Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Bachpan Day Care Centres
Why in News?
The Uttar Pradesh government is set to expand its initiatives for children with special needs and persons with disabilities by opening Bachpan Day Care Centres in 26 more districts, alongside launching new schemes to improve accessibility, education, rehabilitation, and training.
Key Points
- About the Bachpan Day Care Centres: They are specialized facilities established by the Uttar Pradesh government to provide early intervention, care, education, and social training to children with special needs.
- These centres aim to nurture the overall development of differently-abled children by offering a supportive and inclusive environment from an early age.
- Currently, these centres operate in 25 districts, covering all divisional headquarters and seven aspirational districts.
- The seven aspirational districts of UP– Chitrakoot, Fatehpur, Bahraich, Shrawasti, Balrampur, Siddharthnagar, and Chandauli.
- Accessibility and Infrastructure Improvements:
- A new scheme has been proposed to ensure that all stadiums and sports complexes are made fully accessible to persons with disabilities.
- Additionally, infrastructure across the state will be upgraded to enhance accessibility and comfort for individuals with disabilities, promoting inclusivity and equal participation in public spaces.
- The step aims not only to promote their participation in sports but also to reinforce the spirit of ‘Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat’.
- A new scheme has been proposed to ensure that all stadiums and sports complexes are made fully accessible to persons with disabilities.
- Digital Transformation in Special Education:
- Introduction of an E-Learning Management System portal for special schools.
- Enables real-time monitoring of academic activities and student talents.
- Enhances educational quality and fosters the holistic development of children with special needs.
- Rehabilitation and Support for the Intellectually Challenged:
- Plans to establish shelter homes-cum-training centres in every district.
- These centres will provide a safe environment and skill-based training.
- Supported by government and private entities to encourage independent living.
- Training and Support for Special Educators:
- Introduction of in-service refresher courses and training programmes for special educators.
- Aim to keep teachers updated with modern pedagogical methods.
- Helps educators better address the evolving needs of students with disabilities.
Schemes Related to Children with Special Needs
- Divyang Pension Yojana: The state government’s pension scheme provides monthly financial assistance to disabled persons of 18 years or more, helping improve their livelihood and standard of living. The pension amount is periodically increased to offer better support.
- Deen Dayal Disabled Rehabilitation Scheme (DDRS): The scheme was launched in 1999 and was revised and renamed in 2003. It was previously known as the "Scheme for Promoting Voluntary Action for the Disabled".
- DDRS is a Central Sector Scheme that provides financial assistance to voluntary organizations working for the education and rehabilitation of persons with disabilities.
West Bengal Switch to Hindi
City Gas Distribution Project in West Bengal
Why in News?
The Prime Minister laid the foundation stone for a new City Gas Distribution (CGD) project in Alipurduar, West Bengal marking a significant step in expanding India's CGD network.
Key Points
- City Gas Distribution Project:
- About: Under the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB) Act 2006, PNGRB grants authorization to the entities for developing a CGD network in a specified Geographical Area (GA) of the country.
- Over 2.5 lakh households are expected to benefit from this project, which aims to deliver clean, safe, and affordable piped natural gas while generating employment opportunities across the region.
- The project aligns with the government's Minimum Work Programme (MWP) targets.
- City gas services have expanded from just 66 districts in 2014 to over 550 in 2025, reaching even rural areas and small towns.
- Benefits:
- The initiative will reduce reliance on Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) cylinders, offering a more secure and convenient gas supply.
- Expansion of Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) stations will make eco-friendly fuel more accessible for vehicles.
- About: Under the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB) Act 2006, PNGRB grants authorization to the entities for developing a CGD network in a specified Geographical Area (GA) of the country.
- Impact of Other Clean Fuel Government Initiatives on West Bengal:
- Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana:
- The Ujjwala Yojana (launched in 2016) was praised during the event for promoting the use of clean fuel in households.
- The scheme has improved the health and dignity of poor women by freeing them from hazardous indoor air pollution caused by traditional cooking methods.
- LPG distributors have risen from 14,000 to over 25,000, greatly improving rural access to clean cooking fuel.
- Urja Ganga Project:
- The Urja Ganga Project (launched in 2016) to cater energy requirements of five states namely Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal.
- The initiative marked a transformative leap in strengthening gas infrastructure across eastern India, significantly improving regional energy access.
- It also generated widespread employment opportunities, ranging from pipeline construction to grassroots-level gas distribution.
- Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana:
- Infrastructure Boost in West Bengal:
- Key central government infrastructure projects include:
- Purva Expressway and Durgapur Expressway
- Modernisation of Shyama Prasad Mukherjee Port
- Expansion of Kolkata Metro
- Upgradation of New Jalpaiguri Station
- New train services along the Dooars route
- Key central government infrastructure projects include:
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Airports Inaugurated in Madhya Pradesh under UDAN Scheme
Why in News?
The Prime Minister virtually inaugurated the newly constructed Satna Airport and the upgraded Datia Airport in Madhya Pradesh, taking a major step towards strengthening regional connectivity and advancing infrastructure development under the UDAN scheme.
Key Points
- Satna Airport:
- Developed by the Airports Authority of India (AAI) at a cost of Rs 36.96 crore, Satna Airport is set to become a key regional hub in northeast Madhya Pradesh.
- The airport will enhance connectivity to prominent destinations such as Chitrakoot and Maihar, strengthening both cultural and industrial linkages.
- Key features include a recarpeted runway, parking bays for Dornier-228 aircraft, an ATC tower, and a fire station.
- Sustainable features include 100% LED lighting, solar-powered streetlights, and a treated water reuse system for horticulture.
- Developed by the Airports Authority of India (AAI) at a cost of Rs 36.96 crore, Satna Airport is set to become a key regional hub in northeast Madhya Pradesh.
- Datia Airport:
- The upgraded Datia Airport has been developed at a cost of Rs 60.63 crore, connecting this historic town to the national aviation grid.
- Datia, known for landmarks like Peetambara Peeth and the Datia Palace, stands to gain from increased religious and cultural tourism.
- The airport is currently suitable for ATR-72 aircraft and is being prepared for future operations of Airbus A-320 aircraft.
- Infrastructure includes a recarpeted runway, apron bays, an ATC tower, and firefighting services, along with rainwater harvesting and energy-efficient lighting systems.
- The upgraded Datia Airport has been developed at a cost of Rs 60.63 crore, connecting this historic town to the national aviation grid.
- Driving Socio-Economic Transformation:
- The operationalisation of both airports will boost economic activity, create employment, and improve access to key services in the Bundelkhand and Baghelkhand regions.
- These projects reflect the Centre’s focus on inclusive growth under the UDAN scheme, making affordable air travel a reality for underserved regions.
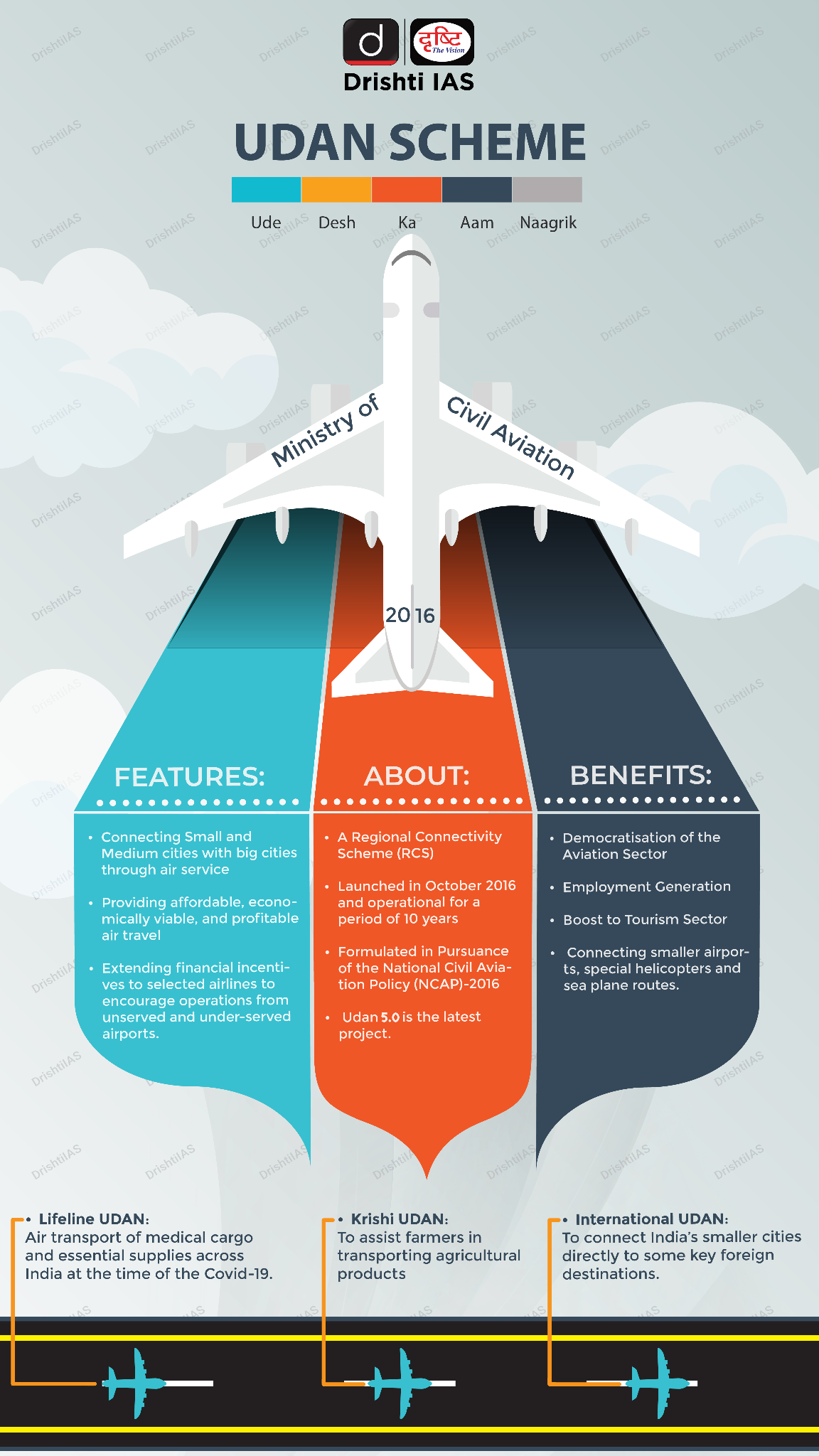
UDAN Scheme
- About:
- UDAN aims to democratize aviation and enhance regional connectivity, ensuring that even remote regions of the country are accessible by air.
- The scheme was designed under the National Civil Aviation Policy (NCAP) 2016, with a focus on connecting Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities through a market-driven yet financially supported model.
- The Airports Authority of India (AAI) serves as the nodal agency responsible for its implementation.
- Key Features of UDAN Scheme:
- Viability Gap Funding (VGF): Financial support to airlines to ensure affordable fares.
- Regional Connectivity Fund (RCF) was created to meet the viability gap funding requirements under the scheme.
- Airfare Cap to ensure affordability.
- Reduced taxes on Aviation Turbine Fuel (ATF) and other concessions to airlines to make operations viable on regional routes.
- Collaborative Governance between the Centre, States, the AAI, and private airport operators.
- Viability Gap Funding (VGF): Financial support to airlines to ensure affordable fares.
- Key Innovations under UDAN:
- UDAN Yatri Cafes: Affordable Yatri Cafes have been launched at Kolkata and Chennai airports, offering quality food at accessible prices.
- Krishi UDAN Scheme: Designed to support farmers and improve value realisation for agri-produce, Krishi UDAN facilitates timely and cost-effective air logistics, particularly from Northeast, hilly, and tribal regions.
- Lifeline Udan was launched to transport essential medical cargo to remote areas during the Covid-19 pandemic.
Airports Authority of India (AAI)
- The AAI is a statutory body under the Directorate General of Civil Aviation, Ministry of Civil Aviation.
- It was formed in 1995, by merging the National Airports Authority and the International Airports Authority of India.
- It also provides Air Traffic Management Services over Indian airspace and adjoining oceanic areas.
- The functions of AAI include airport development, airspace control, passenger and cargo terminal management, and provision of communication and navigation aids.
- AAI provides air navigation services over 2.8 million square nautical miles of air space.
Pitambara Peeth
- Pitambara Peeth is a Hindu temple complex which also includes an ashram, located in Datia city of Madhya Pradesh.
- The Shri Vankhandeshwar Shivalinga located here is believed to be from the Mahabharata period. This temple is one of the major centers of Shakti Sadhana.
- The Peetha was established in 1935 by Swamiji Maharaj with the cooperation of Raja Shatrujit Singh Bundela of Datia.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Sustainable Aviation Fuel Manufacturing Policy-2025
Why in News?
The Uttar Pradesh government has unveiled plans for the Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) Manufacturing Policy-2025, aimed at converting agricultural waste into jet fuel.
- A high-level roundtable conference was organized by Invest UP in Lucknow to discuss the policy framework.
Key Points
- About the SAF: It is produced from renewable sources such as agricultural waste, municipal solid waste, and forestry residues.
- It has the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 80% compared to conventional jet fuel.
- Indigenous feedstock like sugarcane molasses and Make in India technology are being used to produce SAF.
- About the Policy: The policy targets the production of sustainable aviation fuel from agricultural residues like sugarcane bagasse, rice husk, and wheat straw.
- It aims to establish industrial units within Uttar Pradesh for bio-jet fuel manufacturing.
- This initiative will directly benefit around 2.5 crore farmers by creating new markets for their crop waste.
- Significance of the Policy:
- First of Its Kind in India: Marks a pioneering step towards integrating agricultural waste-based biofuels into India’s aviation fuel mix.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Supports India’s commitment under the Paris Agreement to reduce carbon intensity and promote renewable energy.
- Agricultural Waste Management: It can reduce stubble burning, a major cause of air pollution and smog in northern India, improving public health and ecological balance.
- Rural Economy Upliftment: Creates new markets and value chains for agricultural residues, generating additional income sources for farmers.
- Industrial Growth: Promotes establishment of SAF manufacturing units, leveraging UP’s strategic logistics and agro-industrial base.
- Related Challenges:
- Technological Viability: Developing reliable and scalable processes to convert varied agricultural wastes into aviation fuel efficiently remains a major hurdle.
- Price Competitiveness: Producing SAF at a cost close to conventional jet fuel is necessary to encourage adoption without heavy subsidies.
- Infrastructure Development: Effective collection, transport, and storage of dispersed crop residues need robust logistics to maintain a steady supply.
- Policy Integration: Aligning state and central policies on biofuels and aviation is essential to streamline approvals and incentives.
- Way Forward:
- Incorporate Stakeholder Feedback: Engaging farmers, industry, and experts will help tailor the policy to real-world challenges.
- Facilitate Research & Development: Investment in R&D can improve technology efficiency and reduce production costs.
- Create Incentives: Financial benefits for SAF producers and users will promote market growth.
- Strengthen Farmer Outreach: Educating farmers and ensuring fair prices will secure reliable feedstock supply.
- Promote Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between government and private sector can drive large-scale, sustainable SAF production.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
20th Governor's Cup Golf Tournament - 2025
Why in News?
The 20th Governor's Cup Golf Tournament - 2025, organized by the Raj Bhavan Golf Club, Nainital, concluded successfully on 1st June 2025.
- The Governor of Uttarakhand presented awards to winners and runners-up across multiple categories.
Key Points
- About the Tournament: The tournament was held over three days from 30th May to 1st June 2025, in Nainital, Uttarakhand.
- A total of 177 golfers from various states across India participated in the event.
- Significance:
- The Raj Bhavan Golf Course was opened in 2024 to encourage children, youth, and students to take an interest in golf.
- Special efforts have been made to encourage female players and youth participation in the sport.
- Winners of 2025:
|
Category |
Winner |
|
Super Veteran Gross Category |
Colonel S.C. Gupta |
|
Women’s Category |
Shrishti Dhan |
|
Gross Category |
Zafar Iqbal |
|
Net Category (15-17 age group) |
Amyra Bajaj |
|
Amateur Category (12-14 age group) |
Samridh Chand Thakur |
Raj Bhawan Golf Club, Nainital
- The Raj Bhawan Golf Club in Nainital was established in 1926 as part of the Government House estate.
- The course is located in a lush, pristine mixed forest at an elevation ranging from 6,700 to 7,000 feet above sea level in the hill station of Nainital.
- The Raj Bhawan Golf Club has a rich history and is regarded as a prominent destination for golfers across India.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Rajasthan to Manufacture Rifles and Machine Guns
Why in News?
Under the ‘Make in India’ and ‘Rising Rajasthan’ initiatives, Rajasthan secured defence clearance for projects worth over Rs 1500 crore.
- It marks a significant milestone for the state’s defence manufacturing sector, positioning it as a key player in India’s defence production and exports.
Key Points
- Rajasthan’s Role in Defence Manufacturing:
- Gun parts will be manufactured in locations like Jodhpur and Jaipur, with barrels produced at a specialised facility in Boranada, Jodhpur—ensuring supply chain security through a decentralised, infrastructure-driven approach.
- A key challenge is meeting safety norms for ammunition storage, which requires facilities to be 8–10 km from inhabited areas; the government is being approached for suitable land allocation.
- Gun parts will be manufactured in locations like Jodhpur and Jaipur, with barrels produced at a specialised facility in Boranada, Jodhpur—ensuring supply chain security through a decentralised, infrastructure-driven approach.
- Advanced Weapon Systems Under Production:
- Military-Grade Sniper Rifle: Engineered for long-range precision with sub-minute of angle (MOA) accuracy up to 2.4 km, this fully indigenous weapon is built to perform reliably across diverse environments.
- Multi-Barrel Machine Gun: Boasting a firing rate of 6,000 rounds per minute and a 1,000-yard range, it can fire 15,000 rounds per belt, with future upgrades planned for C-RAM (Counter Rocket, Artillery, and Mortar) and anti-aircraft roles.
- Significance for India’s Defence Ecosystem:
- Alignment with ‘Make in India’: The initiative embodies India’s vision of self-reliance in defence manufacturing by producing fully indigenous, cutting-edge weapon systems.
- Decentralised and Robust Production: Multiple production hubs reduce risk, improve security, and leverage regional industrial infrastructure, contributing to resilience in the supply chain.
- Boost to Defence Start-ups: Involvement of defence startups in the project reflects the growing role of innovation and private sector participation in the defence sector.
- Export Potential: Early interest from countries such as Togo and Thailand indicates promising export opportunities, supporting India’s goal to become a global defence supplier.
- Complement to Existing Defence Production: Following Uttar Pradesh’s success with BrahMos missile production, Rajasthan’s entry into small arms manufacturing diversifies India’s defence production capabilities.
BrahMos Missile
- The BrahMos missile, which has a range of 290 km, is an Indo-Russian joint venture and is the world's fastest cruise missile with a top speed of Mach 2.8 (about three times the speed of sound).
- BrahMos is named after the Brahmaputra (India) and Moskva (Russia) rivers.
- It is a two-stage missile (solid propellant engine in the first stage and liquid ramjet in the second stage).
- It is a multiplatform missile i.e. it can be launched from land, air and sea and is a multi-capability missile with high accuracy which operates both during day and night irrespective of weather conditions .
- It operates on the "fire and forgets" principle i.e. it does not require guidance after launch.
- Vietnam, the United Arab Emirates and Indonesia are among other potential customers for the BrahMos missile.
‘Make in India’ Initiative
- About: The campaign was launched to facilitate investment, foster innovation, enhance skill development, protect intellectual property & build best-in-class manufacturing infrastructure.
- Objectives:
- Increase the growth rate of the manufacturing sector to 12-14% per annum.
- Create 100 million additional manufacturing jobs by 2022 (revised to 2025).
- Increase the manufacturing sector's contribution to GDP to 25% by 2025.
- Pillars of ‘Make in India’:
- New Processes: Recognized 'ease of doing business' as vital for entrepreneurship, implementing measures to improve the business environment for startups and established enterprises.
- New Infrastructure: The government prioritised developing industrial corridors and smart cities to create world-class infrastructure.
- It also enhanced innovation and research through streamlined registration systems and improved intellectual property rights (IPR) infrastructure.
- Make in India 2.0: The ongoing "Make in India 2.0" phase, encompassing 27 sectors, continues to propel the program forward, consolidating India’s role as a significant player in the global manufacturing arena.






















.jpg)









.png)


.jpg)

 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)



