Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
High-Yielding Varieties of Soybean
Why in News?
Ahead of the Kharif 2025 season, the Department of Agriculture has recommended specific high-yielding soybean varieties for cultivation in the Bundelkhand region of Uttar Pradesh to optimize yields under local agro-climatic conditions.
Key Points
- Centrally Notified High-Yielding Varieties: These varieties have demonstrated excellent adaptability to the rainfall patterns, soil types, and temperature profiles typical of the Bundelkhand region.
- No additional state-specific soybean varieties have been notified exclusively for Uttar Pradesh.
- Suitability to Regional Conditions: They are expected to perform well in medium to deep black soils and under monsoon-dependent rainfall patterns.
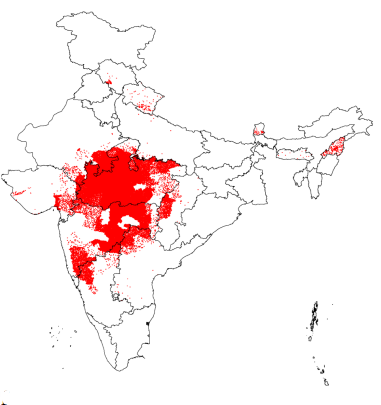
- Soybean Cultivation in India: The cultivation is currently concentrated in a few key states, contributing around 4% to global soybean production.
- The major soybean-growing states include Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra and Gujarat.
- Significance of Soybean Cultivation:
- Water Efficiency: Soybean requires considerably less water than paddy, making it a highly suitable crop for regions with limited water availability.
- Economic Viability: Due to its lower input costs and decent yield potential, soybean cultivation can offer farmers earnings that are comparable to, or even better than, those from paddy farming.
- Soil Health: As a legume, soybean enriches soil nitrogen, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
- Crop Diversification: Soybean can be effectively integrated into crop rotation systems such as soybean–wheat, soybean–peas–summer moong etc., helping farmers diversify their cropping patterns and reduce reliance on water-intensive paddy cultivation.
- Market and Nutrition Value: Soybean is rich in both protein and oil content, making it valuable for food, animal feed, and various industrial applications.
Kharif Crops
- Kharif crops are the crops that are sown during the rainy season, which in India typically lasts from June to September.
- These crops require a lot of water and hot weather to grow, and they depend heavily on monsoon rains.
- Sowing and Harvesting:
- Sowing Time: June to July (beginning of the monsoon)
- Harvesting Time: October to November (end of the monsoon)
- Common Kharif Crops:
- Paddy (rice), Maize (corn), Groundnut (peanut), Cotton, etc.
Rabi Crops
- Rabi crops are grown in the winter season, from October to March.
- These crops are typically sown after the monsoon ends and require cooler climates during the growth period and warm, dry conditions at the time of harvesting.
- Sowing and Harvesting:
- Sowing Time: October to November
- Harvesting Time: March to April
- Common Rabi Crops: Wheat, Gram (chana), Pea, Mustard, Linseed, etc.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Project Alankar
Why in News?
Project Alankar, an educational reform initiative by the Uttar Pradesh government, has been widely appreciated during a meeting chaired by the Prime Minister in New Delhi.
Key Points
Project Alankar
- About: It was launched on 1st October 2021, by the Government of Uttar Pradesh.
- It aims to achieve 100% compliance with 35 infrastructure and facility benchmarks in 2,441 government secondary schools.
- Its primary goal is to create a more conducive, inclusive, and modern learning environment for students across the state.
- Key Features of Project Alankar:
- Upgradation of physical infrastructure including newly constructed classrooms, science labs, libraries, computer labs, and smart classrooms.
- Provision of essential amenities such as clean drinking water and hygienic toilets, particularly focusing on girls' sanitation facilities.
- Development of specialized schools under the scheme:
- Chief Minister Model Schools (pre-primary to Class 12) and Chief Minister Abhyudaya Schools (pre-primary to Class 8) are also being developed.
- These schools have state-of-the-art facilities, including Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) laboratories, computer labs, etc.
- Each Abhyudaya School, designed to accommodate 450 students, was allocated Rs 1.42 crore for development
- Chief Minister Model Schools (pre-primary to Class 12) and Chief Minister Abhyudaya Schools (pre-primary to Class 8) are also being developed.
- Renovation and modernization of 141 Sanskrit schools across 7 districts, with dedicated funding of Rs 14.94 crore for their rejuvenation.
- Funding and Implementation:
- Funding sources for Project Alankar include the state government, Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan, Gram Panchayats, urban local bodies, corporate Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) contributions, and voluntary donations.
- Implementation is rigorously monitored by district-level committees headed by district magistrates and overseen by the state education director.
- Impact and Outcomes:
- According to the Annual Status of Education Report (ASER) 2024, government secondary school enrolment increased by 23% between 2022-23 and 2024-25.
- Primary school attendance (classes 1–5) rose by 11.5% from 2010 to 2024, while upper primary attendance (classes 6–8) grew by 9.6% between 2018 and 2024 — the highest in the country.
- Usage of school libraries surged by 55.2%, and access to girls’ toilet facilities improved by 54.4%, reflecting better sanitation and learning support.
Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan
- About: Introduced in the Union Budget 2018-19, Samagra Shiksha is a comprehensive program covering education from pre-nursery to Class 12 to ensure equitable learning outcomes.
- Key Features:
- Integration of Schemes: It subsumes three earlier schemes:
- Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA): Focused on universal primary education.
- Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA): Aimed at secondary education.
- Teacher Education (TE): Focused on training teachers.
- Sector-Wide Development Approach: It streamlines implementation across all levels (state, district, and sub-district) instead of fragmented project-based objectives.
- Alignment with SDGs: Ensures free, equitable, and quality education (SDG 4.1) while eliminating gender disparities and ensuring access for vulnerable groups (SDG 4.5).
- Implementation: It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) implemented through a single State Implementation Society (SIS) at the State/UT level.
- SIS is a state-registered body implementing CSS and development programs.





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan