Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Valley of Flowers
Why in News?
The Valley of Flowers in Uttarakhand officially opened to tourists on 1st June 2025, marking the start of the annual four-month visiting season.
Key Points
- About the Valley of Flowers: It is located in the Chamoli district of Uttarakhand and lies within the Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve.
- It spans over 87 sq km and lies at an altitude of 3,600 meters above sea level.
- Historical Background:
- It was introduced to the Western world in 1931 when British mountaineers Frank S. Smythe, Eric Shipton, and R.L. Holdsworth discovered it during their return from Mount Kamet.
- Smythe’s 1938 book, Valley of Flowers, brought it global recognition.
- It was introduced to the Western world in 1931 when British mountaineers Frank S. Smythe, Eric Shipton, and R.L. Holdsworth discovered it during their return from Mount Kamet.
- Flora and Fauna: The valley is famous for its wide variety of flowering plants, including orchids, poppies, primulas, marigolds, daisies, and anemones.
- Rare and sacred flowers like the brahmakamal, often offered in religious rituals, also bloom here.
- The valley is home to many medicinal plants and herbs used in traditional healing.
- Several wildlife species inhabit the region, such as the snow leopard, the Himalayan weasel, the black bear, the red fox, the gray langur, the flying squirrel and various species of butterflies including the lime butterfly.
- Natural Features: The valley offers breathtaking views of alpine meadows, cascading waterfalls, glacial streams, and thick forests.
- It lies in a unique transition zone between the Zanskar and Greater Himalaya mountain ranges.
- Conservation Efforts: Due to concerns over ecological damage, the valley was declared a National Park in 1982.
- In 1988, it became part of the Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve, and tourism was reintroduced gradually under strict controls.
- It was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2005, for its exceptional beauty and biodiversity.
- Cultural Significance: The valley holds spiritual importance in Hindu mythology and is traditionally inhabited by the Bhotiya tribe. Sacred flowers like the Brahmakamal are used in religious rituals.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Miss World 2025
Why in News?
Opal Suchata Chuangsri of Thailand was crowned Miss World 2025 during the grand finale of the 72nd Miss World pageant held at the HITEX Exhibition Centre in Hyderabad, Telangana on 31st May 2025.
Key Points
- About:
- It was a month-long celebration featuring 108 contestants from around the globe, including historical tours, cultural showcases, and advocacy campaigns led by the participants.
- The event was hosted by Miss World 2016 Stephanie Del Valle and Indian TV personality Sachiin Kumbhar.
- Format:
- Contestants advanced through several fast-track events, including the Head to Head Challenge, Top Model, Beauty with a Purpose, Talent, Sports, and Multimedia competitions.
- From the initial pool of 108 entrants, the competition was gradually narrowed down to the Top 40 quarterfinalists, then the Top 10 contestants from each continental group, followed by the Top 5, Top 2, and finally, one crowned winner.
- Winner:
- Opal Suchata Chuangsri, representing Thailand, won the Miss World 2025 crown.
- She was crowned by Krystyna Pyszková, (Czech Republic) Miss World 2024.
- Ethiopia's Hasset Dereje emerged as the first runner-up and Maja Klajda from Poland won the second runner-up title.
- Opal Suchata Chuangsri, representing Thailand, won the Miss World 2025 crown.
- Continental Queens: Winners were selected from each continent through a rapid-fire round:
- Miss Martinique – Americas and Caribbean
- Miss Ethiopia – Africa
- Miss Poland – Europe
- Miss Thailand – Asia and Oceania
- Other Highlights:
- Miss Indonesia Monica Kezia Sembiring won the Beauty with a Purpose Round for her project “Pipeline for Lifeline,” aimed at improving access to clean water and sanitation.
- Actor Sonu Sood was honored with the Miss World Humanitarian Award, presented by Rana Daggubati.
- India’s Participation:
- Nandini Gupta, Miss India 2025, secured a place as one of the four continental winners at the 72nd Miss World by excelling in the Top Model Challenge segment but was eliminated after reaching the Top 20.
Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
Jharkhand Demands Increased Tax Devolution for Development Needs
Why in News?
The Jharkhand government has urged the Sixteenth Finance Commission to increase the state’s share in central tax devolution from the current 41% to 50%, citing its economic contributions and unique developmental needs.
Key Points
- Higher Tax Devolution for Developmental Needs: Jharkhand, contributing significantly through mining and bearing its environmental and social costs, stressed the need for increased financial support to improve key sectors like agriculture, health, education, and livelihoods.
- The state highlighted its large farming-dependent population and potential for agricultural growth, calling for flexible fund usage to address local needs effectively.
- Issues Related to Mining Activities: The state emphasized planned land reclamation, proposing that mined land be returned after operations end. It also seeks the release of ₹1.40 lakh crore owed by mining companies operating in the region.
- State Budget and Welfare Initiatives: Jharkhand’s ₹1.45 lakh crore budget allocates ₹62,844 crore for social welfare targeting the poor, women, and vulnerable groups. ₹13,363 crore is dedicated to women’s financial support schemes, and ₹5,000 crore for free electricity to eligible residents.
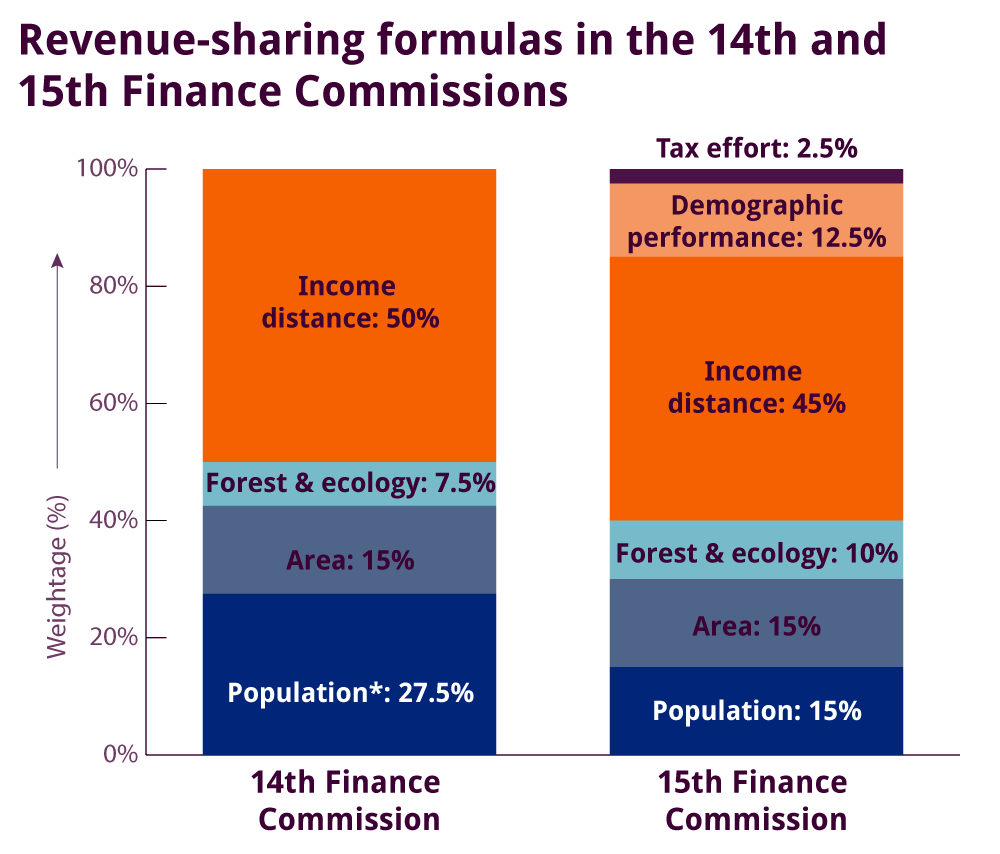
16th Finance Commission
- The 16th Finance Commission, established under Article 280 of the Indian Constitution, will cover the five-year period starting 1st April 2026.
- It is chaired by Dr. Arvind Panagariya, with members Ajay Narayan Jha, Annie George Mathew, Manoj Panda, and Soumya Kanti Ghosh (part-time).
- Ritvik Ranjan Pandey serves as Secretary.
- Role and Terms of Reference: The Finance Commission is a constitutional body formed every five years to maintain fiscal federalism and recommend:
- Tax revenue distribution between the Union and the States.
- Principles for grants-in-aid to revenue-deficient States.
- Support for local bodies (Panchayats and Municipalities).
- Review of disaster management financing under the Disaster Management Act, 2005.
- Measures to strengthen the Consolidated Fund of States.
- Importance:
- Ensures equitable resource allocation to address regional disparities.
- Supports grassroots governance and local development.
- Advises on fiscal discipline, expenditure efficiency, and public finance reforms.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
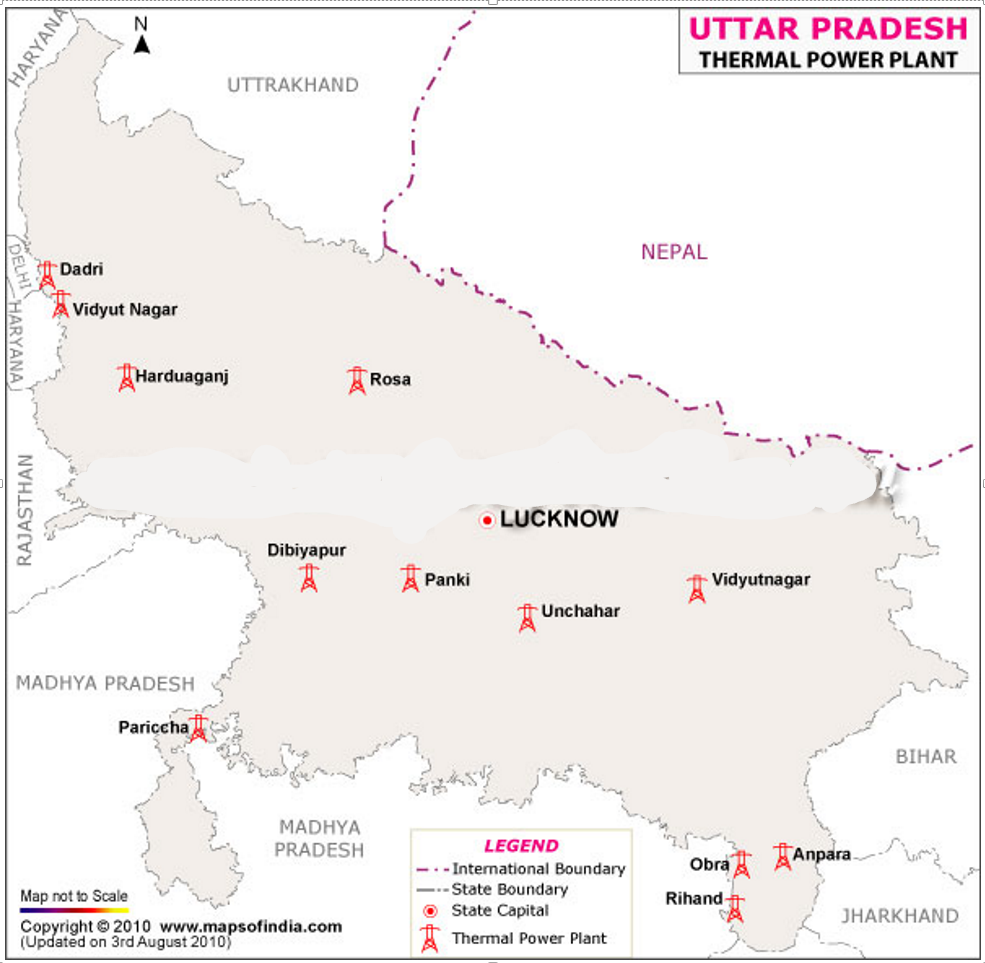
Ghatampur Thermal Power Project
Why in News?
The Prime Minister, on 30th May 2025, dedicated Unit-1 of the Ghatampur Thermal Power Project in Kanpur (U.P.) to the nation, marking a significant milestone in India’s energy sector.
Key Points
- About the Project:
- The Ghatampur Thermal Power Project has a total installed capacity of 1,980 MW, comprising three supercritical units of 660 MW each.
- The remaining two units are scheduled to be commissioned by the financial year 2025–26.
- It is being implemented by Neyveli Uttar Pradesh Power Limited (NUPPL), a joint venture between NLC India Limited and Uttar Pradesh Rajya Vidyut Utpadan Nigam Limited (UPRVUNL).
- The total project cost is estimated at ₹21,780.94 crore.
- The Ghatampur Thermal Power Project has a total installed capacity of 1,980 MW, comprising three supercritical units of 660 MW each.
- Power Allocation:
- A Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) has been signed to allocate 1,487.28 MW (75.12%) of the generated power to Uttar Pradesh and the remaining 492.72 MW (24.88%) is earmarked for Assam.
- Environmental Safeguards:
- The plant is equipped with Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) technology to reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions.
- Flue Gas Desulphurization (FGD) systems have been installed to control sulphur dioxide (SOx) emissions.
- The project will have a Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) system to ensure no water is discharged from the plant.
West Bengal Switch to Hindi
Sikari Utsav
Why in News?
South-west Bengal faces ongoing wildlife protection challenges, including the ritualistic hunting celebrated during the regional festival Sikari Utsav.
Key Points
- About Sikari Utsav:
- The event takes place during the dry season, specifically from March to May, across the districts of Jhargram, Paschim Medinipur, Bankura, Purulia, and Birbhum.
- During this period, thousands of villagers participate, joined by people from neighbouring districts and states, including Jharkhand, Odisha, and Bihar.
- The primary activity involves entering the forests to hunt small wildlife species, such as wild boars and wild hares.
- Issues:
- It harms wildlife populations in the short term and has long-term ecological consequences.
- Since the festival coincides with the peak season for forest fires, it exacerbates environmental damage.
- The vast, open forests in this region, located near human settlements, are easily accessible and thus vulnerable to exploitation, especially during festivals.
- The Forest Department has limited manpower, which hampers its ability to enforce conservation laws effectively, resulting in the continued allowance of destructive activities.
- Way Forward:
- Community-Based Forest Management: Building on the success of West Bengal’s Joint Forest Management (JFM) committees, it is essential to broaden this participatory model across more regions.
- Intensify Awareness and Education Campaigns: Shifting the narrative from exploitation to coexistence through dialogue and education will cultivate a shared commitment to protecting ecosystems for future generations.
- Enhance Law Enforcement and Infrastructure for Forest Protection: Strengthening legal frameworks, enforcing existing forest protection laws rigorously, and investing in infrastructure are necessary to curb destructive human activities such as encroachment and overexploitation.
- Foster Multi-Stakeholder Cooperation for Long-Term Sustainability: Collaborative action plans and continuous dialogue must prioritize ecological balance, ensuring that environmental protection remains a collective and sustained priority for the future.
Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
Dharavi Project Master Plan Approved
Why in News?
The Maharashtra government approved the master plan for the Dharavi redevelopment project, emphasizing that it should be developed in an environmentally friendly and integrated manner while preserving its original concept.
Key Points
- Dharavi Redevelopment Plan (DRP):
- The Dharavi Redevelopment Plan is a joint venture between the Adani Group and the Maharashtra government.
- The redevelopment plan aims for an integrated development approach encompassing residential, commercial, and industrial aspects.
- The redevelopment plan's floor space index of over 4 indicates a significant intensity of land use, emphasizing the multi-dimensional nature of the project.
- This project highlights the public-private partnership aspect in addressing urban redevelopment challenges.
- Concerns:
- Many residents have expressed concerns about the future of small-scale manufacturing units and informal industries, which form the economic backbone of Dharavi.
- Concerns have also been raised regarding the lack of public consultation and the absence of a clear rehabilitation roadmap.
- However, the government has emphasized that the top priority of the project should be the rehabilitation of local artisans and those running small-scale businesses.
- About Dharavi:
- Dharavi is the biggest slum cluster of Asia that lies on prime property right in the middle of Mumbai.
- It was founded in 1882 at the time of the British Raj.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Operation Shield
Why in News?
On 31st May, the Haryana authorities carried out a statewide civil defence exercise called “Operation Shield” to strengthen emergency preparedness and response capabilities.
Key Points
- Simulated Emergency Scenarios: The mock drills included scenes of volunteers acting as injured victims, firefighting operations, and emergency evacuations.
- The drills focused on scenarios like air raids, drone attacks, and other wartime emergencies to test response mechanisms.
- The exercise witnessed seamless coordination among various departments including Fire and Emergency Services, Police Forces, Health Departments, Disaster Management Authorities, Civil Defence, along with trained volunteers from National Service Scheme (NSS) and National Cadet Corps (NCC).
National Service Scheme (NSS)
- The NSS is a Central Sector Scheme of the Government of India, Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports, launched in 1969 with the objective of developing the personality and character of student youth through voluntary community service.
- The ideology of NSS is inspired by the ideals of Mahatma Gandhi. Its motto is “Not me but You.”
- The scheme provides opportunities for student youth in 11th and 12th classes at the +2 Board level, as well as students of technical institutions, undergraduate, and postgraduate colleges and universities across India to participate in various government-led community service activities and programmes.
National Cadet Corps (NCC)
- About: The NCC was formed in 1948 (on the recommendation of H. N. Kunzru Committee-1946), and has its roots in British era uniformed youth entities like University Corps or University Officer Training Corps.
- Its history can be traced back to the ‘University Corps’, which was created under the Indian Defence Act 1917 with an objective to make up for personnel shortage in the Indian Army.
- The NCC also expanded later on to include the Girls Division in 1949 to provide equal opportunities to women willing to serve the country's defences.
- NCC is the largest uniformed youth organisation in the world. It enrolls cadets at high school and college level and also awards certificates on completion of various phases.
- The NCC cadets receive basic military training at various levels and also have academic curriculum basics related to Armed forces and their functioning.
- Ministry: The NCC falls under the purview of the Ministry of Defence and is headed by a Director General of three-star military rank.






















.jpg)









.png)


.jpg)

 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan