- Filter By :
- Polity & Governance
- International Relations
- Social Justice
-
Q. Discuss the strategic importance of the Strait of Hormuz for global energy security and international trade. (150 words)
03 Jan, 2023 GS Paper 2 International RelationsApproach
- Start your answer by briefly introducing Strait of Hormuz.
- Discuss its strategic and global energy security importance.
- Discuss significance of Strait of Hormuz in Indian Perspective.
- Conclude accordingly.
Introduction
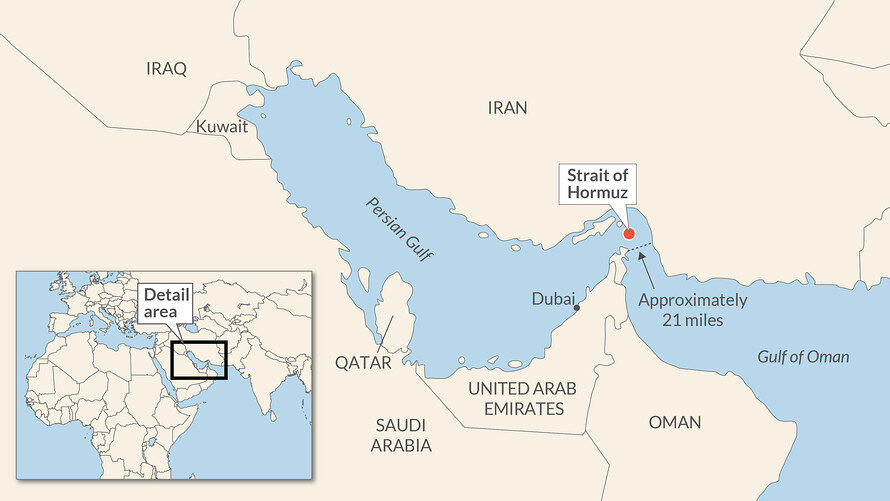
- The Strait of Hormuz is the world’s single most important oil passageway, forming a chokepoint between the Arabian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman.
- It lies between Oman and Iran, linking the sea passage from the countries on the Gulf (Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates) with the Arabian Sea and beyond.
- Strategic Importance:
- Volatile and Contested Region: The Strait is located in a volatile and contested region, and it has been the site of several conflicts and tensions in the past. As a result, the Strait is considered a key factor in regional security and stability, and it has been the focus of attention for various actors seeking to protect their strategic interests in the region.
- The potential consequences of disruptions to shipping in the Strait of Hormuz are significant, as they could disrupt the global energy trade and lead to economic and political instability.
- Heavily Militarized: In order to address these risks, various strategies have been adopted by different actors, including the deployment of military forces and the establishment of international agreements to ensure the freedom of navigation in the Strait.
- Therefore, the United States Fifth Fleet, based in Manama, Bahrain, is responsible for protecting maritime shipping lanes.
- Importance of Hormuz strait for Global Energy Security and International trade:
- Important Shipping Lane: The 39km strait is the only route to the open ocean for over one-sixth of global oil production and one-third of the world’s liquified natural gas (LNG).
- As a result, the Strait of Hormuz is a critical gateway for the global energy trade, as approximately 20% of the world's oil and 35% of the world's liquefied natural gas pass through it each year.
- Further, around one-sixth of the world’s oil moves through the strait – 17.2 million barrels per day.
- This includes most of the oil from Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) members Saudi Arabia, Iran, the UAE and Kuwait. Qatar, the world’s biggest exporter of LNG, sends most of its LNG through the strait as well.
- Energy Chokepoint: The Energy information Assessment (EIA) defines a chokepoint as a narrow channel along widely used global sea routes that are critical to energy security.
- Therefore, the inability of oil to transit a major chokepoint such as strait of Hormuz, even temporarily, can lead to substantial supply delays and higher shipping costs, resulting in higher world energy prices.
- Most chokepoints can be circumvented by using other shipping channels but some, such as the Strait of Hormuz, have no practical alternatives.
- Significance for India:
- Energy Procurement: India is heavily dependent on imported oil and gas to meet its energy needs, as it imports almost 84% of crude oil through the Strait of Hormuz.
- These imports come from the Middle East, including countries in the Persian Gulf region.
- As a result, the Strait of Hormuz is of particular importance to India, as any disruption to shipping in the Strait could have significant consequences for India's energy security.
- Any major disruption in the strait will directly and adversely affect India. There are few alternatives and even fewer potential options to bypass the Strait of Hormuz.
- Security Implication: The recent tensions between US-Iran and series of attacks on oil carrier watercrafts, had made India vary of its energy and trade security.
- Therefore, India initiated its own operation namely “Sankalp” to protect the routing of its shipping oil tankers in the Gulf of Oman and Persian Gulf.
- Further, Indian navy claims to be a Net Security Provider in Indian Ocean Region through Maritime Security Operation and deployed its assets, namely Ships Chennai and Sunayna, to re-assure Indian-flagged vessels operating and transiting through the strait.
- Volatile and Contested Region: The Strait is located in a volatile and contested region, and it has been the site of several conflicts and tensions in the past. As a result, the Strait is considered a key factor in regional security and stability, and it has been the focus of attention for various actors seeking to protect their strategic interests in the region.
Conclusion
Overall, it is clear that the Strait of Hormuz is of strategic importance for India and global energy security and international trade due to its geography, the volume of oil and gas passing through it, and its geopolitical context. As a result, it will likely continue to be a focus of attention for various actors seeking to protect their strategic interests in the region.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.
Print PDF