Haryana Switch to Hindi
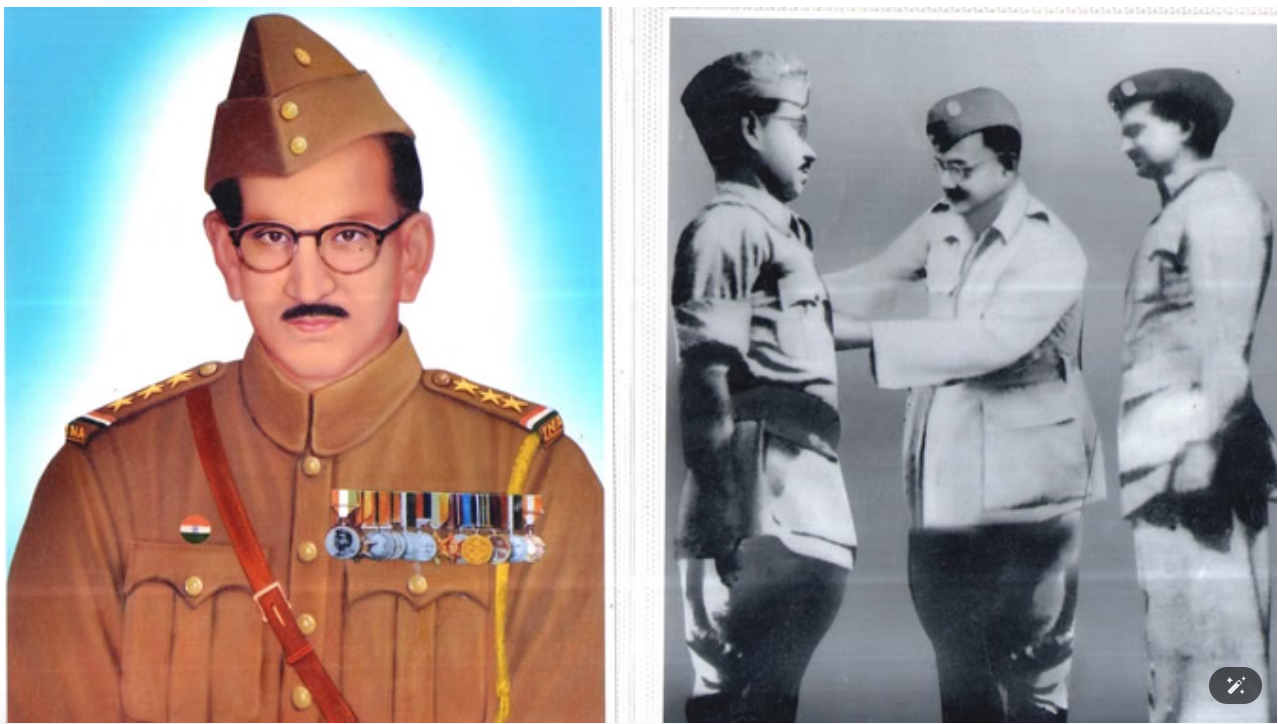
Captain Hardwari Singh Ahlawat
Why in News?
Captain Hardwari Singh Ahlawat of Azad Hind Fauj, played an instrumental role in liberating the Jhansi Regiment (Rani of Jhansi Regiment) from British siege.
- Rani of Jhansi Regiment was an armed unit of women warriors headed by Captain Lakshmi Swaminathan. It is believed to be the first female infantry in military history.
Key Points
- Liberation of Jhansi Regiment: In 1945, Captain Ahlawat, under Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose's orders, led a successful operation to free the Jhansi Regiment from British forces, firing over 4,000 rounds and killing around 300 British soldiers.
- Role in the INA: Captain Ahlawat, born in Deighal village (Jhajjar, Haryana), joined the Azad Hind Fauj in 1942, along with 32 soldiers from his village.
- Netaji Bose honored him with the prestigious “Sher-e-Hind” award for his courage and appointed him as his Personal Staff Officer (PSO).
- Military Achievements: Under Ahlawat’s leadership, INA forces freed the Lepoppa Hills area near Burma, defeating the British forces and hoisted India’s flag on the mountain post (elevation of 7,000-8,000 feet).
- Post-War Life: After the surrender of Azad Hind Fauj in 1945, Ahlawat, along with 17,000 INA soldiers, was imprisoned in Delhi’s Red Fort.
- He was released on 31st December 1945, by the British government (after INA trials or Red Fort trials).
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Alert for Bird Flu in UP
Why in News?
Uttar Pradesh has issued a state-wide alert due to the growing threat of Bird Flu (H5N1), directing relevant departments to implement strict safety protocols to protect animals and birds, especially in zoos and wildlife sanctuaries.
- CM Yogi has instructed to reinforce safety measures in zoos, bird sanctuaries, national parks, wetlands, and cow shelters to prevent any outbreak of Bird Flu.
Key Facts About Bird Flu
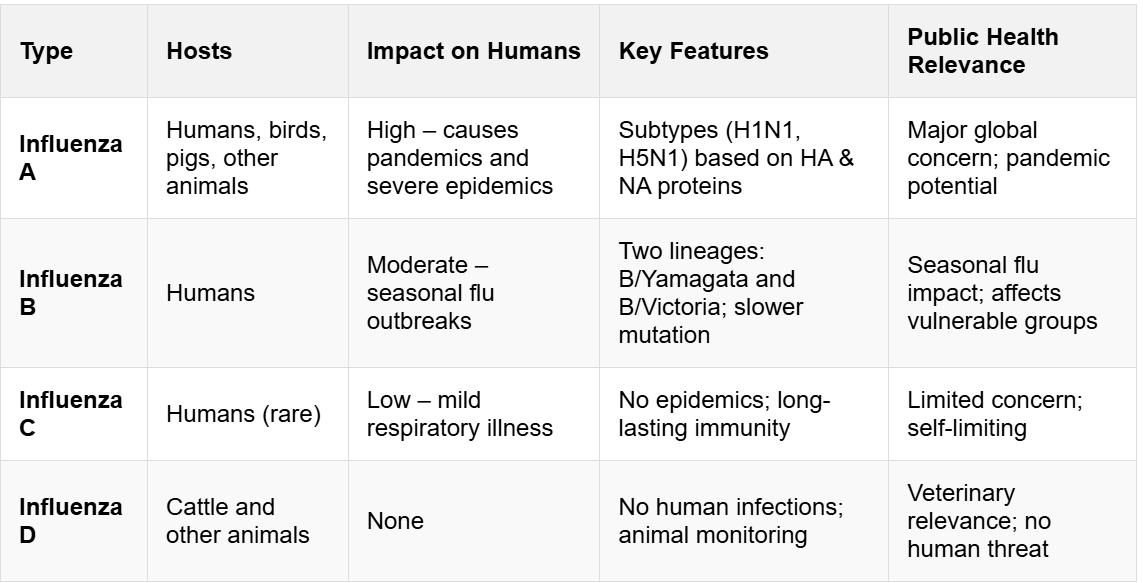
- About: Bird flu (avian influenza) is a highly contagious viral disease caused by avian influenza A viruses, particularly subtypes H5N1 and H5N8, affecting both wild and domestic birds.
- History of Human Cases: First human cases were reported in 1997 (Hong Kong). Most have occurred in Asia and were linked to close contact with infected birds.
- Transmission: H5N1 spreads primarily through direct contact with infected live or dead birds or contaminated environments (e.g., live bird markets).
- Symptoms: Common symptoms include high fever, cough, sore throat, and muscle aches.
- Severe cases can lead to respiratory failure or neurological complications. Some individuals may remain asymptomatic despite exposure.
- Treatment: Current seasonal flu vaccines do not protect against H5N1.
- Antiviral drugs like oseltamivir are effective, especially when administered early in high-risk or severe cases.
Bihar Switch to Hindi
Bihar Government Doubles Pension for JP Senanis
Why in News?
The Bihar government has announced an increase in the pension for Jayaprakash (JP) Movement fighters (JP Senanis), who were imprisoned during the Emergency (1975-77) for supporting socialist leader Jayaprakash Narayan’s movement (1974).
- CM Nitish Kumar emphasized that the initiative was taken to honor the contributions of these fighters and their role in Bihar’s development.
Note: 5th June 2025 marks the 51st anniversary of Jayaprakash Narayan's call for Sampoorna Kranti (Total Revolution), also known as the JP Movement, which was launched on 5th June 1974 by Jayaprakash Narayan at Gandhi Maidan, Patna.
Key Points
- Pension Increase: Fighters who were imprisoned for more than six months will now receive a pension of ₹30,000 per month, up from ₹15,000.
- Those who were jailed for up to six months will see their pension increase from ₹7,500 to ₹15,000 per month.
- In the event of the pensioner’s death, their surviving spouse will also receive the same pension amount.
Key Points About JP Senani Samman Pension Scheme
- Scheme: This adjustment falls under the "JP Senani Samman Pension Scheme", which was initiated by Chief Minister Nitish Kumar in 2009.
- The scheme is named after the iconic socialist leader, Loknayak Jayaprakash Narayan.
- Beneficiaries: Currently (2025), 3,354 individuals in Bihar are receiving this pension, while CM Nitish Kumar, despite being eligible, has never availed of it.
- The notable beneficiaries of the scheme are Lalu Prasad Yadav (ex-chief minister of Bihar) and Sushil Kumar Modi (former Deputy CM of Bihar).
- Eligibility Conditions:
- Period of Participation: 18th March 1974- 21st March 1977.
- Beneficiaries must have been imprisoned under the Maintenance of Internal Security Act (MISA) or Defence of India Rules (DIR).
- Duration Categories:
- Category 1: 1 to 6 months of imprisonment.
- Category 2: Imprisonment exceeding 6 months.
- Additional Benefits: Eligible individuals receive free medical care equivalent to that provided to freedom fighters.
Swatantrata Sainik Samman Pension Scheme
- The Swatantrata Sainik Samman Pension Scheme was launched in 1972 as the Freedom Fighters Pension Scheme and was later renamed and liberalized in August 1980.
- Administered by the Union Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India, it provides financial support to the freedom fighters who participated in India's independence struggle.
- Total Beneficiaries (Ever): 171,689 freedom fighters and their dependents.
- Current Active Pensioners (as of July 2025): 13,212 living freedom fighters.
- Widows Receiving Pension: 9,778.
- Annual Budget (2024-25): ₹600 crore.
- Coverage:
- Time Period: Freedom fighters who participated in movements between 1857 and 1947.
- Recognized Movements: Includes 40 major movements, such as the Quit India Movement, Jallianwala Bagh, and others.
Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
Chhattisgarh Celebrates World Biofuel Day
Why in News?
The Chhattisgarh Biofuel Development Authority (CBDA) celebrated World Biofuel Day (on 10th August 2024) in Gorhi village, Durg district, with enthusiasm and dignity.
- The event highlighted green energy, rural engagement, and biofuel promotion, with CBDA successfully producing biodiesel from non-edible oilseeds and used cooking oil, and future plans for biojet fuel, bioethanol, and green hydrogen.
Key Points About World Biofuel Day
- It aims to raise awareness about non-fossil fuels as sustainable energy alternatives and to highlight government initiatives that support the biofuel industry.
- The day commemorates the successful operation of an engine on peanut oil by German engineer Sir Rudolf Diesel on 9th August 1893.
- Theme for 2025: "Biofuels: A Sustainable Pathway to Net Zero"
Biofuels
- Biofuels are fuels derived from plant biomass or animal waste and are renewable energy sources. Common biofuels include:
- Ethanol: Made by fermenting crop residues like corn and sugarcane, then blended with petroleum to reduce emissions. The common blend is Ethanol-10 (10% ethanol).
- Biodiesel: A biodegradable fuel produced from used cooking oil, recycled grease, or animal fats, made by reacting oil or fat with alcohol and a catalyst.
- Significance of Biofuels:
- Environmental Benefits: Biofuels reduce greenhouse gas emissions, resource depletion, and improve waste management.
- Energy Security: With over 85% of oil imported, biofuels can enhance India's energy security.
- Economic Benefits: Biofuels can reduce oil imports, lower the import bill, and boost farm incomes, especially from surplus crops like corn and sugarcane.
- Abundant Availability: Biofuels can be produced from crops, waste, and algae.
Note
- India is the world's 3rd largest oil consumer (behind the US and China).
- India aims to achieve a 20% ethanol blending target by 2025.
- The first 2G ethanol project was inaugurated in Panipat, Haryana in 2022.
- 2G ethanol is a biofuel produced from non-food sources like agricultural residues and waste.
Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
Chhattisgarh Celebrates World Biofuel Day
Why in News?
The Chhattisgarh Biofuel Development Authority (CBDA) celebrated World Biofuel Day (on 10th August 2024) in Gorhi village, Durg district, with enthusiasm and dignity.
- The event highlighted green energy, rural engagement, and biofuel promotion, with CBDA successfully producing biodiesel from non-edible oilseeds and used cooking oil, and future plans for biojet fuel, bioethanol, and green hydrogen.
Key Points About World Biofuel Day
- It aims to raise awareness about non-fossil fuels as sustainable energy alternatives and to highlight government initiatives that support the biofuel industry.
- The day commemorates the successful operation of an engine on peanut oil by German engineer Sir Rudolf Diesel on 9th August 1893.
- Theme for 2025: "Biofuels: A Sustainable Pathway to Net Zero"
Biofuels
- Biofuels are fuels derived from plant biomass or animal waste and are renewable energy sources. Common biofuels include:
- Ethanol: Made by fermenting crop residues like corn and sugarcane, then blended with petroleum to reduce emissions. The common blend is Ethanol-10 (10% ethanol).
- Biodiesel: A biodegradable fuel produced from used cooking oil, recycled grease, or animal fats, made by reacting oil or fat with alcohol and a catalyst.
- Significance of Biofuels:
- Environmental Benefits: Biofuels reduce greenhouse gas emissions, resource depletion, and improve waste management.
- Energy Security: With over 85% of oil imported, biofuels can enhance India's energy security.
- Economic Benefits: Biofuels can reduce oil imports, lower the import bill, and boost farm incomes, especially from surplus crops like corn and sugarcane.
- Abundant Availability: Biofuels can be produced from crops, waste, and algae.
Note
- India is the world's 3rd largest oil consumer (behind the US and China).
- India aims to achieve a 20% ethanol blending target by 2025.
- The first 2G ethanol project was inaugurated in Panipat, Haryana in 2022.
- 2G ethanol is a biofuel produced from non-food sources like agricultural residues and waste.
- India aims to achieve a 20% ethanol blending target by 2025.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Uttarakhand Freedom of Religion (Amendment) Bill 2025
Why in News?
The Uttarakhand Cabinet has approved the Uttarakhand Freedom of Religion (Amendment) Bill 2025, introducing tougher penalties for forced, fraudulent, or coercive religious conversions.
- The new amendments include life imprisonment, hefty fines, and increased provisions for protecting victims of illegal conversions.
Key Points
- Stricter Penalties:
- The amended bill proposes life imprisonment for the gravest cases of forced conversions, alongside fines up to ₹10 lakh.
- General offences will carry 3 to 10 years imprisonment, while crimes involving sensitive classes such as minors or women will face 5 to 14 years imprisonment.
- Promotion through Digital Platforms: The bill criminalizes promoting conversions through social media, messaging apps, and other online channels.
- Expanded Definition of Inducement: The bill broadens the definition of “inducement”, now including gifts, cash, goods, employment offers, promises of marriage, or portraying another religion negatively.
- Protecting Victims: The bill includes provisions for victim protection, rehabilitation, financial assistance for medical care and travel, as well as legal aid for victims of forced conversions.
- Marriage and False Identity: It criminalizes marriage under false pretenses, where an individual conceals their religion, with penalties of 3 to 10 years in prison and fines of ₹3 lakh.
- Asset Seizure and Warrants: Authorities will have the power to seize assets acquired through illegal conversions.
- Arrests can be made without a warrant in these cases (cognizable offenses), and bail will only be granted if the accused is not found guilty or is not likely to repeat the offense.





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan