International Relations
Strengthening India-West Asia Ties
- 12 May 2025
- 14 min read
For Prelims: Iran and Israel, West Asian region, United Nations, Strait of Hormuz, Palestinian-Israeli conflict, Gulf Cooperation Council, Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreements, Belt and Road Initiative, Organization of Islamic Cooperation.
For Mains: India’s Relation with West Asian Countries, Challenges Related to India-West Asia Relations, Measures can India Adopt to Balance its Relations to Western Asian Countries
Why in News?
West Asia holds major strategic and economic importance for India under the ‘Link West’ policy. India's deepening ties with the countries like UAE, Saudi Arabia, Iran, and Israel reflect its strategic shift to secure energy, enhance trade, and assert its role in West Asian geopolitics.
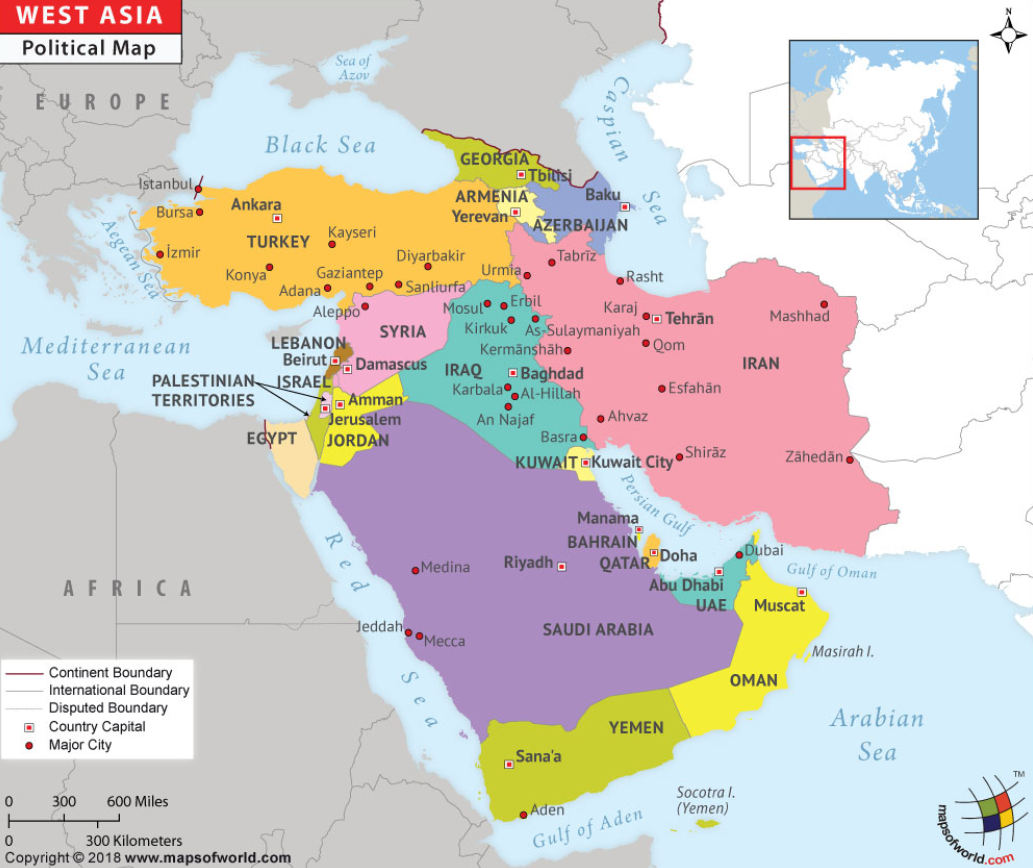
How is West Asia Geographically Classified?
- West Asia is a subregion of Asia, located West of Central and South Asia, South of Eastern Europe, and North of Africa.
- It is bordered by major water bodies including the Mediterranean Sea, Persian Gulf, Red Sea, Caspian Sea, and the Gulf of Oman.
- The region comprises 18 countries, with key subregions like the Arabian Peninsula (e.g., Saudi Arabia, UAE), the Fertile Crescent (e.g., Iraq, Syria), the Caucasus (e.g., Armenia, Azerbaijan), and Anatolia (Turkey).
- Home to around 283 million people, the region is geopolitically significant due to its vast oil reserves, particularly in the Arabian Peninsula.
- Saudi Arabia, with 35 million people, has the region’s largest economy, while Bahrain is the smallest by population.
India’s Look West Policy:
Launched in 2005, It aims to enhance India’s political, economic, and security cooperation with West Asia, focusing on energy security, trade, and regional stability, while maintaining neutrality in regional political conflicts.
- India views the Gulf as part of its extended neighbourhood, with Iran being a key part of its proximate neighbourhood, emphasizing geographic, economic, and cultural ties.
What is the Significance of West Asia for India?
- Energy and Economic Ties: West Asia is vital for India’s energy security, supplying nearly 50% of its crude oil. With over 40% of global natural gas reserves and more than 50% of global oil reserves, the region is crucial for India’s oil-dependent economy.
- Iraq, a key oil supplier, was India’s fifth-largest trading partner in 2021–22, while Qatar, providing 41% of India’s natural gas imports, plays a vital role in India’s security strategy.
- The UAE is India’s 3rd largest trading partner, with trade bolstered by the CEPA, while Saudi Arabia ranks 4th, formalized through the 2019 Strategic Partnership Council.
- Iraq, a key oil supplier, was India’s fifth-largest trading partner in 2021–22, while Qatar, providing 41% of India’s natural gas imports, plays a vital role in India’s security strategy.
- Connectivity & Trade Corridors: West Asia is key to enhancing India’s strategic connectivity. Initiatives like the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC) connect India to Europe, countering China's Belt and Road Initiative.
- The International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) links India to Central Asia and Russia via Iran's Chabahar Port, supporting India's Central Asia policy.
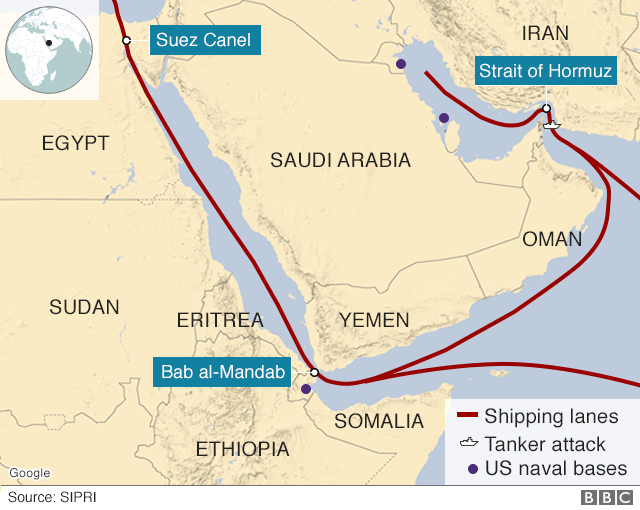
- Vital maritime chokepoints like the Strait of Hormuz and Bab el-Mandeb ensure secure trade and energy flow for India.
- Security & Counterterrorism Cooperation: West Asia is vital for India’s defense, security, and counterterrorism cooperation. India has strengthened ties with nations like Saudi Arabia and the UAE in defense, IT, and counterterrorism efforts.
- The rising missile and drone threats from Yemen’s Houthi rebels underscore the region's security vulnerabilities, as demonstrated by the recent Red Sea Crisis.
- India's joint military exercises, Desert Cyclone with the UAE and Naseem Al Bahr with Oman, underscore its deepening strategic ties and enhanced interoperability with key Gulf partners.
- Balanced Multilateral Diplomacy: India-Israel cooperation spans defence, cybersecurity, agriculture, and water management.
- India’s participation in mini-lateral initiatives like I2U2 (India, Israel, UAE, US) reflects its focus on interest-based coalitions.
- India’s continued engagement in Afghanistan through infrastructure, education, and humanitarian aid supports its regional stability objectives, countering China and Pakistan’s influence in the region.
- Diaspora and Remittance: West Asia is home to over 9 million Indian expatriates, whose remittances play a vital role in supporting India’s economy.
- In 2021, India received around USD 87 billion in remittances, with a major share coming from Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries.
- Additionally, the large Indian diaspora enhances India’s soft power and socio-cultural engagement in the region. Eg: BAPS Hindu Temple in Abu Dhabi is the first traditional Hindu stone temple in the Middle East.
What are the Challenges to India-West Asia Relations?
- Limited Economic Ties: Although efforts have been made to expand economic relations, trade between India and West Asia remains relatively limited compared to other regions.
- For instance, in 2019, India’s total trade with West Asia accounted for only 7.5% of its global trade.
- Geopolitical Tensions: West Asia is a politically volatile region, and India faces the challenge of navigating these complex geopolitical dynamics, such as maintaining ties with both Israel and Palestine, as well as managing strategic relationships with regional rivals like Iran and Saudi Arabia.
- Also, political instability in several West Asian countries, including Syria, Iraq, and Yemen, has had a negative impact on India’s strategic and economic interests in the region.
- Competition with Other Major Powers: India’s interests in West Asia are influenced by the competing interests of global powers, particularly China, which has been increasing its regional influence.
- India’s interests in West Asia are shaped by the growing presence of global powers, particularly China, which has expanded its regional influence through strategic investments in infrastructure and ports, such as the development of the Jebel Ali Port in the UAE and partnerships in Oman’s Duqm Port, posing a challenge to India’s own maritime and economic outreach in the region.
- Energy Diplomacy Issues: West Asia supplies a significant share of India’s crude oil and natural gas, making it vital to India’s energy security.
- Geopolitical instability or conflict in the region could disrupt supplies, impacting India’s economy.
- While India is steadily transitioning to renewable energy, maintaining stable traditional energy ties with West Asia remains crucial during this transition phase.
- Geopolitical instability or conflict in the region could disrupt supplies, impacting India’s economy.
What Measures can India Adopt to Balance its Ties to West Asia?
- Balanced Diplomatic Approach: India should uphold its strategic autonomy and non-alignment policy in West Asia, fostering strong bilateral ties with key players like Saudi Arabia, Iran, Israel, and the UAE.
- By avoiding overt alignment with any particular faction, India can navigate regional rivalries while safeguarding its national interests.
- By supporting and engaging in diplomatic efforts like Abraham Accords 2.0 between Israel, Saudi Arabia, and Iran, India can strengthen its role as a constructive partner, fostering regional stability and peace.
- Strengthen Economic and Energy Ties: India should diversify its energy imports to reduce dependency on West Asia. Enhancing renewable energy capabilities will help reduce reliance on West Asian oil over time.
- Strengthening trade and investment relations with GCC countries is essential, focusing on sectors like technology, defense, and infrastructure.
- The India-UAE Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) can significantly boost trade, and similar agreements with other GCC nations will safeguard India’s economic interests, fostering sustained growth and diversification of commercial ties.
- Countering Terrorism and Security Cooperation: India should collaborate with Israel, Saudi Arabia and Bahrain through a mutual security and military pact with focus on intelligence sharing, counter-terrorism operations, and joint military exercises to address regional security concerns and combat common threats like extremism.
- Enhancing defense cooperation with these countries will help India ensure the safety of its interests in the region.
- Climate Change Resilience and Sustainable Development: India should enhance regional cooperation on climate change through frameworks like I2U2, expanding it to include more West Asian countries.
- As West Asia faces desertification, India can assist by sharing expertise in desertification management, water conservation strategies, and Desalination. Collaborative initiatives can enhance the resilience of arid landscapes. Knowledge exchange and joint efforts in sustainable agriculture and water management will be key.
- Enhanced Cultural Exchange and People-to-People Ties: India should strengthen academic partnerships, cultural diplomacy, and tourism, while engaging with the region’s youth and academic institutions to build long-term cooperation.
- Cultural ties can be further deepened through digital collaborations, media co-productions, youth diplomacy, and sports engagement, exemplified by IPL matches in the UAE and the IPL Auction in Saudi Arabia, fostering mutual understanding and shared experiences.
Conclusion
India’s strategic interests in West Asia require a balanced approach to navigate regional tensions. By prioritizing issue-based diplomacy and multilateral cooperation, India can position itself as a stabilizing force in the region, safeguarding its national interests while contributing to peace and stability.
|
Drishti Mains Question Discuss the factors behind the persistent instability in West Asia and how India can maintain a balanced approach in its relations with the region. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which one of the following countries of South-West Asia does not open out to the Mediterranean Sea? (2015)
(a) Syria
(b) Jordan
(c) Lebanon
(d) Israel
Ans: B
Q. The term “two-state solution” is sometimes mentioned in the news in the context of the affairs of (2018)
(a) China
(b) Israel
(c) Iraq
(d) Yemen
Ans: B
Mains
Q. “India’s relations with Israel have, of late, acquired a depth and diversity, which cannot be rolled back.” Discuss. (2018)