Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
MP’s CM Kisan Kalyan Yojana
Why in News?
Chief Minister Dr. Mohan Yadav is set to transfer the second installment of Rs. 17,500 crore under the CM Kisan Kalyan Yojana for the year 2025-26 to the accounts of farmers in Madhya Pradesh on 14th August 2025.
- By March 2025, over 83 lakh beneficiaries had received a cumulative Rs. 17,500 crore under this initiative, supporting the agricultural community in the state.
Key Facts About CM Kisan Kalyan Yojana
- Scheme: The scheme, launched in September 2020, aims to provide direct financial support to farmers.
- The CM Kisan Kalyan Yojana is designed to empower small and marginal farmers by providing an extra Rs. 6,000 annually, in addition to the Rs. 6,000 provided under the PM Kisan Samman Nidhi scheme.
- The benefit is provided in three installments of Rs. 2,000 each.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- Farmers must be registered under the PM Kisan Samman Nidhi Scheme (mandatory e-KYC).
- The applicant should be a permanent resident of Madhya Pradesh.
- The farmer must have arable land where they carry out farming activities.
- Ineligible farmers include income tax payees, elected representatives, and government employees.
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN)
- Launched: December 2018
- Type: Central Sector Scheme (100% funded by the Government of India)
- Objective: Provide financial assistance to land-holding farmer families across India
- Income Support: Rs 6,000 annually (3 equal installments of Rs 2,000 each)
- 100% Direct Benefit Transfer via Aadhaar-based verification and real-time payment tracking.
- Eligibility: All landholding farmer families (with certain exclusions)
- Beneficiary Identification: Done by State Governments and Union Territories as per guidelines
- Implementing Agency: Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare (DA&FW)
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Bhojpur Temple Hosts Cleanliness Drive
Why in News?
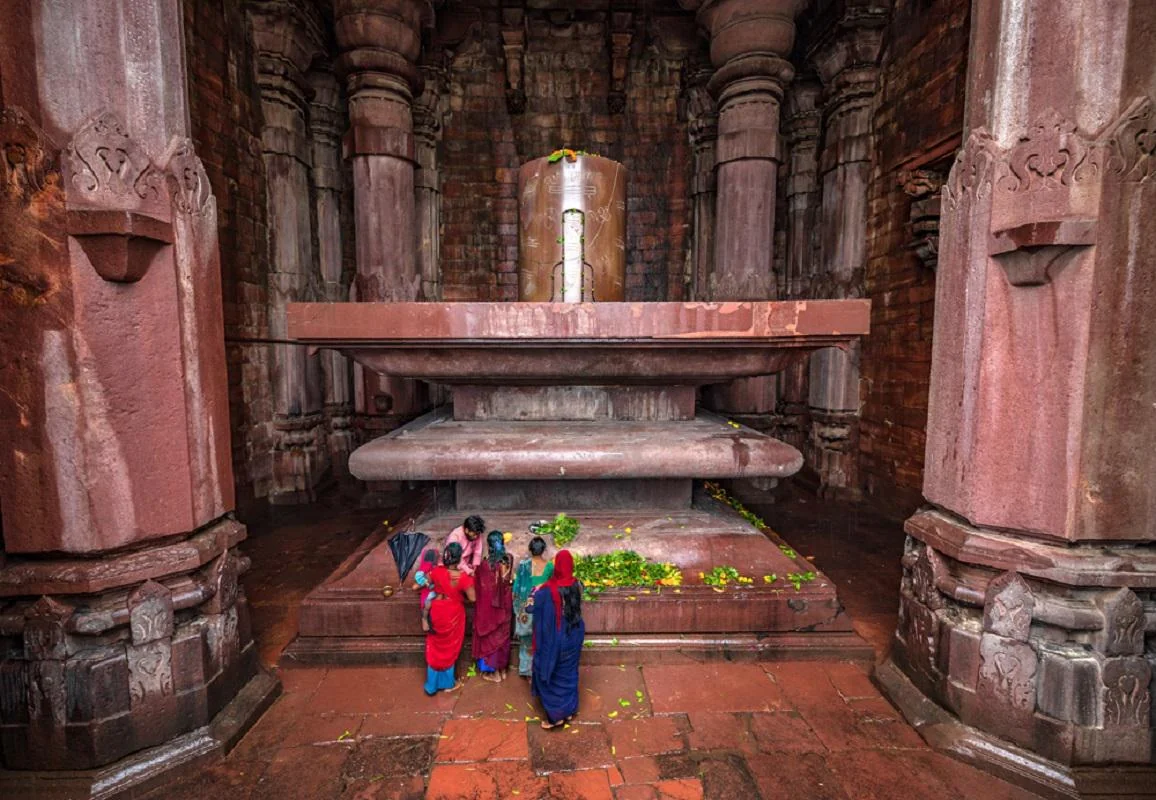
On 10th August 2025, Madhya Pradesh Tourism Board organized a successful cleanliness drive at the tentative UNESCO World Heritage site Bhojpur Temple (Bhojeshwar Mahadev Temple), spreading the message of national pride and environmental responsibility.
