Important Facts For Prelims
Governor’s Constitutional Powers
- 23 Dec 2025
- 8 min read
Why in News?
The Uttarakhand Governor has returned the amendment Bills on the Uniform Civil Code (UCC) and the Freedom of Religion and Prohibition of Unlawful Conversion Act, 2018 citing technical and legal flaws, renewing focus on the scope of the Governor’s powers.
Summary
- The Uttarakhand Governor returning amendment Bills on the UCC has brought renewed attention to the constitutional powers of Governors, especially their authority under Article 200 to return or withhold assent to State legislation.
- While the Governor functions as a constitutional head acting mainly on ministerial advice, his legislative and discretionary powers are meant as constitutional safeguards, but their use often sparks debates on federalism, democratic accountability, and Centre–State relations.
What are Constitutional Provisions Related to the Governor?
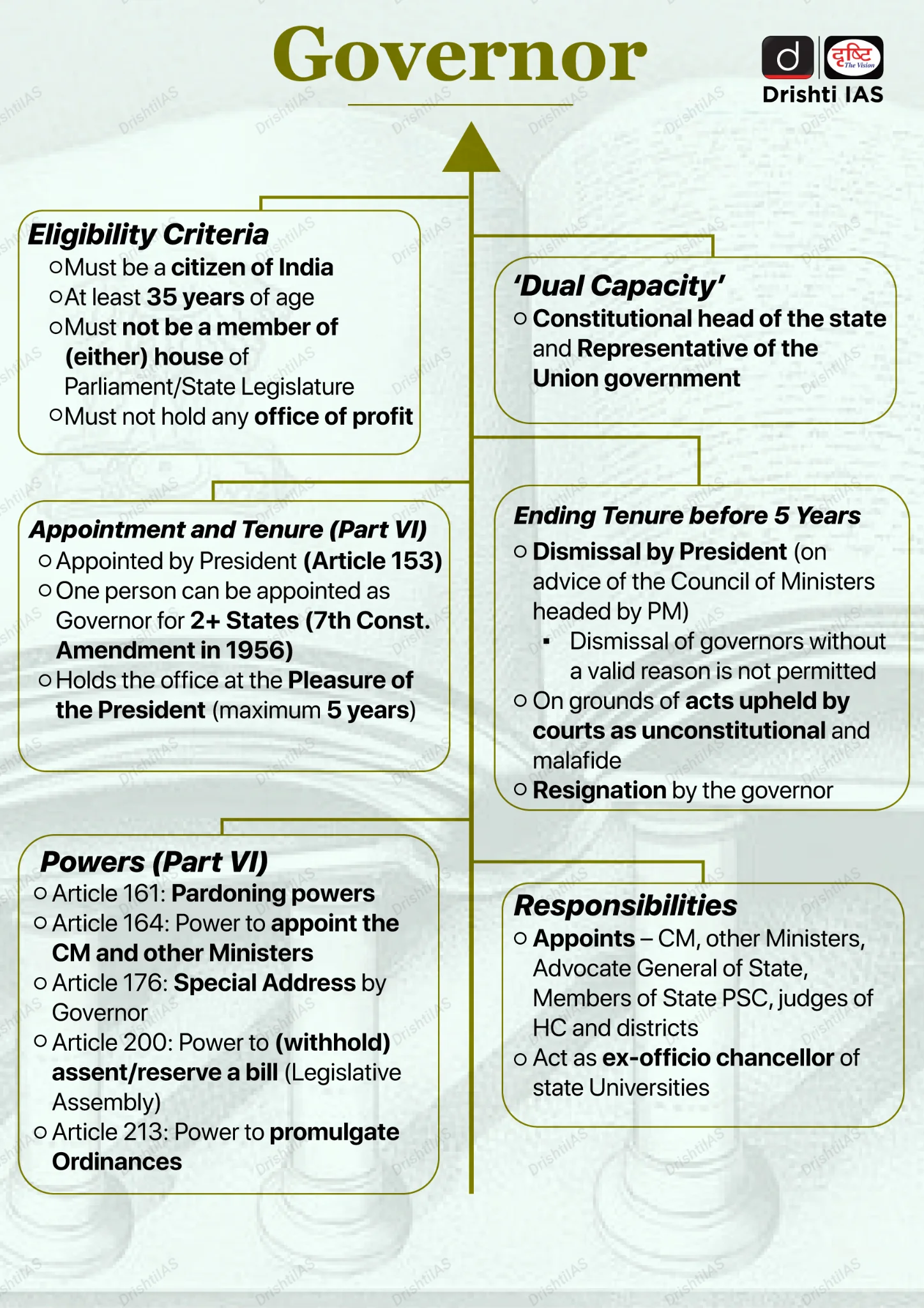
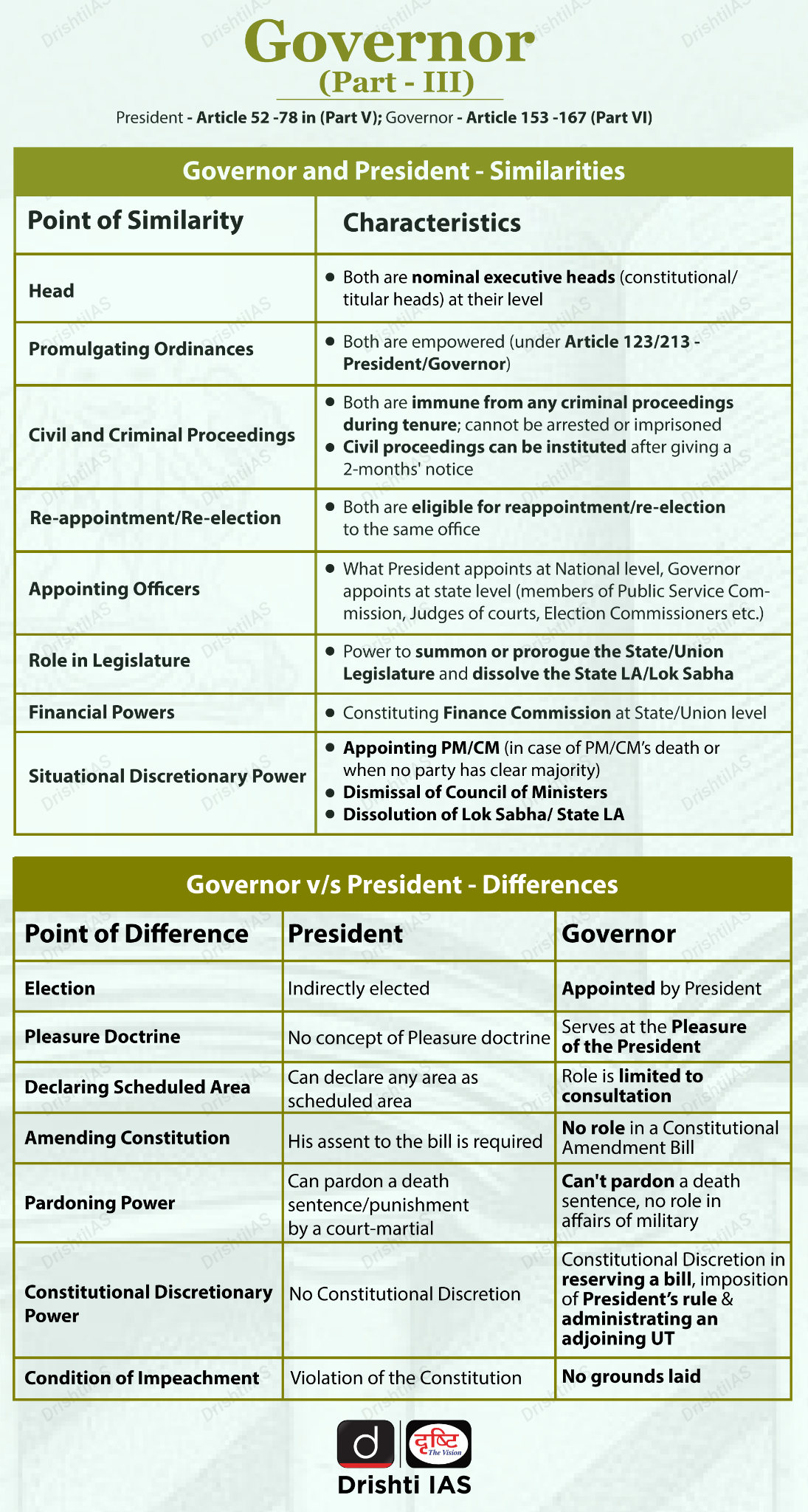
- Constitutional Position of the Governor: The Governor is the constitutional head of the State under Article 153, with the executive power of the State vested in him under Article 154. He acts as a link between the Union and the State.
- Appointment, Status, and Eligibility: The Governor of a State shall be appointed by the President by warrant under his hand and seal (Article 155).
- A person to be eligible for appointment as Governor should be citizen of India and has completed age of 35 years (Article 157).
- The Governor shall not be a member of the Legislature or Parliament; shall not hold any office of profit, shall be entitled to emoluments and allowances. (Article 158)
- Every Governor and every person discharging the function of the Governor shall make a subscribe an oath or Affirmation (Article 159).
- Legislative Powers: The Governor has key legislative functions under Articles 174 to 176, including summoning, proroguing, and dissolving the Legislative Assembly, addressing the House, and sending messages to it.
- Under Article 200, the Governor may assent to Bills, withhold assent, return Bills for reconsideration (except Money Bills), or reserve Bills for the President’s consideration.
- The Governor exercises absolute veto by withholding assent and suspensive veto by returning a non-Money Bill for reconsideration. However, the Governor does not have pocket veto.
- Executive Powers: Under Article 163, the Governor acts on the advice of the Council of Ministers, except in discretionary matters.
- He appoints the Chief Minister and other Ministers under Article 164, appoints the Advocate General of the State under Article 165, and all executive actions of the State are carried out in the name of the Governor as per Article 166.
- Financial Powers:
- Article 202: Causes the Annual Financial Statement (State Budget) to be laid before the Legislature.
- Article 203(3): No demand for grants without the Governor’s recommendation.
- Article 205: Causes supplementary, additional, or excess grants to be laid before the House.
- Ordinance-Making Power: Under, Article 213 Governor may promulgate Ordinances when the Legislature is not in session and immediate action is required.
- Judicial-Related Powers: The Governor exercises clemency powers under Article 161, including granting pardons and commutations.
- He is consulted in the appointment of High Court judges, and judges take their oath or affirmation before the Governor under Article 217.
Note: A five-judge Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court, in its advisory opinion on the 16th Presidential Reference under Article 143, held that courts cannot impose timelines on the President or Governors for granting assent to State Bills, as this would violate federalism and the separation of powers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Who appoints the Governor and what is his constitutional position?
The Governor is appointed by the President under Article 155 and acts as the constitutional head of the State under Articles 153–154.
2. What options does a Governor have when a Bill is presented for assent?
Under Article 200, the Governor may grant assent, withhold assent, return the Bill (except Money Bills), or reserve it for the President.
3. Does the Governor enjoy pocket veto over State Bills?
No, the Governor has absolute and suspensive veto powers but does not enjoy pocket veto.
4. What is the Governor’s role in financial matters of the State?
The Governor lays the State Budget before the Legislature and ensures that no demand for grants is made without his recommendation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the Indian polity, consider the following statements: (2025)
- The Governor of a State is not answerable to any court for the exercise and performance of the powers and duties of his/her office.
- No criminal proceedings shall be instituted or continued against the Governor during his/her term of office.
- Members of a State Legislature are not liable to any proceedings in any court in respect of anything said within the House.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q. Consider the following statements: ( 2025)
- The Constitution of India explicitly mentions that in certain spheres, the Governor of a State acts in his/her own discretion.
- The President of India can, of his/her own, reserve a bill passed by a State Legislature for his/her consideration without it being forwarded by the Governor of the State concerned.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)