- Filter By :
- Polity & Governance
- International Relations
- Social Justice
-
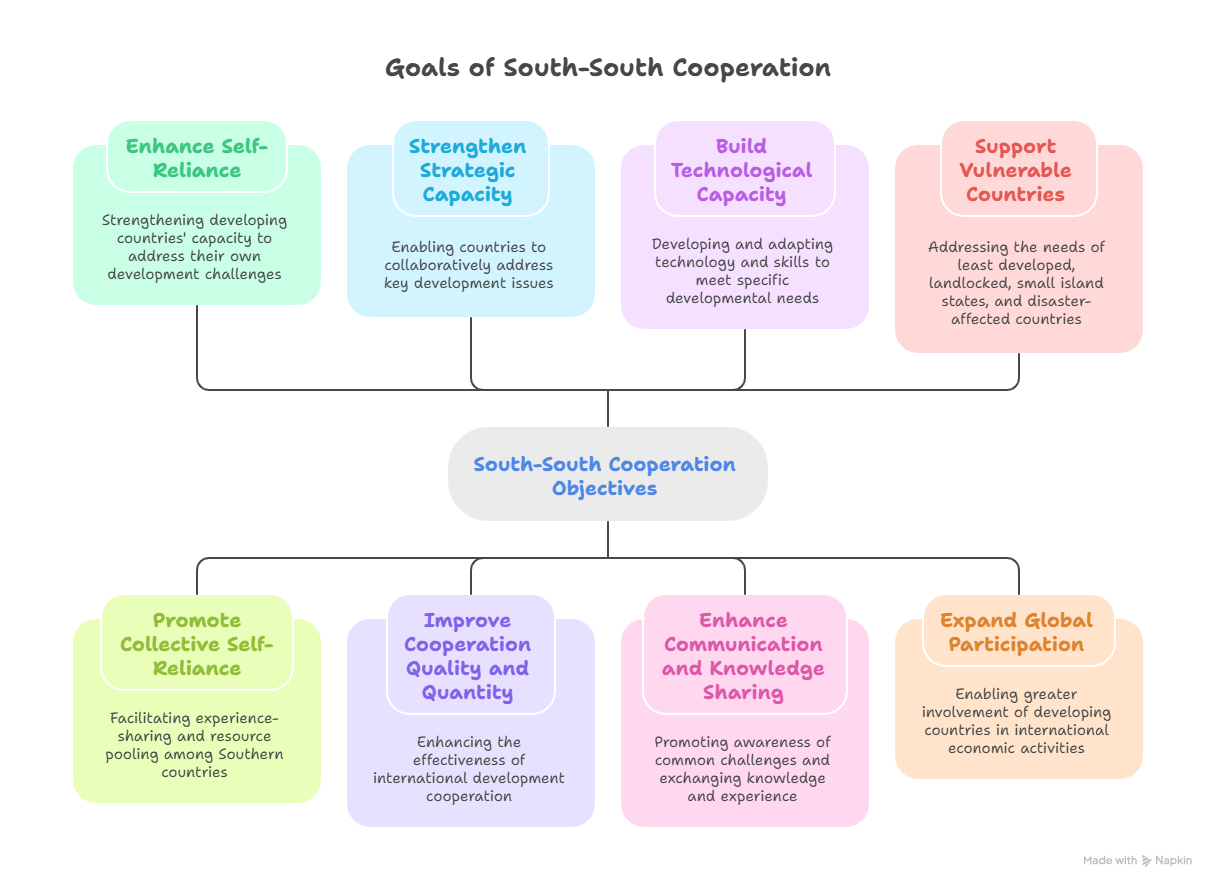
Q. "South-South and Triangular Cooperation (SSTC) aims to promote knowledge sharing and sustainable development among developing countries." Examine India’s role in SSTC and its impact on global development partnerships. (250 words)
07 Oct, 2025 GS Paper 2 International RelationsApproach :
- Provide a brief introduction to the South-South and Triangular Cooperation (SSTC).
- Discuss India’s Role in Advancing South-South and Triangular Cooperation
- Discuss its impact on global development partnerships.
- Conclude with a suitable way forward
Introduction:
South-South and Triangular Cooperation (SSTC) is a collaborative development framework where two or more developing (Global South) countries exchange knowledge, skills, resources, and technology to advance mutual development goals, often with the support of a developed country or multilateral agency; it is guided by principles of equality, solidarity, respect for sovereignty, and aims to empower countries through shared experience and collective self-reliance, complementing traditional North-South aid.
Body :
India’s Role in Advancing South-South and Triangular Cooperation
- Leadership in Capacity Building and Knowledge Sharing: India launched the India-UN Global Capacity-Building Initiative to share Indian best practices with other Global South nations.
- It facilitates skills training, knowledge exchanges, pilot projects, and institutional cooperation to accelerate the SDGs.
- Contributions through the India-UN Development Partnership Fund: Established in 2017 with a contribution of $150 million, the fund backs demand-driven, transformational projects across the Global South.
- Promotion of Digital Public Infrastructure for Equitable Development: India leverages scalable digital tools like Aadhaar and UPI to support digital finance in partner countries.
- Institutionalising and Strengthening Regional Networks: India hosts Voice of the Global South Summits, reinforcing its role as a voice for developing countries.
- During its G20 presidency, India secured the African Union’s permanent membership in the G20, enhancing the political and economic influence of Africa and other southern countries.
- Innovative Agricultural and Food Security Initiatives: Through partnerships with ICRISAT and DAKSHIN (Development and Knowledge Sharing Initiative), India promotes agricultural innovation and climate-smart farming.
- Advocacy for Global South Priorities in Multilateral Forums: India actively promotes initiatives such as the UN Day for South-South and Triangular Cooperation (SSTC), emphasising innovative collaborations, climate resilience, and socio-economic development.
Impact on Global Development Partnerships
- Empowerment through Solidarity and Equality: SSTC is based on principles of mutual respect, solidarity, equality, and shared learning among developing countries.
- This approach builds political and economic self-reliance in the Global South, a key principle since the 1978 Buenos Aires Plan of Action.
- Driving Global Economic Growth: Countries of the Global South have contributed to over half of the recent global economic growth.
- Intra-South trade now accounts for more than one-quarter of world trade, and foreign direct investment (FDI) outflows from the South represent a third of global flows.
- SSTC harnesses these dynamics for shared development outcomes.
- Cost-effective, Scalable, and Context-specific Development Solutions: SSTC offers locally tailored solutions to pressing challenges like climate change, health, and digital finance.
- The cooperation enables replication of cost-effective innovations such as India’s Aadhaar digital ID system and UPI payments model shared with other developing countries.
- Enhancing Institutional and Technical Capacities: South-South partnerships strengthen institutional capacities, technical knowledge, and resource mobilisation.
- Costa Rica, the Dominican Republic, and Germany collaborate through a triangular partnership on coral reef restoration, combining finance, technical expertise, and community practices to boost reef resilience and marine biodiversity in the Caribbean region.
- Mainstreaming SSTC within Global Development Agendas: SSTC is increasingly institutionalised in UN policies and development frameworks, with over 60 resolutions and outcome documents recognising its importance.
- United Nations entities are integrating SSTC strategies globally to support member states in areas such as health, climate action, social protection, and more, reflecting rising demand from developing countries.
Conclusion:
South-South and Triangular Cooperation (SSTC) embodies solidarity and shared innovation among developing countries, but its full potential requires addressing funding, capacity, and coordination challenges. It is crucial for advancing sustainable and resilient development aligned with the SDGs. Moving forward, strengthening institutional capacities, scaling nature-positive solutions, and fostering inclusive partnerships remain vital to harness SSTC’s full potential for a greener and equitable future.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.
Print PDF