International Relations
22nd ASEAN-India Summit
- 29 Oct 2025
- 8 min read
For Prelims: Indo-Pacific region, ASEAN, Act East Policy, Free Trade Agreement, Strategic Partnership to Comprehensive Strategic Partnership
For Mains: Areas of Cooperation Between India and ASEAN, Significance of the Indo-Pacific Region for India, Key Issues Hindering India's Active Engagements in the Indo-Pacific
Why in News?
The 22nd ASEAN–India Summit, held in Kuala Lumpur, saw India declare 2026 as the ASEAN-India Year of Maritime Cooperation and marked a major step forward with the adoption of the ASEAN-India Plan of Action (2026–2030) under the Comprehensive Strategic Partnership (CSP).
What are the Key Highlights of the ASEAN-India Summit 2025?
- ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific (AOIP): India reaffirmed its commitment to ASEAN Centrality, Unity, and the ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific (AOIP).
- India welcomed Timor Leste (East Timor) for becoming the 11th Member of ASEAN, welcoming its participation as a full member for the first time.
- ASEAN-India Plan of Action (2026–2030): Endorsement of the ASEAN-India Plan of Action (2026–2030) to implement the Comprehensive Strategic Partnership (CSP) announced in 2022.
- 2025 announced as the ASEAN–India Year of Tourism.
- The year 2026 was designated as the “ASEAN–India Year of Maritime Cooperation” to enhance collaboration in the Blue Economy.
- Cooperation in Capacity Building: Proposal to set up a Centre for Southeast Asian Studies at Nalanda University, enhancing academic and cultural exchange.
- India and ASEAN to deepen cooperation in education, energy, S&T, fintech,with focus on infrastructure, semiconductors, emerging tech, rare earths, and critical minerals.
- Cultural and Maritime Heritage: India to host the East Asia Summit Maritime Heritage Festival at Lothal, Gujarat, and a Conference on Maritime Security Cooperation to promote safe, sustainable maritime governance.
Association of Southeast Asian Nations(ASEAN)
- The ASEAN was established in Thailand’s Bangkok in 1967, with the signing of the ASEAN Declaration (Bangkok Declaration) by the Founding Fathers of ASEAN: Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore and Thailand.
- Brunei Darussalam joined ASEAN in 1984, followed by Vietnam in 1995, Laos and Myanmar in 1997, and Cambodia in 1999 and Timor Leste in October 2025 making up what is today the eleven Member States of ASEAN.
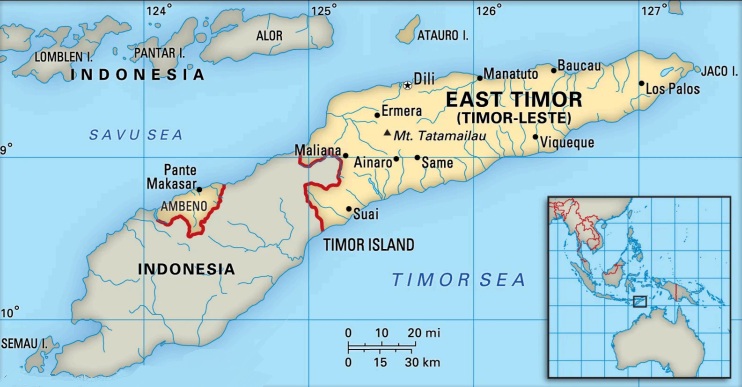
Timor-Leste Becomes the 11th Member of ASEAN
- Timor-Leste has officially become the 11th member of ASEAN-the first expansion of the group since 1999.
- Located in Southeast Asia, the island of Timor is part of Maritime Southeast Asia, and is the largest and easternmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands.
- To the north of the mountainous island are the Ombai Strait, Wetar Strait and the greater Banda Sea, to the south the Timor Sea separates the island from Australia, while to the west lies the Indonesian Province of East Nusa Tenggara.
- Its economy relies heavily on oil and gas reserves in the Timor Sea.
What are the Strategic Significance of India-ASEAN Relations?
- Economic and Trade Linkages: ASEAN, with a GDP of USD 3.2 trillion and a population of 650 million, is India’s 4th largest trading partner.
- Bilateral trade reached USD 122.67 billion in 2023–24, reflecting strong economic interdependence.
- ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITGA) is a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) signed in 2009 to boost trade ties.
- Strategic & Security Engagement: ASEAN provides a strategic counterbalance amid regional tensions, reinforcing India’s Act East Policy and Indo-Pacific vision while supporting ASEAN Centrality.
- India engages through East Asia Summit and ASEAN Regional Forum, ASEAN Maritime Forum, and joint exercises like the ASEAN-India Maritime Exercise (South China Sea, 2023).
- Cooperation spans anti-piracy measures, disaster management, and promoting a rules-based regional order aligned with India’s SAGAR doctrine.
- Defence and Security Cooperation: The BrahMos missile deal with the Philippines and regular maritime exercises demonstrate growing trust and collaboration.
- Connectivity and Technology Integration: Key projects like the India–Myanmar–Thailand Trilateral Highway enhance regional connectivity.
- Cooperation in 5G, fintech, AI, and clean energy strengthens digital and technological partnerships.
- Cultural and People-to-People Ties: Tourism, academic exchanges, and diaspora networks foster deeper social and cultural connections.
Conclusion
The 22nd ASEAN-India Summit reaffirmed the deepening of strategic, economic, and maritime ties under the Comprehensive Strategic Partnership. With the declaration of 2026 as the Year of Maritime Cooperation and the adoption of the Plan of Action (2026–2030), India and ASEAN have outlined a clear roadmap for collaboration in connectivity, security, digital innovation, and sustainable development.
|
Drishti Mains Question Q. Discuss how India can leverage its partnership with ASEAN to enhance its strategic and economic leadership in the Indo-Pacific region |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. What was the key focus of the 22nd ASEAN–India Summit held in 2025?
The summit focused on strengthening ASEAN–India ties through enhanced connectivity, maritime cooperation, sustainable development, and deepening collaboration in technology, energy, and education.
Q. Which country is the 11th member of ASEAN?
Timor-Leste became ASEAN’s 11th member in 2025, marking the bloc’s first expansion since 1999.
Q. How is India enhancing its engagement with ASEAN in new domains?
India plans to expand cooperation in digital payments, semiconductors, renewable energy, critical minerals, and blue economy initiatives while promoting resilient regional supply chains.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to “Look East Policy” of India, consider the following statements: (2011)
1. India wants to establish itself as an important regional player in East Asian affairs.
2. India wants to plug the vacuum created by the termination of the Cold War.
3. India wants to restore the historical and cultural ties with its neighbors in Southeast and East Asia.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q1. The new tri-nation partnership AUKUS is aimed at countering China’s ambitions in the Indo-Pacific region. Is it going to supersede the existing partnerships in the region? Discuss the strength and impact of AUKUS in the present scenario. (2021)