- The event was conducted under the theme "Azadi Ka Utsav Swachhta Ke Sang," encouraging people to celebrate freedom with cleanliness.
Key Points
- Environmental Awareness: Participants focused on eco-friendly waste disposal, especially flowers and offerings, promoting cleanliness and preserving heritage.
- Spiritual Awareness: Karma Yoga teachings from the Bhagavad Gita were shared, blending social, environmental, and spiritual consciousness.
Bhojeshwar Mahadev Temple
- Location: Bhojpur, Raisen District, Madhya Pradesh
- Historical Significance: Built in the 11th century by Raja Bhoj of the Paramara dynasty, dedicated to Lord Shiva.
- Added to the tentative list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites in 2024.
- Architecture:
- Style: Bhumija, with Dravida influences on shikhara.
- The temple's Bhumija-style architecture influenced later temples like Udayeshwara and Bijamandal.
- Notable Features:
- Lingam: Colossal (2.3m tall and 5.4m in circumference).
- Shikhara: Towering, with intricate carvings and projections.
- Incomplete Structure: Includes unfinished mandapa and ceiling.
- Unique Elements:
- Line drawings carved on nearby rocks depicting the intended temple design.
- Carved masonry blocks and earthen ramps around the site.
- Style: Bhumija, with Dravida influences on shikhara.
- Uniqueness of Temple:
- Architectural Grandeur: Massive size, intricate carvings, and the colossal lingam showcase Paramara dynasty’s architectural brilliance.
- Reflects the religious, cultural patronage and architectural vision of Raja Bhoj and the Paramara dynasty.
- The Bhojeshwar Temple is similar to the Chola’s Brihadisvara Temple (Thanjavur) in terms of scale and grandeur.
- If completed, Bhojeshwar's shikhara would be taller than Brihadisvara's, measuring 100m compared to 59.82m.
- Architectural Grandeur: Massive size, intricate carvings, and the colossal lingam showcase Paramara dynasty’s architectural brilliance.
National Current Affairs Switch to Hindi
106th Birth Anniversary of Dr. Vikram Sarabhai
Why in News?
Dr. Vikram Sarabhai (12th August 1919 - 30th December 1971), widely recognized as the Father of India's Space Programme, was remembered and celebrated on his 106th birth anniversary on 12th August.
Key Points
- Early Life and Education:
- He was born in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, into an affluent Jain family. Sarabhai was one of eight children of Ambalal and Sarla Devi.
- Undergraduate degree in Physics and Mathematics from Cambridge University.
- Pursued a PhD under Nobel laureate C.V. Raman at IISc, Bangalore, with the thesis titled "Time Distribution of Cosmic Rays," published in 1942.
- Institutional Legacy:
- Physical Research Laboratory (PRL), Ahmedabad: Founded in 1947, PRL marked the beginning of Sarabhai’s journey in institution building.
- Indian Institute of Management (IIM), Ahmedabad: Played a pivotal role in its creation.
- Community Science Centre, Ahmedabad: Founded in 1966 to promote science education.
- Darpan Academy for Performing Arts, Ahmedabad: Co-founded with his wife, Mrinalini Swaminathan.
- Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), Thiruvananthapuram: A hub for India’s space missions.
- Contributions to Indian Space and Nuclear Programs:
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO): He founded the ISRO, emphasizing the importance of space technology for societal development.
- Satellite Instructional Television Experiment (SITE): Conceptualized with NASA, SITE beamed educational programs to rural areas, laying the foundation for programs like Doordarshan’s Krishi Darshan.
- Aryabhata Satellite: Initiated the fabrication of India’s first satellite, Aryabhata, launched in 1975 from a Russian cosmodrome.
- Atomic Energy Commission: Took over as chairman after Homi Bhabha’s death, advancing nuclear science.
- Awards and Honors:
- Awards:
- Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Award (1962)
- Padma Bhushan (1966)
- Padma Vibhushan (posthumously, 1972)
- Distinguished Positions:
- President, Physics Section, Indian Science Congress (1962)
- President, General Conference of the IAEA, Vienna (1970)
- Vice-President, Fourth UN Conference on Peaceful Uses of Atomic Energy (1971)
- Title: Mahatma Gandhi of Indian Science (By former President APJ Abdul Kalam).
- Legacy:
- Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) was named in his honor.
- A lunar crater, “Sarabhai Crater,” was named after him.
- Awards:
National Current Affairs Switch to Hindi
Mega Tinkering Day 2025
Why in News?
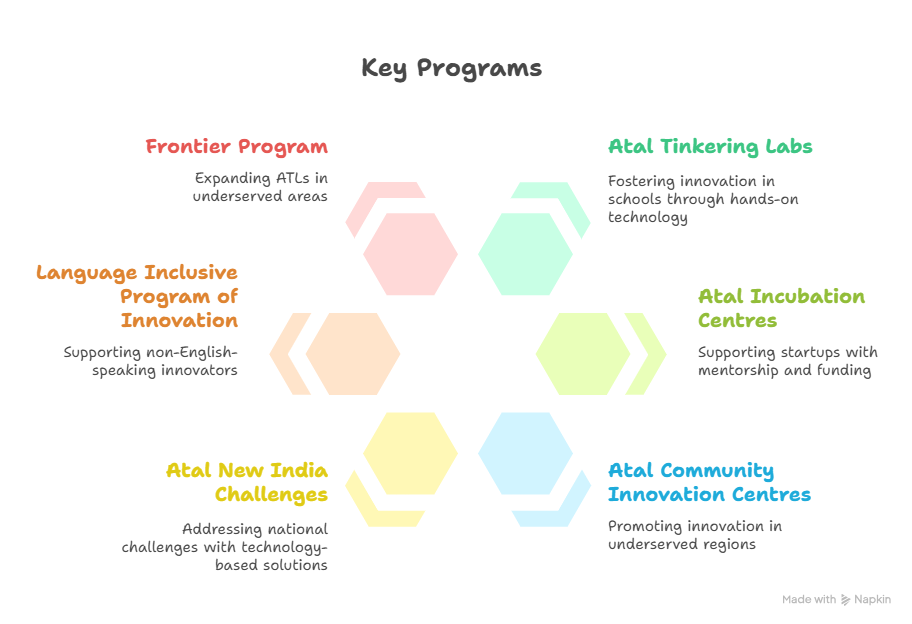
In a first-of-its-kind nationwide innovation movement, the Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), NITI Aayog, hosted Mega Tinkering Day 2025, marking a significant milestone in India's innovation landscape.
Key Points
- About: The nationwide event brought together over 10,000 Atal Tinkering Labs (ATLs) across all 35 states and Union Territories of India.
- The event witnessed 4,73,350 students from 9,467 ATL-equipped schools participating in a hands-on challenge to design and build a do-it-yourself (DIY) vacuum cleaner using everyday materials from their labs.
- Event Format:
- Virtual & Simultaneous: The event was held virtually and simultaneously in schools across India, with regional participation across North (Leh, Ladakh, Kargil, Kashmir), South (Kanniyakumari), West (Bhuj, Kutch), East (Manipur, Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh), and Aspirational Districts (Virudhunagar).
- Collaborative Learning: The online format enabled students to collaborate in real-time, despite geographical distances.
Atal Innovation Mission
- About: Launched by NITI Aayog in 2016, AIM promotes innovation and entrepreneurship by fostering a problem-solving mindset in students and strengthening the entrepreneurial ecosystem in universities and research institutions.
- AIM 2.0 aims to scale and pilot new initiatives to expand and strengthen India's innovation and entrepreneurship ecosystem, building on the success of AIM.
National Current Affairs Switch to Hindi
18th International Olympiad on Astronomy and Astrophysics
Why in News?
The 18th International Olympiad on Astronomy and Astrophysics (IOAA) is being held at Mumbai, India, from 11th to 21st August 2025.
- This is the second time that India is hosting the IOAA, after the 2016 edition in Bhubaneswar.
Key Points
- About: The IOAA is an annual competition for secondary school students (Classes 10 to 12), featuring a rigorous selection process to qualify for the international level.
- The IOAA was conceived in 2006 to address the increasing global interest in astronomy among high school students, with its first edition held in Chiang Mai, Thailand, in 2007.
- Organiser: The event is organised by the Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education (HBCSE), an autonomous institution under the umbrella of the Department of Atomic Energy.
- It is also supported by the Government of India through its Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) via the Vigyan Pratibha Project of HBCSE.
- Theme of the Olympiad: The theme for this year's event is ‘Vasudaiva Kutumbakam’, reflecting the ancient Indian idea that “the world is one family under the one sky”.
- Logo: The IOAA 2025 logo features the Gateway of India, a GSLV rocket representing India’s lunar mission, a spider symbolizing telescopes in the letter “O”, tri-coloured comets above the Gateway, and a colour scheme inspired by the Milky Way galaxy.
- Participants: The Olympiad has attracted over 300 high school students from 64 countries. During the event, students participate in several challenging exams covering theoretical, observational, and data analysis aspects of astronomy.
Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education (HBCSE)
- HBCSE is a National Centre of the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, which is a Deemed University in Mumbai.
- HBCSE is the nodal centre of Olympiad programmes in mathematics, physics, astronomy, chemistry, and biology.
- Another important programme of HBCSE is the National Initiative on Undergraduate Science (NIUS), concerning tertiary science education in India.
Astronomy
- Astronomy is the science that studies celestial objects such as stars, planets, comets, galaxies, and the universe as a whole.
Astrophysics
- Astrophysics is a branch of astronomy that uses the principles and laws of physics (such as gravity, thermodynamics), to understand and explain the physical processes that govern how celestial objects behave, form, and evolve.





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan