Important Facts For Prelims
Stratospheric Aerosol Injection
- 09 Jun 2025
- 5 min read
Why in News?
Scientists are exploring new methods to combat climate change such as Stratospheric Aerosol Injection (SAI), a geoengineering technique inspired by volcanic eruptions that could cool the planet faster and more affordably.
What is Stratospheric Aerosol Injection?
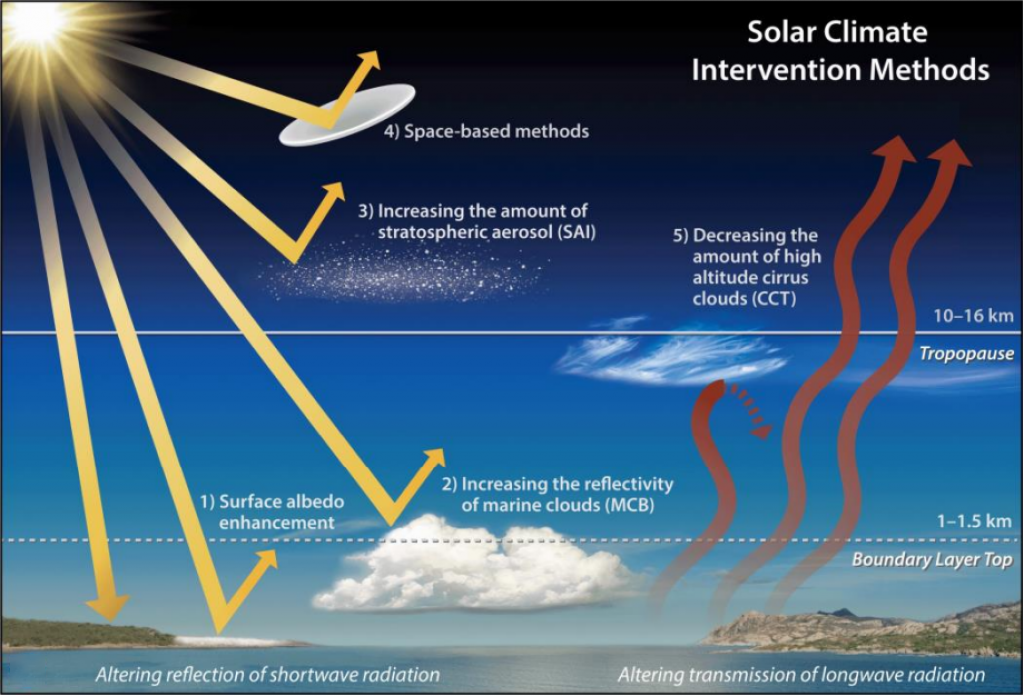
- About: SAI is a proposed solar geoengineering (or solar radiation modification) technique designed to cool the Earth's climate by reflecting a small fraction of sunlight back into space.
- It mimics the natural cooling effects observed after large volcanic eruptions, such as the 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo (Philippines), which injected sulfate aerosols into the stratosphere and temporarily lowered global temperatures by 0.5°C that year.
- Working of SAI: SAI involves releasing small reflective particles (typically sulfate aerosols or alternatives like calcium carbonate) into the stratosphere (10–50 km altitude).
- These particles scatter and reflect a portion of incoming solar radiation, thereby reducing the amount of heat that reaches the Earth's surface.
- By increasing the planet's albedo (reflectivity), SAI can potentially offset some of the warming caused by greenhouse gases.
- Effectiveness: SAI is generally more effective as particles remain in the stratosphere for months to years. In contrast, particles released at lower altitudes are often washed out by rain after being trapped in clouds.
- The cooling effect is typically more pronounced in polar regions, while the tropics, despite experiencing more severe warming, show less impact from SAI.
- Associated Risks:
- Environmental Risks: Ozone layer damage (delaying its recovery), Acid rain from sulfur dioxide and Uneven cooling (stronger in polar regions, weaker in tropics).
- Long Term Impacts: It only masks warming, doesn’t solve the root cause (CO₂ emissions). It can alter precipitation patterns and air circulation, with adverse effects on monsoon regions.
- It may also disrupt stratospheric chemistry, impacting methane lifespan, ice formation, and cloud microphysics.
What are Other Methods of Solar Radiation Modification?
- Marine Cloud Brightening (MCB): It involves spraying fine seawater droplets into low-level ocean clouds (marine stratocumulus), enhancing their reflectivity and persistence by acting as cloud condensation nuclei.
- MCB is seen as more localized and reversible than SAI, but is also more technically challenging and weather-dependent.
- Space Sunshades: It involves placing large mirrors or screens in orbit or at Lagrange Point 1 (Point where Earth and Sun gravity balance each other) to block or deflect incoming solar radiation, reducing the solar energy reaching Earth’s surface.
- Cirrus Cloud Thinning (CCT): CCT aims to reduce global warming by modifying high-altitude cirrus clouds, which trap heat due to their high ice content.
- CCT injects ice-nucleating particles like bismuth triiodide to enlarge ice crystals, making cirrus clouds less persistent, enhancing heat escape, and reducing their warming effect by accelerating crystal fall.
- Spraying Diamond Dust: It suggests spraying synthetic nanodiamonds (1–100 nm) into the stratosphere.
- Being highly reflective and chemically inert, they scatter solar radiation, reducing Earth’s heat absorption and cooling the planet.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Artificial way of causing rainfall to reduce air pollution makes use of (2025)
(a) Silver iodide and potassium iodide
(b) Silver nitrate and potassium iodide
(c) Silver iodide and potassium nitrate
(d) Silver nitrate and potassium chloride
Answer: (a)
Q. In the context of which of the following do some scientists suggest the use of cirrus cloud thinning technique and the injection of sulphate aerosol into the stratosphere? (2019)
(a) Creating the artificial rains in some regions
(b) Reducing the frequency and intensity of tropical cyclones
(c) Reducing the adverse effects of solar wind on the Earth
(d) Reducing the global warming
Ans: (d)