Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Bailey Bridge in Uttarakhand
Why in News?
The residents of Milam village are facing significant accessibility issues due to an avalanche that damaged the Bailey bridge over the Gaokha River.
- The Border Roads Organisation (BRO) has been instructed to repair the damage and reinstall the bridge at the earliest.
Key Points
- Location of the Bridge:
- Situated approximately 8 km from Milam village, the Bailey bridge is a vital connection between the village and several security posts along the China border.
- Milam village with a population of around 400 residents, is the last inhabited settlement in the Johar Valley, located near the India-China border.
- The 65-km-long Munsyari–Milam route is the only access corridor for residents during these seasonal movements.
- Situated approximately 8 km from Milam village, the Bailey bridge is a vital connection between the village and several security posts along the China border.
- About Bailey Bridge:
- A Bailey bridge is a type of modular bridge whose parts are pre-built, so they can be put together quickly as needed.
- Donald Coleman Bailey, an English civil engineer credited with inventing it during World War II.
- Their key features include modular design, ease of transport, high load-bearing capacity, and adaptability to various terrains.
- Bailey bridges are specifically engineered for quick assembly in challenging environments, requiring neither heavy machinery nor advanced construction techniques.
- The Indian armed forces inherited the Bailey bridge design from the British, using it in the 1971 war with Pakistan and in various disaster relief efforts, such as after the 2021 Uttarakhand flash floods.
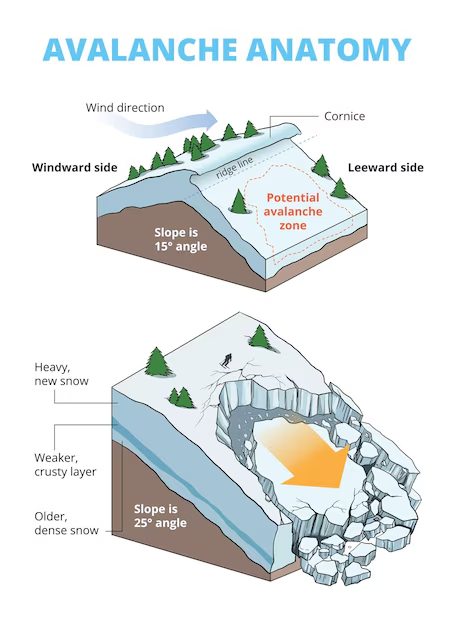
Avalanche
- About:
- An avalanche is the rapid flow of snow, ice, and debris down a mountain slope. It often carries earth, rocks, and rubble, causing destruction.
- Avalanche risk peaks from December to April due to heavy winter snowfall (snow accumulation) and spring thaw (weakening snow layers).
- Types:
- Loose Snow Avalanche: It starts from a single point where snow is not well bonded, spreads in an inverted V-shape as snow particles fall, and is less dangerous due to lower volume and speed.
- Slab Avalanche: It occurs when a cohesive snow slab breaks away from underlying layers, often reaching speeds of 50–100 km/h and causing significant destruction.
- Gliding Avalanche: The snowpack slides down a smooth surface, like grass or rock slabs, leaving a broad fracture line separating it from stationary snow.
- Wet-Snow Avalanche: A wet-snow avalanche is naturally triggered by rising temperatures or rain, as meltwater weakens the snow layer bonds.
Border Road Organisation (BRO)
- BRO was conceived and raised in 1960 for co-ordinating the speedy development of a network of roads in the North and the North Eastern border regions of the country.
- It works under the administrative control of the Ministry of Defence.
- It has diversified into a large spectrum of construction and development works comprising airfields, building projects, defence works and tunneling and has endeared itself to the people.
- The Union Government set up the Border Roads Development Board (BRDB) with the Prime Minister as Chairman of the Board and Defence Minister as Deputy Chairman.
Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
Powai Lake
Why in News?
