a statutory body in India established in 1953 to coordinate, determine, and maintain standards of higher education.
- It was created by the Indian government through the UGC Act of 1956. The UGC's main functions include providing recognition to universities, disbursing funds, and advising the government on matters related to higher education.
- The UGC headquarters is located in New Delhi.





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan