Important Facts For Prelims
Earthquake in Morocco
- 13 Sep 2023
- 4 min read
Why in News?
The most powerful earthquake in Morocco's history struck late on the 8th of September 2023. The earthquake had a magnitude of 6.8 and its epicenter was located in the Al-Haouz province, within the Atlas Mountains near the historic city of Marrakech.
- A series of aftershocks, including a 4.9 magnitude tremor, added to the region's distress.
What are the Causes of the Earthquake in Morocco?
- The earthquake resulted from the convergence of the African plate and the Eurasian plate along a complex plate boundary.
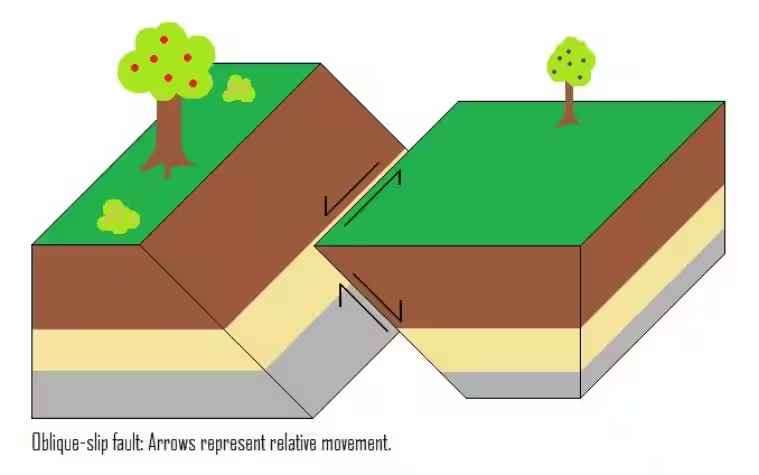
- The earthquake's faulting mechanism was classified as "oblique-reverse," indicating movement along the fault plane where the upper block moves up and over the lower block within the Moroccan High Atlas Mountain range.
- Faults are fractures in rock formations that enable rock blocks to move relative to each other. Rapid movement along faults can trigger earthquakes.
- Faults are categorized by their dip (angle with respect to the surface) and slip direction.
- Dip-slip faults include normal faults (upper block moves down lower block) and reverse faults (upper block moves up and over lower block), reverse faults are common in areas of tectonic compression.
- Strike-slip faults involve horizontal movement along the fault plane.
- Oblique-slip faults exhibit characteristics of both dip-slip and strike-slip faults.
- The earthquake occurred at a relatively shallow depth beneath the Earth's surface, which is a contributing factor to its destructive potential.
- Shallow earthquakes are more dangerous due to their proximity to the Earth's surface.
- They release more energy compared to deeper quakes, making them potentially more destructive.
- Deeper earthquakes lose energy as seismic waves travel greater distances.
- Shallow earthquakes are more dangerous due to their proximity to the Earth's surface.
Key Facts About Morocco:
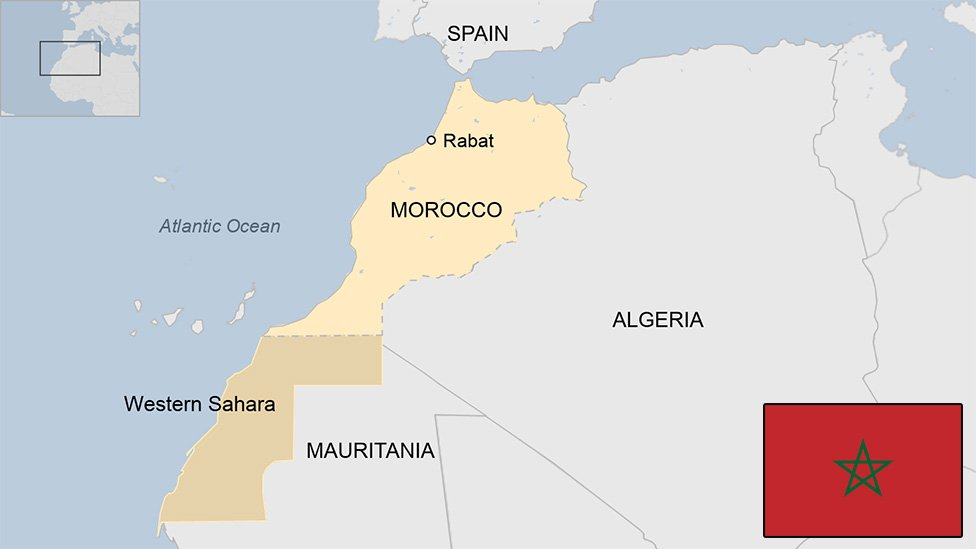
- Morocco is situated in western North Africa, directly across the Strait of Gibraltar from Spain.
- It shares borders with Algeria to the east and southeast, the Western Sahara to the south, and is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the west and the Mediterranean Sea to the north.
- Capital City : Rabat.
- Major Mountain Ranges: The Atlas and Rif Mountains.
- Morocco is situated on the convergence plate of Africa and Eurasia, which are two of the major tectonic plates that make up the Earth’s crust. These plates are constantly moving and colliding, creating mountains, volcanoes, earthquakes, and other geological features.
- The Atlas Mountains in Morocco are a result of the collision between these plates, as they are squeezed and uplifted by the compressional forces.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following: (2013)
- Electromagnetic radiation
- Geothermal energy
- Gravitational force
- Plate movements
- Rotation of the earth
- Revolution of the earth
Which of the above are responsible for bringing dynamic changes on the surface of the earth?
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 4 only
(b) 1, 3, 5 and 6 only
(c) 2, 4, 5 and 6 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. Why are the world’s fold mountain systems located along the margins of continents? Bring out the association between the global distribution of fold mountains and earthquakes and volcanoes. (2014)
Q. Discuss about the vulnerability of India to earthquake related hazards. Give examples including the salient features of major disasters caused by earthquakes in different parts of India during the last three decades. (2021)