Uttar Pradesh
High-Yielding Varieties of Soybean
- 27 May 2025
- 4 min read
Why in News?
Ahead of the Kharif 2025 season, the Department of Agriculture has recommended specific high-yielding soybean varieties for cultivation in the Bundelkhand region of Uttar Pradesh to optimize yields under local agro-climatic conditions.
Key Points
- Centrally Notified High-Yielding Varieties: These varieties have demonstrated excellent adaptability to the rainfall patterns, soil types, and temperature profiles typical of the Bundelkhand region.
- No additional state-specific soybean varieties have been notified exclusively for Uttar Pradesh.
- Suitability to Regional Conditions: They are expected to perform well in medium to deep black soils and under monsoon-dependent rainfall patterns.
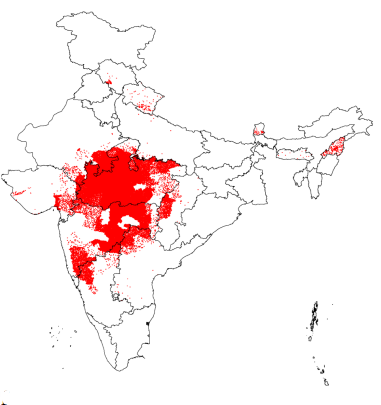
- Soybean Cultivation in India: The cultivation is currently concentrated in a few key states, contributing around 4% to global soybean production.
- The major soybean-growing states include Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra and Gujarat.
- Significance of Soybean Cultivation:
- Water Efficiency: Soybean requires considerably less water than paddy, making it a highly suitable crop for regions with limited water availability.
- Economic Viability: Due to its lower input costs and decent yield potential, soybean cultivation can offer farmers earnings that are comparable to, or even better than, those from paddy farming.
- Soil Health: As a legume, soybean enriches soil nitrogen, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
- Crop Diversification: Soybean can be effectively integrated into crop rotation systems such as soybean–wheat, soybean–peas–summer moong etc., helping farmers diversify their cropping patterns and reduce reliance on water-intensive paddy cultivation.
- Market and Nutrition Value: Soybean is rich in both protein and oil content, making it valuable for food, animal feed, and various industrial applications.
Kharif Crops
- Kharif crops are the crops that are sown during the rainy season, which in India typically lasts from June to September.
- These crops require a lot of water and hot weather to grow, and they depend heavily on monsoon rains.
- Sowing and Harvesting:
- Sowing Time: June to July (beginning of the monsoon)
- Harvesting Time: October to November (end of the monsoon)
- Common Kharif Crops:
- Paddy (rice), Maize (corn), Groundnut (peanut), Cotton, etc.
Rabi Crops
- Rabi crops are grown in the winter season, from October to March.
- These crops are typically sown after the monsoon ends and require cooler climates during the growth period and warm, dry conditions at the time of harvesting.
- Sowing and Harvesting:
- Sowing Time: October to November
- Harvesting Time: March to April
- Common Rabi Crops: Wheat, Gram (chana), Pea, Mustard, Linseed, etc.