Indian Economy
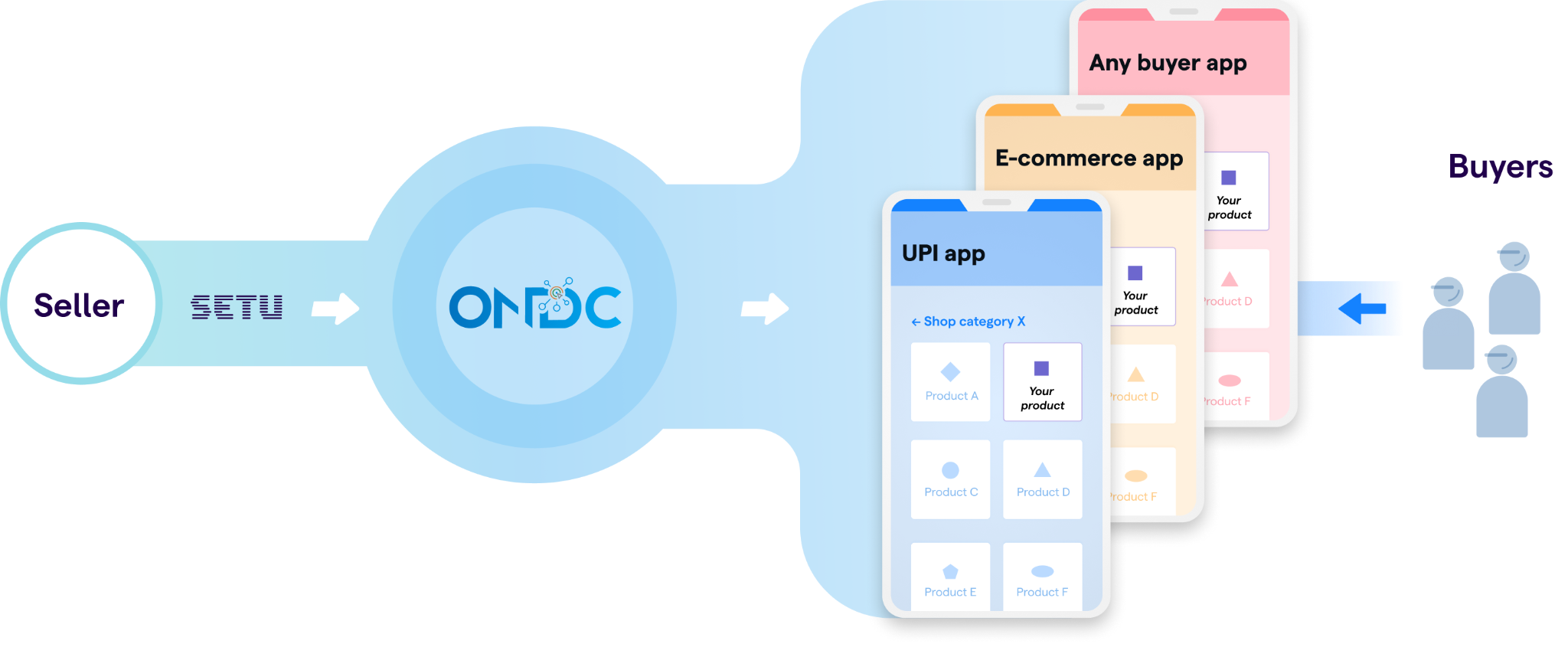
Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC)
This editorial is based on “How India is shaping the future of e-commerce”, which was published in Hindustan Times on 07/08/2022. It talks about the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) and its applications.
For Prelims: Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), Micro, Small and Medium enterprises (MSMEs), Unified Payments Interface (UPI).
For Mains: Benefits of Open Network for Digital Commerce , Grey Areas Related to ONDC.
The future of Open Retail is taking shape in India as the nation rolls out the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) in pursuit of increasing E-commerce penetration in India to 25% of consumer purchases in the next two years.
ONDC will provide a common digital space for buyers and sellers with the goal of democratising e-commerce by transforming it from a platform-centric paradigm to an open network for buying and selling goods and services, ONDC can certainly transform India's E-commerce sector. However, there are a few grey areas that still need to be clarified.
What Benefits Does the Open Network for Digital Commerce Offer?
- Level Playing Field: ONDC is keen to level the playing field for e-commerce operators and widen the digital market access for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) and small traders in the country.
- Additionally, it will help new entrants by bringing discoverability, interoperability, and inclusivity.
- Competitive and Innovative Ecosystem: Existing e-commerce platforms operate in compartments and are strictly regulated.
- ONDC will empower suppliers and consumers by breaking the monopoly of giant platforms to drive innovation and transform businesses in sectors like retail, food, and mobility.
- Freedom of Choice for Consumers: Consumers can potentially discover any seller, product or service in a common platform, thus increasing freedom of choice for consumers.
- It will enable the consumers to match demand with the nearest available supply. This would also give consumers the liberty to choose their preferred local businesses.
- Neutral and Regulated Platform: ONDC aims at fostering open networks developed on open-sourced methodology, using open specifications and network protocols, and independent of any specific platform.
- It will set protocols for cataloguing, vendor match, and price discovery on an open source-basis, like the Unified Payments Interface (UPI).
- Snapdeal is the first E-commerce platform to get on the open network.
What is Open Source?
- Open source implies that the technology or code deployed for the process is freely made available for everyone to use, redistribute, and modify.
- For instance, the operating system of iOS is closed source, it cannot be legally modified or used.
- Whereas, the android operating system is open source, making it possible for smartphone manufacturers, such as Samsung, Nokia, Xiaomi, etc., to modify it for their respective hardware.
What are the Grey Areas Related to ONDC?
- Match-Up Concern: Smaller businesses with low volumes may lack the resources to match the discounts offered by heavyweights like Amazon and Flipkart.
- These two global giants poured a combined USD 24 billion into India and captured 80% of the online retail market with aggressive discounts and promotion of preferred sellers.
- Payment Methods: It is certain that there might be a mismatch in payment gateway compatibility between the different platforms.
- The goal of a seamless transaction may be compromised if different e-commerce platforms do not accept all modes of payment.
- Answerability Concern: As it remains unclear as to how various e-commerce norms will apply to ONDC, and how ONDC fits into the entire legal landscape of e-commerce in India.
- The question arises about liability in case of a consumer facing any issue regarding the transaction or the quality of products or services delivered.
What Should be the Way Forward?
- Digital Infrastructure and Literacy: The government needs to build a better digital space for e-commerce to outdo the dominant e-commerce platforms.
- Along with this, it's important to create a proper digital education policy that takes into account various languages and user-friendly interface for the benefit of the consumers as well as sellers.
- Awareness Campaign: Bringing the tens of millions of existing kirana stores onto the platform will require a massive, well-funded adoption campaign.
- Thrust to Existing Schemes through ONDC: ONDC can enhance the implementation of variou schemes like Pradhan Mantri Van Dhan Yojana.
- PMVDY scheme aims for enhancing the livelihood of forest-dependent tribes through aggregation, processing and forward sales of forest produce.
- The tribal communities neither enjoy the benefits of price realisation nor do they get sufficiently exposed to the market.
- The scheme has been operating since 2018 but a bulk of sales still take place at local haat bazaars or village mandis and are restricted to local traders.
- ONDC can provide them the reach on scale enjoyed by any other big brand.
- Such an integration would also add significant value to customer choices marching towards healthy and sustainable options.
- PMVDY scheme aims for enhancing the livelihood of forest-dependent tribes through aggregation, processing and forward sales of forest produce.
- Proper Grievance Redressal Mechanism: There should be a secured single window to navigate both the demand and supply-side problems like information asymmetry, opaque pricing, quality and product concerns and buyer-seller conflict.
|
Drishti Mains Question Explain how Open Network for Digital Commerce can transform platform-centric paradigm to an open network for E-commerce in India. Highlight the major operational challenges in its implementation. |