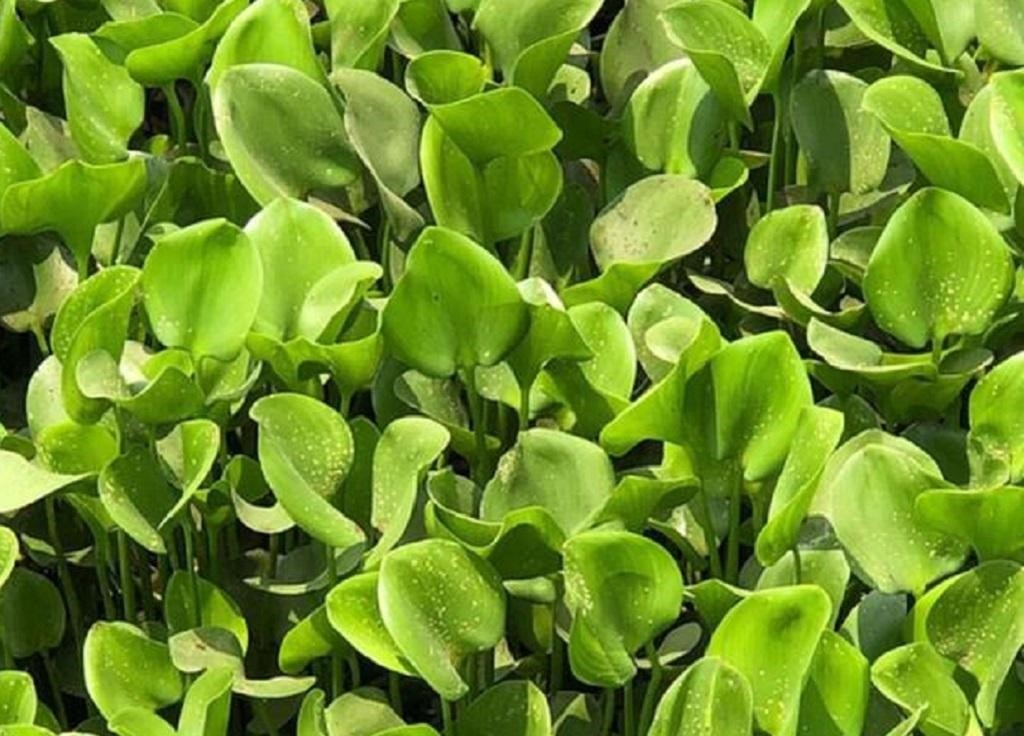
In Maharashtra, locals launched a campaign to save Powai Lake, aiming to raise awareness about pollution and the spread of invasive weeds like hyacinths.
Key Points
- About the Powai Lake:
- Location and Origin:
- Powai Lake is an artificial lake located in the northern suburbs of Mumbai.
- It was constructed in 1891 by building a dam across the Mithi River between two hillocks.
- Hydrological Features:
- The catchment area of the lake spans approximately 600 hectares.
- At its full supply level, the lake covers a water spread area of about 220 hectares.
- The lake water is primarily used for non-potable purposes such as gardening and industrial activities.
- Current Environmental Concerns:
- In recent years, over 40% of the lake has shrunk due to urban pressures.
- The lake’s condition has worsened with the rapid expansion of residential, commercial, and industrial zones around it.
- The discharge of untreated sewage and solid waste, particularly from nearby slums and residential settlements, has severely impacted water quality.
- Inclusion Under the National Lake Conservation Plan (NLCP):
- In 1995, the Ministry of Environment and Forests (MoE&F), under the National Lake Conservation Plan (NLCP), assessed the deteriorating condition of Powai Lake.
- As a result, Powai Lake was selected as one of ten major lakes in India identified for restoration and ecological improvement.
- Restoration Efforts:
- The revival programme for Powai Lake was fully funded by NLCP.
- Restoration work was officially launched in April 2002.
- The programme was implemented by the Bombay Municipal Corporation (BMC), now known as the Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation (BMC).
- Location and Origin:
National Lake Conservation Plan (NLCP)
- Until 2012–13, the Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change (MoEF&CC) extended financial support to States and Union Territories under two separate schemes:
- National Wetlands Conservation Programme (NWCP) – for identified wetlands, including some lakes.
- National Lake Conservation Plan (NLCP) – for urban and peri-urban lakes.
- To ensure better coordination and prevent duplication of efforts, the NWCP and NLCP were merged in February 2013.
- The merged initiative is now known as the National Plan for Conservation of Aquatic Eco-systems (NPCA), a centrally sponsored scheme aimed at the integrated conservation of all aquatic ecosystems.
Water Hyacinth
- Water hyacinth, scientifically known as Eichhornia crassipes Mart. (Pontederiaceae), is an aquatic weed common in waterbodies across South Asia, including India.
- This is not an indigenous species but was introduced to India during British colonial rule as an ornamental aquatic plant from South America.
- The plant produces beautiful purple flowers that have high aesthetic value.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Great Indian Bustard
Why in News?
The Rajasthan Forest Department named newly hatched Great Indian Bustard (GIB) (Ardeotis nigriceps) chicks Sindoor, Vyom, Mishri, and Sophia to honour Operation Sindoor and military personnel involved.
Key Points
- About Great Indian Bustard (GIB):
- GIB, Rajasthan’s state bird, is India’s most critically endangered bird.
- It is one of the heaviest flying birds in the world, and mainly found in Rajasthan’s Thar Desert, with small populations in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh.
- GIB is one among four bustard species found in India, alongside the Lesser Florican, Bengal Florican, and Macqueen's Bustard.
- GIB is omnivorous and vulnerable to power line collisions due to a lack of frontal vision.
- Ecological Importance: GIB acts as an indicator species, it reflects the health of grassland ecosystems. Their decline signals the degradation of native grasslands.
- Protection Status: IUCN Red List (Critically Endangered), CITES (Appendix 1), Convention on Migratory Species (CMS) (Appendix I), and Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 (Schedule I).
- Threats: Habitat loss from agriculture, mining, and infrastructure, along with collisions with power lines (the leading cause of adult mortality) threaten the GIB.
- Poaching has declined but human disturbance and unsustainable land use continue to impact the species.
- Conservation Efforts: Project GIB (launched in 2018), a joint initiative of the Ministry of Environment, Wildlife Institute of India, and Rajasthan Forest Department
- Captive breeding centres in Sudasari and Sam, Jaisalmer, use AI-enabled monitoring, incubators, and sensor-based systems to improve chick survival.
Operation Sindoor
- About: Operation Sindoor was a coordinated precision strike operation launched by the Indian Armed Forces on 7th May 2025, in retaliation for the Pahalgam terror attack.
- It was executed through the coordinated efforts of the Army, Navy, and Air Force, conducted from Indian territory.
- Unlike past operations with aggressive names meant to project strength, this operation’s name was chosen as a personal tribute to the victims, particularly the widows of the Pahalgam attack.
- Targets: Under 'Operation Sindoor,' the Indian Armed Forces targeted terror facilities linked to Jaish-e-Mohammed, Lashkar-e-Taiba, and Hizbul Mujahideen in Pakistan and PoJK.
- These strikes aimed to dismantle terrorist infrastructure used for planning attacks against India.
West Bengal Switch to Hindi
DRUM Web App
Why in News?
A team from IIT Kharagpur developed the Dynamic Route Planning for Urban Green Mobility (DRUM) web app, which functions like Google Maps but with an added advantage—it lets users choose routes based on air quality and energy efficiency.
Key Points
- Purpose of the App:
- The DRUM app offers five route options which are calculated using real-time air quality and traffic data.
- Shortest route, Fastest route, Least Exposure to Air Pollution (LEAP), Least Energy Consumption Route (LECR), Suggested route (a balance of all four factors).
- DRUM uses GraphHopper, a Java-based routing engine, and Mapbox for live traffic updates.
- The team tested DRUM across Delhi’s major corridors, factoring in traffic, road conditions, and pollution levels.
- The system supports multiple vehicle types and is designed to scale to other cities beyond Delhi.
- It eliminates high-pollution and high-energy routes to suggest a balanced path based on time, distance, air quality, and energy use.
- The DRUM app offers five route options which are calculated using real-time air quality and traffic data.
- Technical Challenges:
- Integrating real-time traffic and air quality data into the app was a major technical challenge, requiring efficient data fetching and processing to ensure quick response times.
- The team used the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB)and World Air Quality Index data, applying segment-wise interpolation to estimate pollution in sensor-free zones.
- Future Plans and DRUM 2.0:
- Field Testing & Data Expansion: IIT Kharagpur’s MUST Lab plans real-world DRUM trials and aims to integrate crowdsourced data from low-cost sensors on vehicles, street poles, and commuters, enabling support for micro-mobility modes.
- DRUM 2.0 Development: A predictive version using machine learning (like Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and Prophet) is in progress to forecast air quality, traffic, and energy use, offering smart, real-time route and timing suggestions for urban commuters.
Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB)
- About:
- The CPCB was established in September 1974 under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974.
- In 1981, it was also empowered under the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act 1981.
- It functions as a statutory authority and a field formation for the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC).
- It also provides technical support under the provisions of the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
- Functions:
- Under the Water Act, CPCB is responsible for maintaining cleanliness of streams and wells through prevention and control of water pollution.
- Under the Air Act, it works to improve air quality by preventing, controlling, and reducing air pollution across the country.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Dudhwa Tiger Reserve Boasts Butterfly Diversity
Why in News?
Known for its large tiger population, the Dudhwa Tiger Reserve (DTR), Uttar Pradesh, now boasts 180 species of butterflies, signaling a healthier ecosystem and enhanced conservation efforts.
Key Points
- Rise in Butterfly Species:
- A recent survey by the University of Lucknow recorded over 110 butterfly species in DTR, up from the earlier known count of just 45.
- Migratory and Rare Species:
- Migratory butterflies from Uttarakhand contribute to the growing diversity in Uttar Pradesh.
- Rare and notable species identified include Common Mormon, Common Mine, Common Lime, Tawny Coaster, Gaudy Baron (rare), Striped Tiger, Common Tiger (both sexes), Grey Count (rare), Commander.
- Significance:
- Butterflies, known as bio-indicators, are highly sensitive to climate change and thrive only in ecologically sound environments.
- This sharp increase signals a healthier and more balanced ecosystem.
- About Dudhwa Tiger Reserve (DTR):
- Background:
- Conservationist Billy Arjan Singh played a key role in securing the National Park status for Dudhwa in 1977.
- It was later designated a Tiger Reserve in 1987.
- Conservationist Billy Arjan Singh played a key role in securing the National Park status for Dudhwa in January 1977.
- Composition:
- The Dudhwa Tiger Reserve (DTR) includes:
- Dudhwa National Park
- Kishanpur Wildlife Sanctuary
- Katerniaghat Wildlife Sanctuary
- Buffer zones from North Kheri, South Kheri, and Shahjahanpur forest divisions.
- The Dudhwa Tiger Reserve (DTR) includes:
- Flora and Fauna:
- The region represents a Tarai-Bhabar ecosystem of the Upper Gangetic plains.
- The vegetation is primarily North Indian Moist Deciduous Forest.
- The reserve is known for its rich biodiversity, home to a wide variety of flora and fauna including the Bengal tiger, Indian rhinoceros, swamp deer, leopard and several species of birds.
- Biodiversity and Conservation Status:
- Dudhwa National Park, covering an area of 490.3 sq km, is home to 135 tigers, out of a total of 205 tigers in Uttar Pradesh, marking a significant increase from 82 tigers in 2018.
- In the 2022 All-India Tiger Census, Dudhwa Tiger Reserve (DTR) was ranked fourth in India for its tiger population.
- Background:
Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
Birsa Munda Martyr’s Day
Why in News?
On 9th June 2025, the Prime Minister paid tribute to Bhagwan Birsa Munda on the occasion of his Martyr's Day.
Key Points
- About Birsa Munda:
- Birsa Munda was a tribal leader, religious reformer, and freedom fighter who led a strong resistance against British colonial policies in the Chotanagpur region.
- Also known as Dharti Abba (Father of the Earth), he is remembered for mobilising Adivasi communities around land rights, social reform, and spiritual unity.
- Early Life: Born on 15th November 1875 in Ulihatu (Khunti district, Jharkhand) to a poor Munda tribal sharecropper family, Birsa was initially named Daud Munda due to his father's temporary conversion to Christianity.
- Education: Educated at the German Mission School, Birsa was initially influenced by Christian teachings but rejected them due to cultural alienation.
- He was inspired by Vaishnavism, he founded the Birsait religion and was revered as Bhagwan by his followers.
- Beliefs and Teachings: He preached monotheism through the worship of Singhbonga (sun god), denounced alcoholism, black magic, superstitions, and forced labour (beth begari), and promoted hygiene, spiritual unity, pride in tribal identity, and community land ownership.
- Resistance Against British Rule: British land revenue policies dismantled the traditional Khunt Katti land system (collective land ownership within a clan), empowering zamindars and thikadars who exploited tribal peasants.
- Birsa mobilised tribal masses against these injustices and campaigned to reclaim their rights.
- The Ulgulan Movement (1895–1900): In 1895, Birsa Munda was arrested for rioting and jailed for 2 years; after his release in 1897, he resumed mobilising support across villages for a tribal-led self-rule movement.
- In 1899, he launched the Ulgulan (The Great Tumult) movement, which included guerrilla warfare tactics to resist British authority and promote the establishment of a self-governed tribal state known as "Birsa Raj"
- Aftermath and Legacy: He was captured in February 1900 and died in British custody on 9th June 1900 at the young age of 25, under mysterious circumstances, officially attributed to cholera.
- His movement led to the Chotanagpur Tenancy Act (1908), which recognised tribal land rights (Khuntkatti), banned land transfer to non-tribals, and abolished beth begari (forced labour).
- Since 2021, 15th November is observed as Janjatiya Gaurav Divas (Tribal Pride Day).
- Birsa Munda was a tribal leader, religious reformer, and freedom fighter who led a strong resistance against British colonial policies in the Chotanagpur region.
Key Initiatives Related to Tribal Communities
- Dharti Aaba Janjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan is an umbrella initiative that targets integrated development across 63,000 Scheduled Tribe-majority villages.
- PM-JANMAN was initiated in 2023 to support Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) with targeted schemes, including healthcare, financial inclusion, and community support.
- Pradhan Mantri Adi Adarsh Gram Yojana (PMAAGY) aims to provide basic infrastructure in villages with a significant tribal population.






















.jpg)









.png)


.jpg)

 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan