Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Pakal Dul Hydropower Project
Why in News?
The Central government has taken a significant step by fast-tracking approval for the electricity transmission line of the 1,000 MW Pakal Dul hydropower project in Kishtwar district of Jammu and Kashmir.
Key Points
- About the Project:
- The Ministry of Power approved the Pakal Dul transmission line in 40 days.
- This accelerated clearance reflects the government's urgency to harness more water from the Indus River Basin for domestic use.
- Authorities expect to commission the 1,000 MW project by September 2026.
- The transmission line will pass through 21 villages in Kishtwar district.
- Chenab Valley Power Projects Limited (CVPPL), a subsidiary of National Hydroelectric Power Corporation (NHPC), will implement the Pakal Dul project.
- India's Highest Dam on Indus System:
- Located on the Marusudar River, a tributary of the Chenab, the Pakal Dul project will feature India’s tallest dam on the Indus system at 167 meters.
- The dam also promises a much larger storage capacity compared to previous hydropower projects in the region.
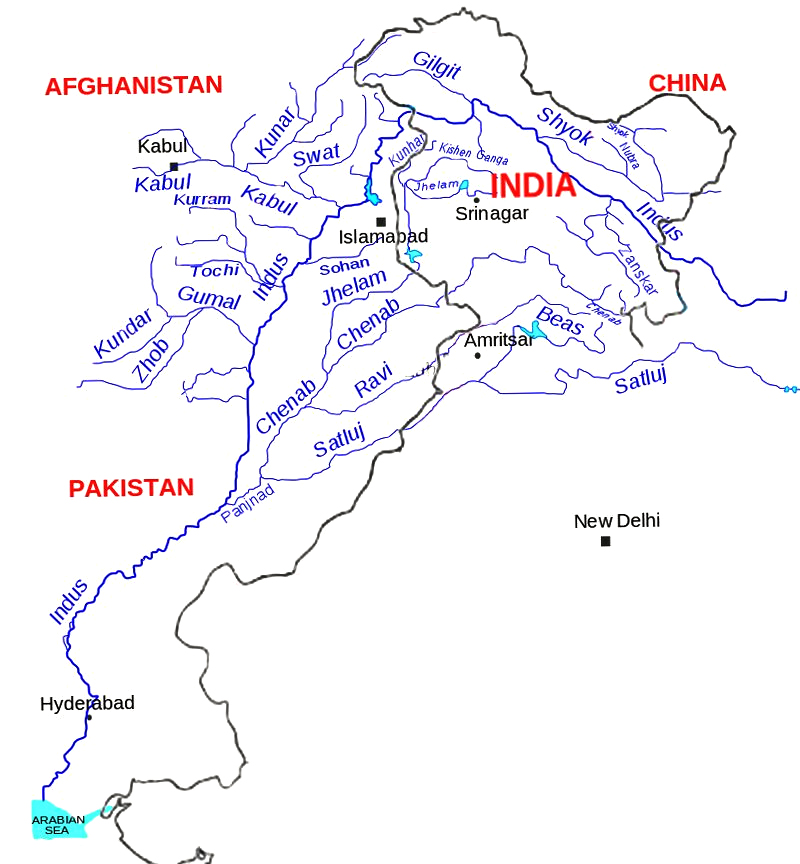
Chenab River
- Source: It rises in the upper Himalayas in the Lahaul and Spiti district of Himachal Pradesh state.
- The river is formed by the confluence of two rivers, Chandra and Bhaga, at Tandi, 8 km southwest of Keylong, in the Lahaul and Spiti district.
- The Bhaga river originates from Surya taal lake, which is situated a few kilometers west of the Bara-lacha la pass in Himachal Pradesh.
- The Chandra river originates from glaciers east of the same pass (near Chandra Taal).
- The river is formed by the confluence of two rivers, Chandra and Bhaga, at Tandi, 8 km southwest of Keylong, in the Lahaul and Spiti district.
- Flows Through: It flows through the Jammu region of Jammu and Kashmir into the plains of Punjab, Pakistan, before flowing into the Indus River.
- Important projects/dams on Chenab:
- Ratle Hydro Electric Project
- Salal Dam- hydroelectric power project near Reasi
- Dul Hasti Hydroelectric Plant- power project in Kishtwar District
- Pakal Dul Dam (under construction)- on a tributary Marusadar River in Kishtwar District.
- Kiru Hydroelectric Project (Kishtwar District)
Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
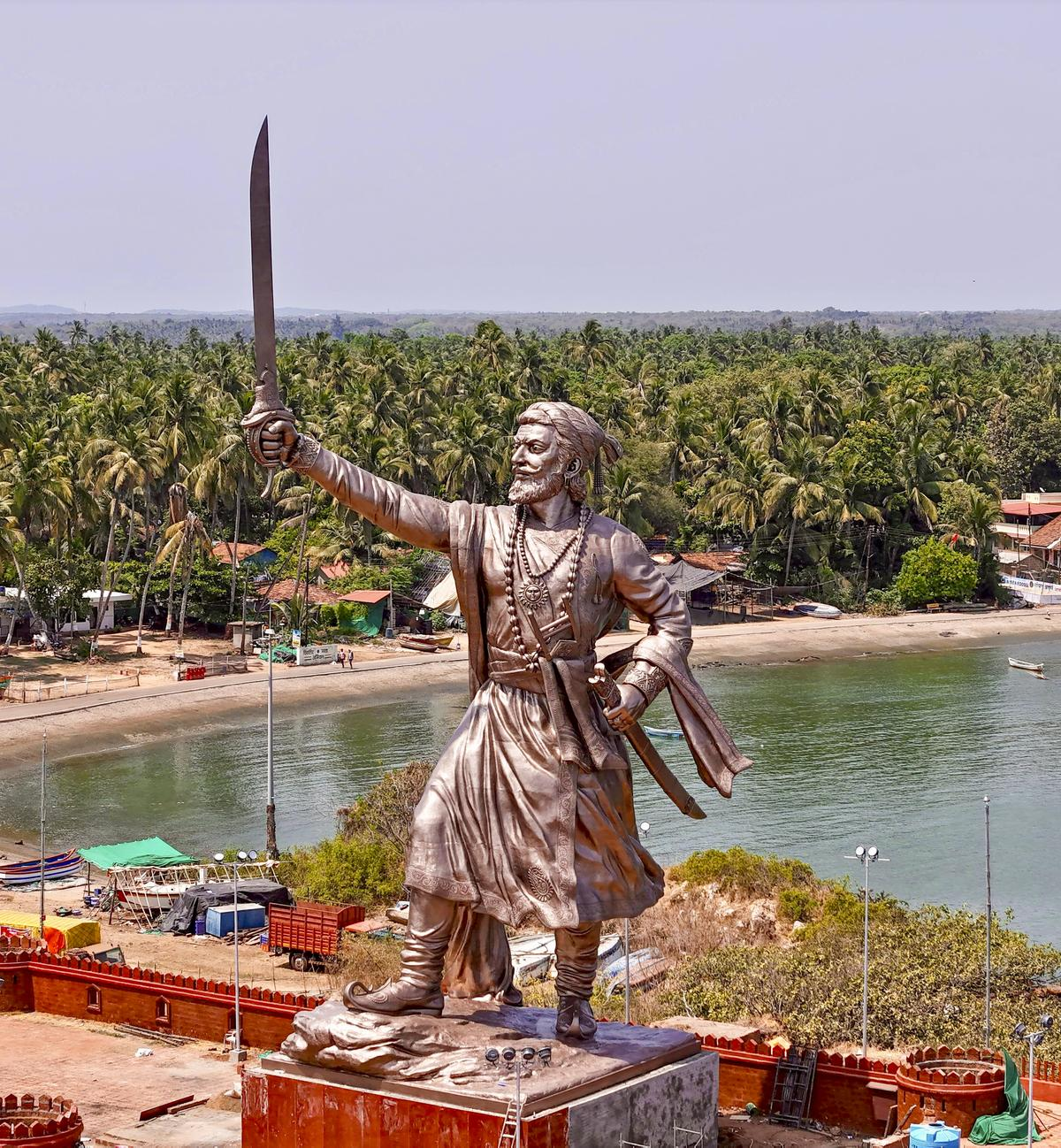
Statue of Shivaji Maharaj at Sindhudurg
Why in News?
On 11 May 2025, Maharashtra Chief Minister Devendra Fadnavis unveiled a statue of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj at the Rajkot Fort in Sindhudurg.
Key Points
- About the Statue:
- The statue stands 91 feet tall, including a 10-foot pedestrian base, making it the tallest statue of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj in India.
- According to the Chief Minister, the grand statue will inspire future generations and boost tourism by spurring development in the Sindhudurg region.
- The Maharashtra Public Works Department constructed the statue at a cost of Rs 31.75 crore.
- Renowned sculptor Ram Sutar’s company executed the project.
- Engineers used stainless steel framework, M50 grade concrete, and stainless steel bars to build the structure.
- The Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Mumbai verified the statue’s concept and design for structural safety and durability.
- About Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj:
- Born on 19th February 1630, at Shivneri Fort, Pune was a visionary leader from the Bhonsle clan and the founder of the Maratha Empire, known for resisting the Mughal Empire and striving for self-rule.
- Major Battles: Battle of Pratapgad, Battle of Pavan Khind, Sacking of Surat, Battle of Purandar, Battle of Sinhagad, and Battle of Sangamner.
- The Wagh nakh, was used by Shivaji to kill Afzal Khan in the 1659 Battle of Pratapgad.
- Titles: Chhatrapati, Shakakarta, Kshatriya Kulavantas, and Haindava Dharmodhhaarak.
- Administration: Centralized administration with the Ashtapradhan (Council of Eight Ministers), abolished the Jagirdari System, implemented the Ryotwari System, and built a strong naval force for coastal defense.
- Major Battles: Battle of Pratapgad, Battle of Pavan Khind, Sacking of Surat, Battle of Purandar, Battle of Sinhagad, and Battle of Sangamner.
- Shivaji is renowned for his innovative guerrilla warfare tactics, which influenced subsequent rulers and shaped the Maratha Military Landscapes.
- Born on 19th February 1630, at Shivneri Fort, Pune was a visionary leader from the Bhonsle clan and the founder of the Maratha Empire, known for resisting the Mughal Empire and striving for self-rule.
Rajkot Fort
- Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj constructed Rajkot Fort between 1664 and 1667 in Malvan, Maharashtra, as part of his coastal defence strategy.
- The fort functioned as a vital military outpost for protecting coastal trade routes and was integrated into the broader Sindhudurg Fort complex.
- Positioned near the Arabian Sea, the fort's robust walls and strategic coastal location reflect the region’s rich maritime heritage and naval foresight under Shivaji’s rule.
- In 1766, the British entered into a treaty with the Chhatrapati of Karveer (a branch of the Maratha royal family).
- As part of this engagement, the British sought permission to establish a shipbuilding yard at Rajkot, highlighting the fort's continued strategic value even in the colonial era.
Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
Illinois Tech University New Campus in India
Why in News?
Illinois Tech University announced that India’s University Grants Commission (UGC) had formally approved its plan to open a new campus in Mumbai, making it the first American university to receive authorisation to establish a degree-granting campus in India.
Key Points
- About Mumbai Campus:
- Illinois Tech University will welcome students to its new Mumbai campus starting in Fall 2026.
- The campus will offer undergraduate and graduate degrees in high-demand fields such as Computer Science, Engineering, and Business.
- It will deliver the same experiential and industry-aligned curriculum as Illinois Tech’s Chicago campus.
- It will also include the university’s signature Elevate program, which guarantees students access to hands-on research, internships, and career-enhancing opportunities.
University Grants Commission (UGC)
- About:
- India's first effort to establish a national education system began with the 1944 Sargeant Report, which recommended creating a University Grants Committee.
- Formed in 1945, the committee initially supervised Aligarh, Banaras, and Delhi universities. By 1947, its scope expanded to include all existing universities.
- In 1948, the University Education Commission, led by Dr. S. Radhakrishnan, recommended its restructuring based on the UK model.
- In 1952, the Union Government designated the University Grants Commission (UGC) to oversee grants for Central Universities and higher education institutions.
- Formally inaugurated by Maulana Abul Kalam Azad in 1953 , it became a statutory body in 1956. The head office of the UGC is located in New Delhi.
- India's first effort to establish a national education system began with the 1944 Sargeant Report, which recommended creating a University Grants Committee.
- Composition:
- UGC is made up of a Chairman, a Vice-Chairman, and 10 other members. The Central Government appoints all members of the UGC.
- Key Functions:
- Assess universities' financial needs, and allocate and disburse grants for maintenance, development, and other purposes.
- Recommends improvements in higher education and assists in implementation.
- Assess universities' financial needs, and allocate and disburse grants for maintenance, development, and other purposes.
Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
Worship Rights on Parasnath Hill
Why in News?
After the Jharkhand High Court ordered a ban on non-veg food, animal harm, and tourism at Parasnath Hill, the Santhal group Marang Buru Sanvta Susaar Baisi (MBSSB) announced to continue its traditional hunting ritual, citing the hill’s religious importance to Adivasis.
Key Points
- About the Ritual:
- The symbolic hunt takes place in the forests of Marang Buru, where Santhals spend a night symbolically hunting (without killing animals), followed by a two-day tribal assembly in a nearby village.
- The event is used to address community-level matters and has long-standing religious value for the Adivasi community.
- The Court Order:
- The state High Court directed the State government to enforce a Union Environment Ministry ban on certain activities at Parasnath Hill.
- The hill was declared an eco-sensitive zone in 2019, and the Ministry's order prohibits non-vegetarian food, animal harm, and excessive tourism.
- The Ministry’s memorandum also halted the State government’s plans to promote religious eco-tourism in the area—an initiative strongly opposed by the Jain community.
- A Century-Old Dispute:
- The conflict over worship rights on Parasnath Hill (Marang Buru) between the Jain and Adivasi communities has persisted for over a century.
- The 1911 Census documented a legal case by a Swetambar Jain sect, which reached the Privy Council, where the customary rights of Adivasis were upheld.
Parasnath Hills
- Parasnath Hills are a range of hills located in Giridih district of Jharkhand.
- The highest peak is 1350 metres. It is one of the most important pilgrimage centre for Jains. They call it Sammed Sikhar.
- The hill is named after Parasnath, the 23rd Tirthankara.
- Twenty of Jain Tirthankaras attained salvation on this hill. For each of them there is a shrine (gumti or tuk) on the hill.
- Some of the temples on the hill are believed to be more than 2,000 years old.
- The Santhals call it Marang Buru, the hill of the deity. They celebrate a hunting festival on the full moon day in Baisakh (mid-April).
- Every year, thousands of Jains from across the world undertake the 27 km long trek of climbing the hills to reach the summit.
Santhal Tribe
- It is the third largest scheduled tribe in India after the Gonds and Bhils, known for their calm and peaceful nature. They originally led a nomadic life but settled in Chota Nagpur plateau and migrated to Santhal Parganas in Bihar and Odisha.
- They are located in Jharkhand, Odisha, and West Bengal, and are involved in cultivation, industrial labour, mining, and quarrying.
- They follow an autonomous tribal religion and worship nature at sacred groves. Their language is Santhali and they have their own script called ‘OL chiki’ is recognised as one of the scheduled languages in the Eighth Schedule.
- Their artforms like the Phuta Katcha pattern saree and dress are popular. They celebrate various festivals and rituals related to agriculture and worship. Santhal houses, known as 'Olah', are easily recognizable due to their large, neat, and attractive appearance, adorned with multi-coloured paintings on the exterior walls.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Uttar Pradesh Skill Development Mission (UPSDM)
Why in discussion?
Under Uttar Pradesh Skill Development Mission (UPSDM), the UP government signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Roorkee to provide world-class technical skills to the youth of the state .
Key Points
- About the MoU:
- Through this agreement , technical collaboration has been established between the State Government and IIT Roorkee with the aim of equipping the youth with cutting-edge technical skills .
- The youth will get the following facilities under the guidance of experts from IIT Roorkee :
- Advanced Technical Training
- Innovation-Driven Education
- Research opportunities
- Startup Support & Consulting
- This initiative will enable the youth to compete at the national and international level , thereby strengthening their employability.
Uttar Pradesh Skill Development Mission (UPSDM)
- Uttar Pradesh Skill Development Mission was established on September 13, 2013 as a society registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860 under the Department of Vocational Education & Skill Development, Government of Uttar Pradesh.
- A National Skill Development Policy was launched in 2009 with a target to skill 500 million people by 2022.
- Under the national scheme, the state of Uttar Pradesh aims to skill over 4 million youth by the end of the 12th Five Year Plan.
- UPSDM has been established to achieve this goal and provide employable skills to the youth of the state.
- It is essential to coordinate all skill development initiatives by leveraging the State Skill Development Policy.
- It empanelled private training partners besides government training partners to conduct skill development training.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
'AI Bharat @ MP' Workshop
Why in News?
A two-day workshop titled “AI Bharat @ MP” was organized in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh.
Key Points
- About the Workshop:
- It aimed to make governance more efficient, transparent and citizen-oriented through artificial intelligence, Aadhaar and digital innovations.
- The workshop was organised by Madhya Pradesh State Electronics Development Corporation (MPSEDC) and National e-Governance Division (NeGD) in collaboration with the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- In the technical sessions of the workshop, topics like Data Protection, Cyber Security, Digital Health (e-Sanjeevani), DIKSHA Platform and Digital Education were discussed.
- This workshop presented Madhya Pradesh as a model state of digital governance .
- Achievements of MP in Digital Infrastructure:
- Madhya Pradesh has become the first state in the country where SD-WAN enabled State Wide Area Network (SWAN) is operating at 2 Gbps speed.
- The state has its own data centre with 1 petabyte capacity, which ensures secure and quick operation of digital services.
- The State has become a leader in digital governance through digital innovations like 'Sampada 2.0' and end-to-end service automation.
- Policy and Innovation:
- The state government has issued policies and guidelines for sectors like AVGC (Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming & Comics), Drone Technology, Global Captive Centre (GCC) and Semiconductor Manufacturing.
- These efforts are likely to create new opportunities for industry, investment and employment in the state.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- AI is defined as the ability of machines and systems to acquire knowledge, apply it, and behave intelligently.
- The term "artificial intelligence" was first used by American computer scientist and cognitive scientist John McCarthy. He is considered the father of AI.
- It includes techniques like machine learning, deep learning, big data, neural networks, computer vision, large language models, etc.
- The ideal characteristic of artificial intelligence is the ability to perform and rationalize actions that have the best probability of achieving a specific goal.
e-Sanjeevani
- e-Sanjeevani is a telemedicine service between doctors in the country, providing an alternative to traditional face-to-face consultation through a digital platform.
- e-Sanjeevani is an important part of Ayushman Bharat Digital Health Mission and more than 45,000 Aabha numbers have been issued through e-Sanjeevani application.
- The ten leading states using it are: Andhra Pradesh, West Bengal, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Bihar, Telangana and Gujarat.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Malwa Festival
Why in News?
The Chief Minister of Madhya Pradesh participated in the Malwa Utsav organized at Lalbagh Complex, Indore from 6 to 12 May 2025.
Key Points
- About Malwa Utsav:
- It is a five-day cultural festival organised by Lok Sanskriti Manch.
- This festival has been organised regularly for the last 25 years.
- Objective:
- Preservation and propagation of folk culture and traditions.
- To provide a platform and market to local artists and craftsmen.
- To promote national integration and cultural exchange.
- Exhibition of Folk Arts and Handicrafts:
- In this festival, folk artists from different states of the country and different areas of Madhya Pradesh presented folk dance and music.
- Weavers and handicraft artists displayed weaving, clay and metal artefacts.
- Murals, Reza work, Batik prints, copper and brass statues, and tribal paintings were the main attractions of the festival.
Folk Dances of Madhya Pradesh
- Kathi : This is a dance performed by the Balai community, in which clothes decorated with peacock feathers and a bamboo 'kathi' are used. This dance is performed on the 'Dhak' instrument.
- Gangaur : In the month of Chaitra, women worship Goddess Parvati by dancing on clapping and thali. Its two forms – Thalaria and Thola are famous.
- Phaphriya : It is a group dance performed by men and women together to the sound of pungi.
- Madalya : In this, women dance at a fast pace with hand and foot movements to the beat of the drum.
- Ada-Khada : This dance is performed by women to the beat of drums on occasions like marriage, birth and death.
- Danda Dance : It is performed by men with a stick to the beats of drums and plates during the nights of Chaitra-Vaishakh.
- Matki : Women balance several matkis on their heads and dance in a circular motion to the beat of drums. Aada-Khada is one form of this.
- Rai : This dance performed by the Bedia tribe is in a conversational form based on makeup and social topics. Ram Sahay Pandey is its main artist.
- Saira : This dance is performed as a prayer to Lord Indra for rain by young men holding sticks accompanied by dholak and flute.
- Jawara : Women perform this dance while balancing a crop basket on their head, which shows the importance of crops.
Bihar Switch to Hindi
Buddha Purnima
Why in News?
Bihar Chief Minister highlights the importance of Lord Buddha's teachings and extends greetings on the occasion of Buddha Purnima.
Key Points
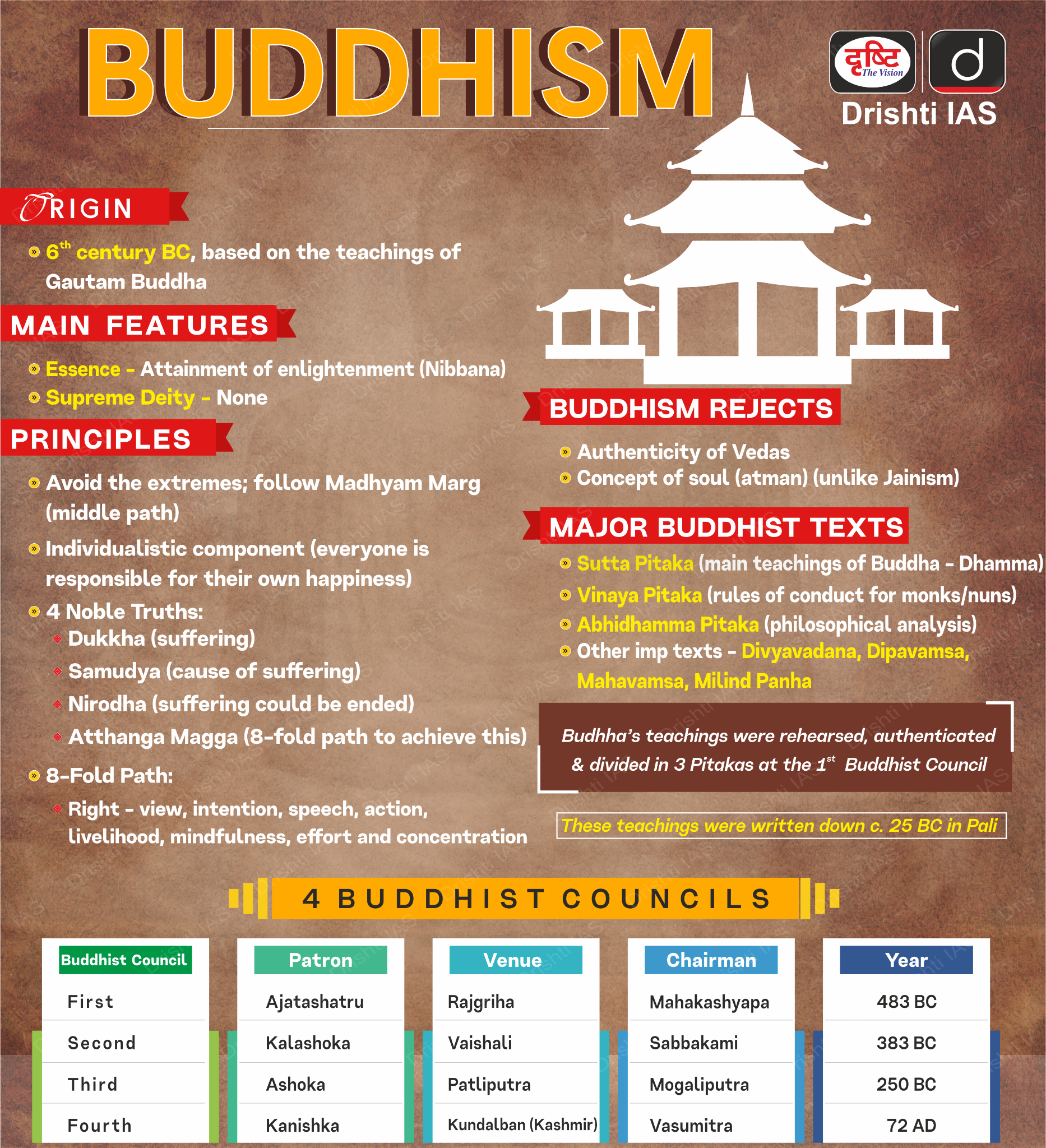
- About Gautam Buddha:
- Gautama Buddha, the founder of Buddhism, was born as Siddhartha Gautama in Lumbini around 563 BCE and belonged to the Shakya clan.
- Gautama attained bodhi (enlightenment) under a pipal tree at Bodh Gaya in Bihar.
- Buddha gave his first sermon at Sarnath near Varanasi in Uttar Pradesh. This event is known as Dharmachakra Pravartan (the turning of the wheel of law).
- He died in 483 BC at the age of 80 in Kushinagar, Uttar Pradesh. This event is known as Mahaparinirvana.
- He is revered as the eighth incarnation of Lord Vishnu in the Dashavatara, the ten principal avatars of the deity.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Maharana Pratap Jayanti
Why in News?
On 9th May 2025, the 485th birth anniversary of Maharana Pratap, one of the courageous and iconic warriors, was celebrated with reverence and honour across the country. 
Key Points
- About Maharana Pratap:
- Rana Pratap Singh , also known as Maharana Pratap, was born on 9 May 1540 in Kumbhalgarh, Rajasthan.
- He was the 13th king of Mewar and the eldest son of Udai Singh II.
- Maharana Udai Singh II ruled the Mewar kingdom and made Chittor his capital.
- Udai Singh II was also the founder of the city of Udaipur (Rajasthan).
- Battle of Haldighati:
- The Battle of Haldighati was fought in the year 1576 between Rana Pratap Singh of Mewar and Raja Man Singh of Amer , who was the general of the Mughal Emperor Akbar.
- Maharana Pratap fought bravely but was ultimately defeated by the Mughal army.
- It is believed that Maharana Pratap's loyal horse Chetak sacrificed his life while leaving the battlefield.
- Re-control:
- After 1579, the influence of the Mughals on Mewar decreased and Maharana Pratap re-established his dominance over western Mewar including Kumbhalgarh, Udaipur and Gogunda.
- During this period he also built a new capital, Chavand, near present-day Dungarpur.
- Death:
- Maharana Pratap died on 19 January 1597. After that, his son Rana Amar Singh ascended the throne and accepted the supremacy of Akbar's son Emperor Jahangir in the year 1614.





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan