Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
Legal Action on Dharavi Rehab Project
Why in News?
A legal notice has been sent to the Maharashtra government and Mumbai Municipal Commissioner, demanding cancellation of the cabinet decision to hand over Deonar dumping ground for the Dharavi rehab project, citing violation of Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) guidelines.
Key Points
- About Dumping Ground:
- The State government has decided to hand over 124 acres of Deonar dumping ground for the Dharavi Rehabilitation Project (DRP).
- The Mulund dumping ground is also being considered for inclusion in the DRP.
- Environmental and Legal Concerns:
- Mulund-based activist issued a legal notice opposing the decision.
- He flagged serious environmental risks highlighting that high-rises built on rotting mixed waste at Deonar and Mulund generate methane, which causes 21 times more global warming than Carbon Dioxide (CO₂).
- He pointed out that these sites also produce leachate, a toxic liquid that pollutes groundwater, making them unsuitable for residential construction.
- Active Methane-Emitting Site:
- The activist emphasized that Deonar is not a closed landfill.
- It remains one of India’s top 22 methane hotspots, releasing around 6,202 kg of methane per hour.
Central Pollution Control Board
- CPCB is a statutory organisation which was constituted in September, 1974 under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974.
- It was entrusted with the powers and functions under the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981.
- It serves as a field formation and also provides technical services to the Ministry of Environment and Forests of the provisions of the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
- Principal Functions of the CPCB, as spelt out in the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974, and the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981.
- to promote cleanliness of streams and wells in different areas of the States by prevention, control and abatement of water pollution.
- to improve the quality of air and to prevent, control or abate air pollution in the country.


Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
School Registration Portal Launched
Why in News?
The Maharashtra government launched a portal for private pre-schools to register, aiming to build a unified database of all pre-schools in the state.
Key Points
- About the Portal:
- The State government has made pre-school registration voluntary for the time being.
- A dedicated Act to regulate pre-primary education is currently in progress.
- Until now, formal education in Maharashtra began at Class 1, after children turned 6.
- Pre-schools (nursery to senior kindergarten, for ages 3–6) were not part of the mainstream system.
- The State government has made pre-school registration voluntary for the time being.
- ECCE under NEP 2020:
- The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 includes Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) in formal schooling.
- With Maharashtra implementing NEP in schools, pre-schools will also be brought into the mainstream.
- The school education department has data on government-run anganwadis and balwadis (under Women and Child Development Department).
- However, there is no formal data on the large number of privately run pre-schools.
- The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 includes Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) in formal schooling.
National Education Policy 2020
- About:
- The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 aims to address India's evolving development needs by overhauling the education system to meet 21st century goals and Sustainable Development Goal 4 (SDG4), while preserving India's cultural heritage.
- It replaced the National Policy on Education, 1986, which was modified in 1992.
- Salient Features:
- Universal Access: Focuses on providing access to education from pre-school through secondary levels.
- Early Childhood Education: Transitions from the 10+2 to a 5+3+3+4 system, including children aged 3-6 in the school curriculum with an emphasis on Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE).
- Multilingualism: Promotes using mother tongues or regional languages as the medium of instruction up to Grade 5, with options for Sanskrit and other languages. Indian Sign Language (ISL) will be standardised.
- Inclusive Education: Emphasises support for Socially and Economically Disadvantaged Groups (SEDGs), children with disabilities, and the establishment of "Bal Bhavans."
- Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) Enhancement: Aim to raise the Gross Enrolment Ratio from 26.3% to 50% by 2035, adding 3.5 crore new seats.
- Research Focus: Establishes the National Research Foundation to enhance research culture and capacity.
- Language Preservation: Supports Indian languages through the Institute of Translation and Interpretation (IITI) and strengthens language departments.
- Internationalisation: Encourages international collaborations and the entry of top-ranked foreign universities.
- For example, in 2023 UGC released regulations to facilitate foreign universities to set up campuses in India.
- Funding: Targets increasing public investment in education to 6% of GDP.
- PARAKH Assessment Center: Introduces PARAKH (Performance Assessment, Review, and Analysis of Knowledge for Holistic Development) for competency-based and holistic assessments.
- Gender Inclusion Fund: Establishes a fund to promote gender equality in education and support initiatives for disadvantaged groups.
- Special Education Zones: Creates Special Education Zones to cater to the needs of disadvantaged regions and groups, reinforcing the commitment to equitable access to quality education.


Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Violation of Ceasefire at LOC
Why in News?
Days after the Pahalgam terror attack, the Pakistan Army fired from multiple posts along the Line of Control (LoC), violating the ceasefire. Indian forces responded with retaliatory fire, Indian Army officials confirmed.
Key Points
- Pahalgam Terror Attack Triggers Crisis:
- On 22 April 2025, terrorists killed 26 tourists in a brutal attack in Pahalgam, Jammu and Kashmir.
- The attack has sparked nationwide outrage and triggered widespread protests demanding tougher action against Pakistan.
- India Takes Diplomatic Countermeasures:
- The central government closed the Integrated Check Post (ICP) at Attari.
- It suspended the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) Visa Exemption Scheme (SVES) for Pakistani nationals and gave them 40 hours to return.
- India also reduced the strength of diplomatic staff in both High Commissions.
- India has suspended the 1960 Indus Waters Treaty (IWT) until Pakistan ceases its support for cross-border terrorism.
- It reflects a shift in India’s strategic calculus, using hydrological leverage as a pressure tool.
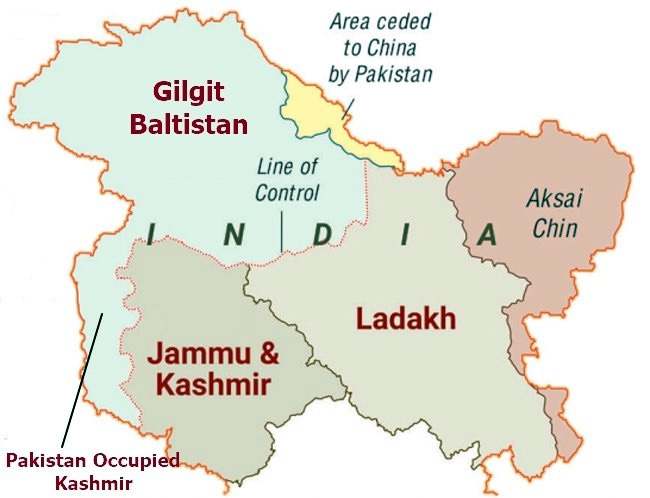
Line of Control
- The Line of Control (LoC) emerged from the 1948 ceasefire line negotiated by the United Nations (UN) after the Kashmir War.
- It was designated as the LoC in 1972, following the Shimla Agreement between the two countries.
- LoC is demarcated up to the Siachen Glacier (Point NJ9842)- the world's highest battlefield.
- LoC is delineated on a map signed by the Director General of Military Operations (DGMO) of both armies and has the international sanctity of a legal agreement.
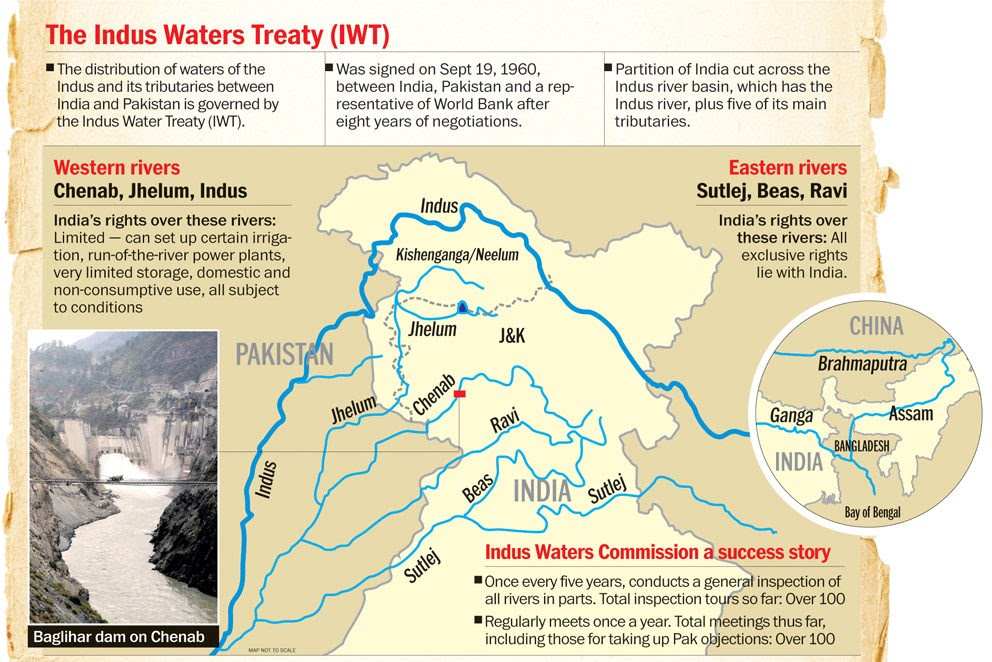
Indus Waters Treaty
- The IWT, signed in 1960 in Karachi after nine years of negotiations between India and Pakistan, was mediated by the World Bank.
- The treaty allocates the "Eastern Rivers" of the Indus system (Ravi, Beas, and Sutlej) to India for unrestricted use, while the "Western Rivers" (Indus, Jhelum, and Chenab) are reserved for Pakistan, effectively giving Pakistan access to about 80% of the total water.
- India is allowed limited non-consumptive uses of the Western Rivers, such as for navigation, agriculture, and hydroelectricity, subject to design and operational conditions under the treaty.
- IWT established a Permanent Indus Commission (PIC) to ensure annual dialogue and cooperation, and laid out a three-tier dispute resolution mechanism, including resolution at the PIC level, through a Neutral Expert (appointed by the World Bank or jointly by the India and Pakistan), or if needed, a Court of Arbitration.
- The treaty allocates the "Eastern Rivers" of the Indus system (Ravi, Beas, and Sutlej) to India for unrestricted use, while the "Western Rivers" (Indus, Jhelum, and Chenab) are reserved for Pakistan, effectively giving Pakistan access to about 80% of the total water.


Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
MNREGA Scheme
Why in News?
The Rajasthan government has changed the work timing under Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) keeping in mind the convenience and health of workers during the summer season.
Key Points
- About MNREGA:
- MGNREGA is one of the world's largest employment guarantee programmes launched in 2005 by the Ministry of Rural Development.
- The scheme provides a legal guarantee of a minimum of one hundred days of employment in every financial year to adult members of any rural household willing to do unskilled manual work related to public works at minimum wages.
- Active Employees: 14.32 Crore (Session 2023-24)
- Key Features:
- The cornerstone of MGNREGA's design is its legal guarantee , which ensures that any rural adult can request work and should be provided with work within 15 days.
- If this commitment is not fulfilled then “unemployment allowance” should be provided.
- This requires that women be given priority in such a way that at least one-third of the beneficiaries who have registered and requested for work are women.
- Section 17 of MGNREGA makes social audit of all works executed under MNREGA mandatory.
- The cornerstone of MGNREGA's design is its legal guarantee , which ensures that any rural adult can request work and should be provided with work within 15 days.
- Implementing Agency:
- The Ministry of Rural Development (MRD), Government of India is monitoring the entire implementation of the scheme in collaboration with the state governments.
- Objective:
- This act was introduced with the aim of improving the purchasing power of the rural people , it mainly aims to provide semi or unskilled work to the people living below the poverty line in rural India.
- It attempts to reduce the gap between the rich and the poor in the country.


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
IIT BHU Tops at Forensic Hackathon 2025
Why in News?
The research team from the School of Biochemical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology (BHU), Varanasi has won top honours at the Forensic Hackathon 2025.
- This hackathon was part of the All India Forensic Science Summit organised by the National Forensic Sciences University (NFSU) .
Key Points
- About the Award:
- The award was presented by the Union Home Minister at Vigyan Bhavan in New Delhi .
- The team was awarded a cash prize of Rs 2 lakh and a memento for their innovative research .
- Developed Technology:
- The team has developed a glycan-based forensic technique that allows accurate age estimation based on biological fluids, i.e., it can be used to estimate the exact age of a person even without DNA .
- This technology combines glycomic profiling with machine learning algorithms to estimate both chronological age and biological age .
- Currently practiced DNA-based forensic analyses , which incorporate epigenetic markers , have biological variability and technical limitations .
- DNA methylation-based models often require ancient and good-quality DNA, which may be unavailable in forensic cases.
- The team has developed a glycan-based forensic technique that allows accurate age estimation based on biological fluids, i.e., it can be used to estimate the exact age of a person even without DNA .
- Importance:
- This innovation can make profiling of suspects based on samples collected from crime scenes more accurate, especially when DNA matches are not available.
- This technology could be useful in identifying missing persons, identifying unidentified victims in mass disasters , and verifying claims of being a juvenile or misrepresenting age .
- Biological age provides important evidence about a person's health, immune status and stress, which can help in reconstructing a crime .
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
- Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is an organic molecule with a complex molecular structure.
- The strands of a DNA molecule are made up of a long chain of monomer nucleotides. It is arranged in a double helix structure.
- James Watson and Francis Crick discovered that DNA is a double-helix polymer in the year 1953.
- This is necessary for the transfer of genetic characteristics of organisms from one generation to another.
- Most of the DNA is found in the nucleus of the cell, so it is called central DNA.


Bihar Switch to Hindi
Veer Kunwar Singh Vijay Diwas
Why in News?
The Governor and Chief Minister of Bihar paid tribute to Babu Veer Kunwar Singh as part of the program organized on his Vijay Diwas.
Key Points
- About Kunwar Singh:
- Veer Kunwar Singh was born in Jagdishpur (present-day Bhojpur district, Bihar) in the year 1777. He belonged to the Ujjainiya clan of Parmar Rajputs of Jagdishpur
- He was the main hero of the fight against the British in Bihar. He led the Indian Rebellion of 1857 in Bihar . He was about 80 years old when he was called to take up arms and his health was also poor.
- He was assisted by both his brother, Babu Amar Singh, and his commander, Hare Krishna Singh. Some believe this was the real reason behind Kunwar Singh's initial military success.
- He displayed excellent war skills and troubled the British army for almost a year and remained invincible till the end. He was an expert in guerrilla warfare.
- He died on April 26, 1858.
- A commemorative postage stamp was issued in his honour by the Republic of India on 23 April 1966 for his contribution to India's independence movement .
- Veer Kunwar Singh University, Ara was established in the year 1992 by the Government of Bihar .
- In the year 2017, Veer Kunwar Singh Setu, also known as Ara-Chhapra Bridge, was inaugurated to connect North and South Bihar.
- In 2018, to commemorate the 160th anniversary of Kunwar Singh's death, the Bihar government moved a statue of him to Harding Park. The park was also officially named 'Veer Kunwar Singh Azadi Park'.
Revolt of 1857
- It was the first expression of organised resistance against the British East India Company .
- It began as a revolt of sepoys of the British East India Company's army but gained public participation as well.
- The rebellion is known by many names: the Sepoy Mutiny (by British historians), the Indian Mutiny, the Great Rebellion (by Indian historians), the Revolt of 1857, the Indian Mutiny, and the First War of Independence ( by Vinayak Damodar Savarkar).







 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan