Governance
United Nations Convention against Cybercrime
- 29 Oct 2025
- 9 min read
For Prelims: Cybercrime, UN Office on Drugs and Crime, Budapest Convention on Cybercrime, National Crime Records Bureau
For Mains: International law and cyber governance, Transnational cybercrime
Why in News?
The United Nations Convention against Cybercrime (UNCC), the world’s first global framework to tackle cybercrime, moved closer to becoming legally binding after 72 of 193 UN member states signed the treaty.
Note: The Convention was opened for signature in Hanoi, Vietnam in October 2025, where 72 countries signed it during the high-level conference. It will enter into force 90 days after 40 countries ratify or accede to it.
What is the United Nations Convention against Cybercrime (UNCC)?
- About: The UNCC officially called the Convention on Cybercrime: Strengthening International Cooperation to Combat Crimes Committed Through Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Systems, is the first international criminal justice treaty to have been negotiated in over 20 years.
- The convention, developed by the UN Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), was adopted by consensus under UN General Assembly Resolution 79/243 in December 2024.
- Key Provisions: UNCC provides legal measures to address crimes committed via ICT systems.
- It facilitates cross-border sharing of electronic evidence in serious crimes crimes such as illegal data interception, hacking, money laundering, and online child sexual abuse material.
- The convention promotes capacity building and technical assistance for developing nations.
- UNCC also includes human rights protections while enabling digital law enforcement.
- Implementation Mechanism: UNCC establishes a Conference of the States Parties to monitor and review implementation.
- UNODC serves as the secretariat for the Convention, providing technical support, training, and assistance for national implementation, along with guidance through its Global Programme on Cybercrime.
- States that did not sign may later accede by depositing an instrument of accession.
- India and UNCC: India has not signed the UNCC as of October 2025, despite being an active participant in its drafting.
- Earlier India also declined to sign the Budapest Convention on Cybercrime, consistent with its approach of wanting a greater role in shaping global digital frameworks.
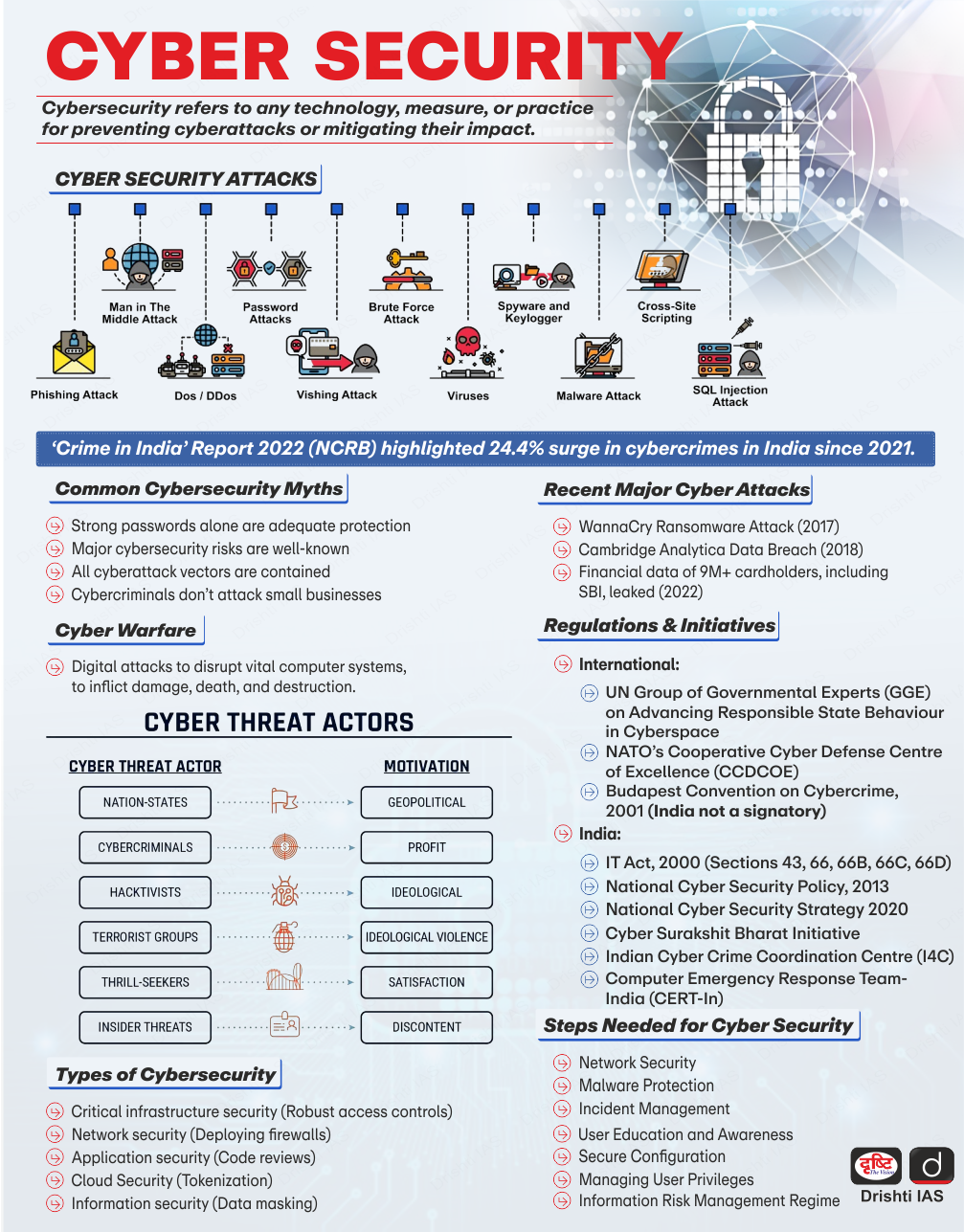
What is Cybercrime and Cybersecurity?
Cybercrime
- About: It refers to criminal activities that use or target digital technologies, networks, or devices.
- Perpetrators range from individual hackers to organized criminal networks, exploiting the anonymity and reach of the internet.
- These crimes transcend borders and can affect national security, financial systems, and personal safety.
- Developing countries are especially vulnerable due to weak cybersecurity infrastructure and low awareness.
- Emerging technologies like AI, deepfakes, and generative tools have created new risks around misinformation, privacy, and copyright infringement.
- Categories:
- Cyber-enabled Crimes: Traditional crimes conducted online, such as fraud, trafficking, hate speech, and incitement to violence.
- Cyber-dependent Crimes: Crimes that can occur only through ICT systems, including phishing, identity theft, malware attacks, and ransomware.
- Cybercrime Threat in India: Cybercrime cases rose by 31.2% in 2023, reaching 86,420 cases, up from 65,893 in 2022 (National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) 2023). Karnataka recorded the highest number of cases.
- Major cybercrimes include Fraud, Extortion, and Sexual exploitation.
- India also faces cross-border scams from Southeast Asian countries like Myanmar, Cambodia, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand.
- Between January and May 2025, Indians lost over Rs 4,800 crore to foreign-based cyber frauds.
Cybersecurity
- About: Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting networks, devices, and data from unauthorized access, damage, or theft. It acts as a digital fortress, defending individuals and organizations against online attacks.
- It includes strategies, policies, and technologies aimed at identifying and assessing threats, preventing and detecting cyberattacks, and mitigating harm while ensuring quick recovery from incidents.
- A strong cybersecurity framework helps maintain privacy, trust, and data integrity in an increasingly interconnected world.
What are the Challenges and Opportunities for India Under the UN Cybercrime Convention?
Challenges
- Privacy Concerns: The Convention’s surveillance provisions may conflict with India’s constitutional right to privacy as highlighted in Justice K.S. Puttaswamy v. Union of India, 2017.
- Data Sovereignty Issues: India opposition to data-sharing without prior written consent from the originating country may clash with the treaty’s cross-border data-sharing clauses.
- Strategic Caution: India’s hesitation to sign the treaty protects autonomy but risks limiting its influence in future digital rule-making.
Opportunities
- Stronger Global Cooperation: Enables India to work more closely with other countries on cybercrime investigations and evidence-sharing.
- Capacity Building Support: Offers access to UN-led training and technical aid to strengthen national cybercrime units.
- Policy Alignment: Could push India to update its National Cybersecurity Strategy and modernize data protection and cyber laws.
Conclusion
The UN Cybercrime Treaty marks a major step in global cybersecurity governance, aiming to ensure no country is left defenceless against cybercrime but it also raises critical questions about privacy, human rights, and digital sovereignty.
For India, the challenge lies in adopting a framework that strengthens cyber resilience without compromising individual freedoms.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Examine the objectives and key provisions of the United Nations Convention against Cybercrime (UNCC). |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the UN Cybercrime Convention (UNCC)?
The UNCC is the first global treaty on cybercrime, adopted by the UNGA in December 2024 to harmonise laws, enable cross-border electronic evidence sharing, and strengthen cooperation and capacity building. - Has India signed the UNCC?
No, as of October 2025 India did not sign the treaty, citing privacy, data sovereignty and governance concerns despite having participated in drafting. - What are the main cyber threats facing India today?
Rising cybercrime — including fraud, extortion and sexual exploitation — with a 31.2% increase in cases in 2023 (NCRB), plus large cross-border financial frauds costing billions of rupees.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 In India, under cyber insurance for individuals, which of the following benefits are generally covered, in addition to payment for the loss of funds and other benefits? (2020)
- Cost of restoration of the computer system in case of malware disrupting access to one’s computer
- Cost of a new computer if some miscreant wilfully damages it, if proved so
- Cost of hiring a specialised consultant to minimise the loss in case of cyber extortion
- Cost of defence in the Court of Law if any third party files a suit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 4 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Q.2 In India, it is legally mandatory for which of the following to report on cyber security incidents? (2017)
- Service providers
- Data centres
- Body corporate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. What are the different elements of cyber security ? Keeping in view the challenges in cyber security, examine the extent to which India has successfully developed a comprehensive National Cyber Security Strategy. (2022)