Indian Polity
Educational Qualifications of Political Representatives
- 24 Aug 2023
- 6 min read
For Prelims: Educational Qualifications of Political Representatives, MPs (Member of Parliament), MLAs (Member of Legislative Assembly).
For Mains: Educational Qualifications of Political Representatives.
Why in News?
The recent termination of a Tutor over remarks about voting for educated candidates has sparked a debate on the correlation between political representatives' education and public sentiment.
- The controversy has drawn attention to the educational qualifications of MPs (Member of Parliament) and MLAs (Member of Legislative Assembly) in India's legislative bodies, leading to discussions on the significance of such qualifications in the political landscape.
What is the Scenario of Educational Qualifications of Political Representatives?
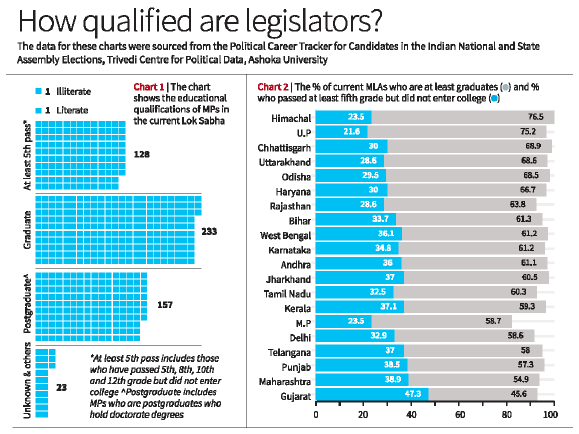
- Educational Qualifications of MPs in the Lok Sabha:
- In the current Lok Sabha 72% of MPs have completed their graduation. A small proportion of MPs (less than 0.5%) are classified as illiterate or just literate.
- This data challenges the notion that political representatives are predominantly uneducated.
- In the current Lok Sabha 72% of MPs have completed their graduation. A small proportion of MPs (less than 0.5%) are classified as illiterate or just literate.
- Variations in Educational Qualifications among State MLAs:
- Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh have the highest percentages of graduate MLAs, while Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Punjab show lower proportions.
- Trends in Educational Qualifications of MLAs:
- There is a rising trend in the proportion of graduate MLAs in most states.
- However, education data was unavailable for some years in specific states.
Are there any Statutory Provisions Related to Educational Qualifications of MPs and MLAs?
- No Provision for Educational Qualification:
- Indian Constitution does not contain any proper provisions regarding the qualifications that are needed for the Candidates for participating in the elections.
- The RPA (The Representation of the People Act) of 1951 acts outline the qualifications, disqualifications, and other essential aspects of elected representatives.
- Till now there are simple qualifications i.e.
- Resident of the country or a particular area/state from where he wants to stand,
- Not less than 25 years of age and not holding any office of profit.
- Till now there are simple qualifications i.e.
- However, there are no such educational and other moral qualifications mentioned for them.
- Need for a Law:
- Proponents argue that educational qualifications can potentially ensure a certain level of competence, understanding, and analytical skills among elected representatives.
- This, in turn, might enhance the Quality of Governance and Decision-Making.
- As per various data and studies, many foreign countries where educational qualification is necessary, perform well at the country’s growth and economic patterns and also maintain their social backgrounds.
- There are certain subjects which play a key role and we used to study since our childhood i.e. Value Education, Moral Science and Basic Science which also plays a key role over here.
- Opposition of Such Law:
- Opponents of such a law emphasize the importance of Inclusivity and Representation of all sections of society.
- India is marked by its diverse demographics and vast socio-economic disparities.
- Requiring educational qualifications could inadvertently exclude marginalized groups and perpetuate Elitism in politics.
- The essence of Democracy lies in the people's right to choose their representatives.
- While educational qualifications might be a marker of competence, they do not guarantee ethical conduct, dedication to public service, or the ability to understand the needs of various constituencies.
What is the Need for Educated Political Representatives?
- Informed Decision-Making:
- Education equips individuals with critical thinking skills, the ability to analyze complex issues, and a broader understanding of various subjects.
- In politics, informed decision-making is vital for crafting effective policies and making choices that consider long-term consequences.
- Policy Formulation and Analysis:
- Crafting well-informed and effective policies requires a deep understanding of various domains such as economics, law, science, and social issues.
- Educated representatives are better equipped to analyze policy proposals, evaluate their impact, and contribute to discussions with informed insights.
- Addressing Complex Issues:
- Modern societies face multifaceted challenges like technological advancements, climate change, and socio-economic disparities. Educated representatives are better positioned to comprehend the intricacies of these issues and propose comprehensive solutions.
- Communication and Advocacy:
- Educated representatives often possess strong communication skills, enabling them to articulate complex ideas to the public and advocate for policies more effectively. This facilitates transparent governance and encourages citizen engagement.
- Effective Lawmaking:
- Legislators are responsible for drafting and passing laws. An educated representative's legal literacy enables them to craft well-structured, fair, and constitutionally sound legislation.