Governance
Global Internet Shut-Offs
- 01 Mar 2023
- 6 min read
Prelims: #KeepItOn coalition, Internet Shut Down, (Public Emergency or Public Safety) Rules, 2017.
Mains: Internet Shutdowns and their implications.
Why in News?
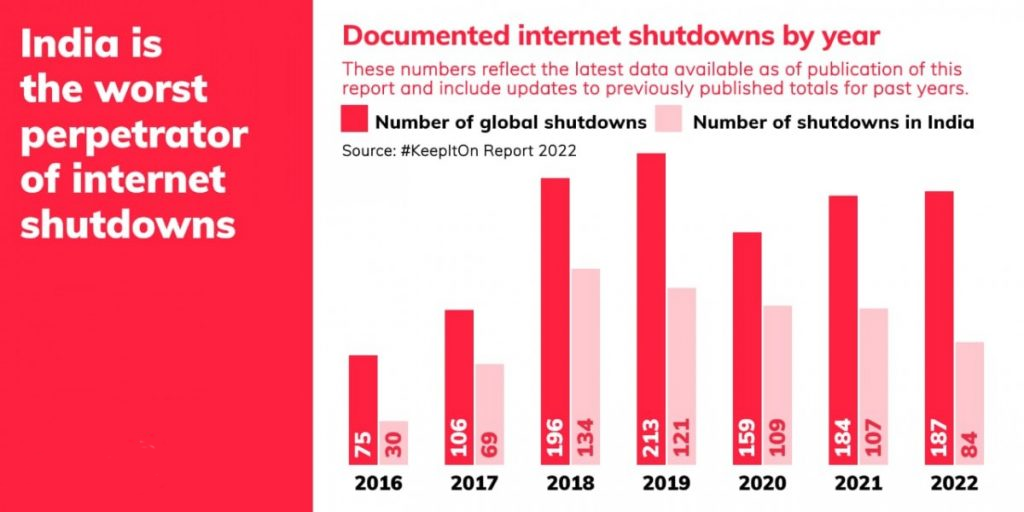
According to a report by Access Now and the KeepItOn coalition, India enforced as many as 84 internet shutdowns in 2022 and was on top of the list for the fifth year in a row.
What are the Highlights of the Report?
- Global Scenario:
- At least 187 internet shutdowns across 35 countries were recorded in 2022.
- Thirty-three of these 35 countries are repeat offenders.
- Ukraine comes a distant second with 22 shutdowns in 2022, followed by Iran with 18, and with seven internet shutdowns, Myanmar stands fourth in the list.
- People in many regions across Myanmar had been in the dark for 500+ days by March 2022.
- By the end of 2022, people in Tigray, Ethiopia had endured 2+ years of full communications blackout, and many remained disconnected.
- Indian Scenario:
- In 2022, the Internet was shut down 49 times in Jammu and Kashmir, the highest of any state in the country.
- Authorities in Rajasthan imposed shutdowns on 12 different occasions followed by West Bengal, which ordered shutdowns seven times.
- Digital Authoritarianism:
- Internet shutdowns are dangerous acts of digital authoritarianism.
- The report states that authorities used shutdowns to try to hide serious rights violations and sever communications between individuals and communities, which also impacted human rights monitoring, including shutdown tracking and provision of humanitarian aid.
- Causes:
- The shutdowns were ordered on various accounts including protests, conflict, school exams, and elections.
What is an Internet Shutdown?
- About:
- Internet shutdowns are a means to wipe out online communication, which directly impacts day to day functioning in an increasingly digital world, but they also have important and serious knock-on effects on democratic movements, and sometimes provide cover for violence, as reporting crime and making contact for support becomes hard to do.
- Impact:
- Economic losses: Internet shutdowns can lead to significant economic losses, particularly for businesses that rely on the internet to operate.
- Social Disruptions: The internet is a crucial communication tool that enables people to connect with each other, share information, and participate in social movements.
- Political Consequences: Internet shutdowns are often used by governments to suppress dissent, control information, and limit political opposition.
- Educational Setbacks: Internet shutdowns can also disrupt educational activities, particularly for students who rely on online resources for learning.
- Health Implications: During the Covid-19 pandemic, the internet has become a critical tool for accessing health information, telemedicine, and online support groups.
Who Governs Internet Shutdowns in India?
- Internet shutdown orders are governed under the Temporary Suspension of Telecom Services (Public Emergency or Public Safety) Rules, 2017, under the Indian Telegraph Act, 1885.
- The 2017 Rules provide for temporary shutdown of telecom services in a region on grounds of public emergency and give senior bureaucrats from the Home Ministry at the central and state levels the power to order shutdowns.
- The 1885 Act empowers the central government to regulate various types of telecom services including internet services and grant licenses for them.
What is the Related SC’s Judgment and Further Amendments?
- In Anuradha Bhasin vs Union of India (2020), the Supreme Court ruled that an indefinite suspension of internet services would be illegal under Indian law and that orders for internet shutdown must satisfy the tests of necessity and proportionality.
- Subsequently, the Union government made some amendments (to limit Internet suspension orders to a maximum of 15 days) to the 2017 Rules in November 2020.
- However, in December 2021 the Standing Committee on Communication and Information Technology was not satisfied with the amendments and recommended more changes in the 2017 Rules.
- The Committee recommended reviewing the Rules to address all aspects of internet shutdown, to make amendments in the Rules that are in tune with changing technology to ensure minimum disturbance to the public and issuing uniform guidelines for states/UTs before ordering an internet shutdown.
Way Forward
- International organizations, such as the United Nations, can put pressure on governments that engage in internet shutdowns to respect human rights and ensure that the internet remains open and accessible.
- Governments can pass laws and regulations that protect citizens' rights to access the internet and prevent arbitrary shutdowns.
- Technological solutions such as mesh networks and satellite communication can be used to provide alternative means of internet access when the internet is shut down.