Important Facts For Prelims
BEE Standards and Labelling Programme
- 02 Jan 2026
- 9 min read
Why in News?
The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) has tightened India’s energy efficiency regime by making star labelling mandatory for a wider range of appliances, thereby expanding compulsory energy performance disclosure under the Standards and Labelling (S&L) Programme.
What is the BEE’s Standards and Labelling (S&L) Programme?
- Background: Launched in 2006 under the Energy Conservation Act, 2001 by the Ministry of Power, Government of India, and implemented by the BEE.
- Objective: S&L Programme enables informed consumer choice, reduces electricity consumption and energy bills, and encourages manufacturers to adopt energy-efficient technologies.
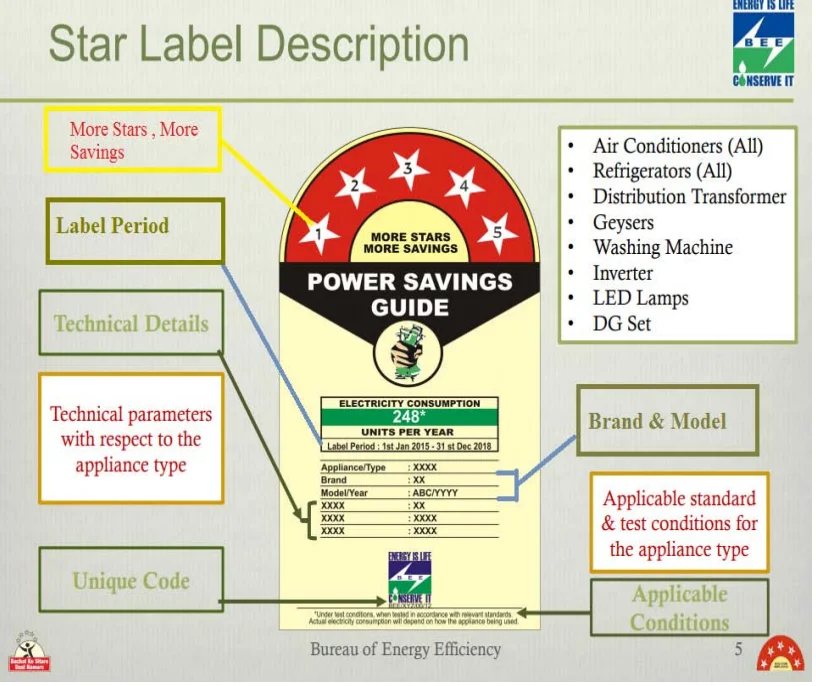
- Star Labelling System: A key feature of the programme is the star labelling system, which rates appliances on a scale of one to five stars based on their energy efficiency.
- Five stars indicating the most energy-efficient product within a given category, making efficiency comparison simple and visual for consumers.
- Under the programme, appliances are tested against prescribed Indian Standards and assigned star ratings based on their energy consumption and performance parameters, with labels displaying essential information such as star rating, annual energy use, product category, and brand.
- Coverage: The programme covers a wide range of household appliances and industrial equipment, with some products brought under mandatory star labelling and others under voluntary labelling, depending on government notifications and market readiness.
- Labels under the S&L Programme:
- Comparative Label: Shows 1–5 star ratings to compare energy efficiency among models of the same product category. It helps consumers easily identify the most energy-efficient appliance.
- Endorsement Label: Certifies products that meet minimum energy performance standards notified by BEE. It assures compliance with efficiency norms rather than comparison.
- Dynamic Nature: To keep pace with technological advancements, BEE periodically revises star rating criteria, ensuring that efficiency benchmarks remain relevant and that manufacturers continuously improve product efficiency.
- Significance: It plays a crucial role in curbing national electricity demand, lowering consumer power bills, and cutting carbon emissions. Notably, Standards and Labelling (S&L) programmes have already reduced around 60 million tonnes of CO₂ annually, while also strengthening India’s long-term energy security.
India’s Energy Efficiency Initiatives
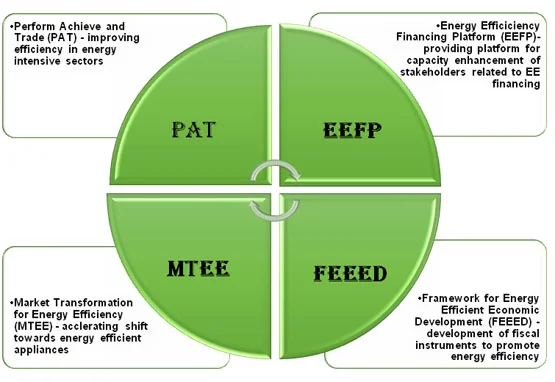
- National Mission for Enhanced Energy Efficiency (NMEEE): It is one of the eight national missions under the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC). NMEEE consist of four initiatives to enhance energy efficiency in energy intensive industries which are as follows:
- Perform, Achieve and Trade (PAT) Scheme: Improves efficiency in energy-intensive industries through mandatory targets and tradable Energy Saving Certificates (ESCerts).
- Energy Efficiency Financing Platform (EEFP): Facilitates access to finance for energy efficiency projects by connecting project developers with financial institutions.
- Market Transformation for Energy Efficiency (MTEE): Encourages uptake of super-efficient technologies through policy and financial interventions.
- Framework for Energy Efficient Economic Development (FEEED): It provides partial credit guarantees to cover default risk on energy efficiency loans, with guarantees for up to 5 years and 40–75% of the loan amount or Rs 15 crore per project.
- Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC), 2017: Sets minimum energy performance standards for commercial buildings to curb energy use.
- Unnat Jyoti by Affordable LEDs for All (UJALA): Accelerates adoption of LED lighting and efficient fans to reduce household bills and peak power demand.
- Bachat Lamp Yojna (BLY): The programme was developed for replacement of inefficient bulbs with Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFLs).
- Street Lighting National Programme: Its objectives include reducing energy consumption, lowering operational costs for municipalities, and fostering a market transformation towards energy-efficient appliances.
- BEE State Energy Efficiency Index: It assesses and compares the energy efficiency performance of Indian States and Union Territories, enabling data-driven monitoring, healthy inter-state competition, and identification of best practices and policy gaps across key sectors.
- States are classified into Front Runners (>60%), Achievers (50-60%), Contenders (30-50%), and Aspirants (<30%), reflecting their relative progress.
Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE)
- The BEE under the Ministry of Power, was established in 2002 under the Energy Conservation Act, 2001
- BEE’s vision is to drive accelerated and sustained adoption of energy efficiency across sectors, contributing to India’s sustainable development.
- The BEE performs key regulatory functions that include developing minimum energy performance standards and star labelling for appliances, formulating Energy Conservation Building Codes, and prescribing energy consumption norms for designated consumers.
- It also certifies and accredits Energy Managers and Energy Auditors, defines the manner and periodicity of mandatory energy audits for tracking energy use and implementation of audit recommendations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the Standards and Labelling (S&L) Programme?
It is an energy efficiency programme launched in 2006 under the Energy Conservation Act, 2001 to rate appliances on a 1–5 star scale based on energy performance. - Who implements the S&L Programme in India?
The programme is implemented by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency under the Ministry of Power. - Why is expansion of mandatory star labelling significant?
It improves transparency, reduces electricity demand, lowers consumer bills, and has already cut about 60 million tonnes of CO₂ annually. - What is the National Mission for Enhanced Energy Efficiency (NMEEE)?
NMEEE is a mission under NAPCC focusing on industrial and market-based energy efficiency through PAT, MTEE, EEFP, and FEEED. - What is the purpose of the State Energy Efficiency Index (SEEI)?
It assesses and compares energy efficiency performance of States and UTs, encouraging data-driven governance and healthy competition.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question:
Prelims
Q. With reference to street lighting, how do sodium lamps differ from LED lamps? ( 2021)
- Sodium lamps produce light at 360 degrees but it is not so in the case of LED lamps.
- As street lights, sodium lamps have a longer lifespan than LED lamps.
- The spectrum of visible light from sodium lamps is almost monochromatic, while LED lamps offer significant colour advantages in street lighting.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Q. On which of the following can you find the Bureau of Energy Efficiency Star Label? (2016)
- Ceiling fans
- Electric geysers
- Tubular fluorescent lamps
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)