Important Facts For Prelims
Bharat Stage Emission Norms
- 20 Dec 2025
- 6 min read
Why in News?
Amid worsening air quality, the Delhi government has tightened vehicular pollution controls by barring non-Bharat Stage (BS) VI private vehicles registered outside Delhi and vehicles without a valid Pollution Under Control Certificate (PUCC) from entering the Capital.
Summary
- Bharat Stage (BS) emission norms are India’s vehicular pollution standards aligned with Euro norms, prescribing progressively stricter limits on pollutants through cleaner fuels and advanced vehicle technologies.
- India moved from BS I (2000) to BS VI (2020) skipping BS V, with BS VI Phase-II (2023) introducing Real Driving Emissions (RDE) testing; BS VII is proposed for 2026–27.
- Older vehicles pollute more due to lack of modern emission-control systems, engine ageing, and poor maintenance, resulting in higher real-world emissions.
What are Bharat Stage (BS) Emission Norms?
- About: Bharat Stage (BS) emission norms are India’s legally enforced standards that regulate the amount of air pollutants emitted by motor vehicles to control vehicular pollution.
- Framed by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) and implemented by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), they are aligned with European (Euro) emission standards.
- The norms set progressively stricter limits on carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter (PM), requiring cleaner fuels, improved engine design, and advanced exhaust-treatment technologies in vehicles.
- The Mashelkar Committee (2002) recommended a detailed roadmap for implementing Euro-equivalent emission norms (Bharat Stage norms) in a phased manner and gradually expanding nationwide.
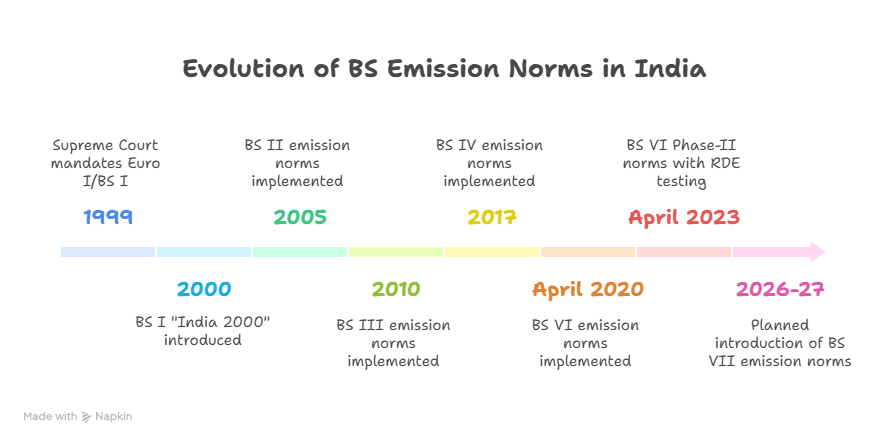
- Evolution of BS Emission Norms: In 1999, Supreme Court of India mandated that all vehicles in India have to meet the Euro I or BS I (also known as India 2000 standard).
- India evolved from BS I (2000) to BS IV (2017), and in a major leap, skipped BS V to implement BS VI in April 2020, sharply tightening vehicular emission standards.
- BS VI Phase-II norms, implemented from April 2023, mandate Real Driving Emissions (RDE) testing to ensure vehicles comply with emission standards under actual on-road conditions.
- Each new stage tightens limits, forcing cleaner fuels and better engine and exhaust technologies.
- To align India’s automobile sector with global standards, the government is planning to introduce BS VII emission norms by 2026-27.
- Delhi has a mixed Bharat Stage (BS) vehicle fleet because it adopted stricter emission norms earlier than the rest of India in response to severe air pollution, implementing BS II in 2001, BS III in 2005, and BS IV in 2010.
- India evolved from BS I (2000) to BS IV (2017), and in a major leap, skipped BS V to implement BS VI in April 2020, sharply tightening vehicular emission standards.
- BS VI Norms: Under BS-VI emission norms, petrol vehicles must cut NOx emissions by 25%, while diesel vehicles are required to reduce HC+NOx by 43%, NOx by 68%, and particulate matter by 82%.
- In addition, sulphur content in fuel has been sharply lowered from 50 mg/kg under BS-IV to 10 mg/kg under BS-VI, enabling advanced emission-control technologies.
Why are Older Vehicles More Polluting?
- Lack of Advanced Emission Controls: Pre-BS IV vehicles lack modern exhaust after-treatment systems such as Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF) and Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR).
- Inferior Exhaust Technology: BS-IV vehicles rely mainly on basic oxidation catalysts, which offer limited control over fine particulate matter and NOx emissions.
- Engine Ageing and Wear: Ageing engines suffer from poor fuel–air mixing, ignition deterioration, and component wear, leading to incomplete combustion.
- Higher Real-World Emissions: Studies show tailpipe emissions rise sharply with vehicle age, especially carbon monoxide and particulate matter.
- Maintenance Issues: High mileage and weak maintenance practices make older vehicles disproportionately more polluting than newer BS-VI vehicles.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are Bharat Stage (BS) emission norms?
They are India’s legally enforced vehicle emission standards regulating pollutants like CO, HC, NOx, and PM, framed by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change and implemented by the Central Pollution Control Board.
2. How is BS VI stricter than BS IV?
BS VI mandates sharply lower NOx and particulate emissions, cleaner low-sulphur fuel, and testing closer to real-world driving conditions.
3. Why are older vehicles more polluting?
They lack modern exhaust-treatment systems, suffer from engine ageing and poor maintenance, and emit higher real-world pollutants than BS-VI vehicles.