International Relations
Unleash the Strategic Power of Indian Diaspora
- 08 Oct 2025
- 21 min read
This editorial is based on “ Don’t blame Indian-Americans for India’s diplomatic failures”, which was published in The Indian Express on 07/10/2025. The article points out that while the Indian-American diaspora has actively contributed to India’s interests through advocacy and leadership, the larger challenge lies in India’s own approach to diplomacy and narrative-building, which could benefit from greater strategic engagement and support for its diaspora community.
For Prelims: Indian Diaspora, Non-Resident Indians (NRIs), Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs), Overseas Citizens of India (OCI), Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD), Know India Programme (KIP), Operation Sindhu (2025), Operation Kaveri (2023, Sudan)
For Mains: Role of the Indian Diaspora in Shaping India’s Development and Global Influence, Key Challenges Currently Confronting the Indian Diaspora, Key Initiatives for the Indian Diaspora Globally
In today’s interconnected world, India’s diplomatic effectiveness hinges not only on its economic clout but also on its ability to strategically engage with global narratives. Despite the Indian diaspora’s rising influence, India faces significant challenges in leveraging this asset fully, largely because “India has never learned to tell its own story,” whereas other nations like Pakistan effectively mobilise and cultivate diaspora networks to shape international policy. This underscores the urgent need for more professional and sophisticated diplomacy that complements diaspora potential with robust statecraft.
What is the Contemporary Status and Influence of the ‘Indian Diaspora’?
- About: The Indian Diaspora refers to people of Indian origin who live outside the territorial boundaries of India, either temporarily or permanently, while maintaining cultural, social, or emotional ties to their homeland.
- Types:
- Non-Resident Indians (NRIs): Indian citizens residing abroad for more than 182 days in a financial year but retaining Indian citizenship.
- Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs): Individuals who are foreign citizens but can trace their ancestry or heritage to India.
- Overseas Citizens of India (OCI): Persons granted a special residency status, allowing lifelong visa-free travel to India and certain rights, but not full citizenship.
- In 2015, the Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs) and OCI categories were merged to streamline documentation and benefits.
- Types:
- Historical Evolution:
- Ancient Movements: Indian traders, craftsmen, and religious leaders migrated to Southeast Asia, Africa, the Middle East, and Europe centuries ago.
- Colonial Era: Large-scale migration during British rule sent Indians as indentured labourers to sugarcane plantations in Mauritius, Fiji, Trinidad, South Africa, and the Caribbean.
- Post-Independence: Skilled professionals moved to developed nations (USA, UK, Canada, Australia), while workers migrated to Gulf countries under contract labour arrangements.
- Scale and Diversity:
- According to UNFPA 2023, India leads the world in emigration, hosting a massive diaspora across the globe.
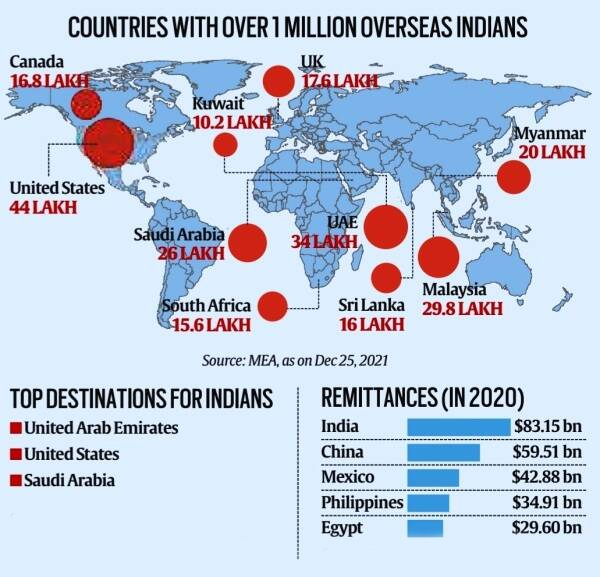
- As of May 2024, the total number of overseas Indians worldwide is approximately 35.42 million, according to India’s Ministry of External Affairs.
- They are spread across more than 200 countries, representing diverse regions, languages, religions, and caste backgrounds.
What is the Role of the Indian Diaspora in Shaping India’s Development and Global Influence?
- Economic Support Through Remittances: India has consistently remained the world’s largest recipient of remittances for over a decade.
- India received a record $135.46 billion in diaspora remittances in FY25, a 14% increase from the previous year.
- These remittances cover 47% of India’s $287 billion merchandise trade deficit, acting as a stabilizing force for India’s external finances.
- Remittances alone contribute a significant share to states like Kerala, where they account for about 20% of the state's GDP.
- With 35.42 million overseas Indians concentrated mainly in 10 countries, including the US, UAE, Malaysia, and Canada, the diaspora wields considerable economic influence globally.
- Diaspora Investments Driving India’s Economy: Diaspora members actively invest in India’s stock markets and businesses, facilitated by government schemes such as NRE accounts and double-taxation treaties.
- From April to September 2024, investments via NRI deposit schemes nearly doubled to $7.8 billion, fueling India’s economic development and entrepreneurship.
- Skilled Workforce and Knowledge Exchange: The Indian diaspora includes a large pool of highly skilled professionals who contribute globally and bring back expertise through return migration or collaborations, significantly impacting sectors like IT, pharmaceuticals, and academia.
- Indian immigrants have significantly impacted global business, with over 20 CEOs of Indian origin leading Fortune 500 companies as of 2024, including Sundar Pichai (Google & Alphabet) and Satya Nadella (Microsoft).
- Political Influence: Diaspora groups supported key initiatives like the US-India Civil Nuclear Agreement (2008) and Justice Dalveer Bhandari’s ICJ re-election (2017).
- Leaders of Indian origin, such as Vivek Ramaswamy (USA), Leo Varadkar (Ireland), and Antonio Costa (Portugal), strengthen diplomatic ties with host nations.
- Diaspora lobbying has promoted India’s permanent UN Security Council membership, shaping global perceptions.
- Cultural Diplomacy: The diaspora serves as cultural ambassadors, promoting Indian heritage, festivals, cuisine, yoga, classical arts, and languages abroad.
- Key initiatives include Pravasi Bharatiya Divas, Promotion of Cultural Ties with Diaspora (PCTD), Know India Programme (KIP), and Festival of India events organised by Indian missions worldwide.
- Observed on June 21, International Yoga Day was declared by the UN in 2014 following India's proposal to promote yoga’s holistic benefits worldwide.
- Diaspora communities in countries like Mauritius, Trinidad, Fiji, the UK, and the US celebrate Diwali, Holi, Eid, and organise Indian classical music and dance festivals, preserving cultural identity.
- Key initiatives include Pravasi Bharatiya Divas, Promotion of Cultural Ties with Diaspora (PCTD), Know India Programme (KIP), and Festival of India events organised by Indian missions worldwide.
What are the Key Challenges Currently Confronting the Indian Diaspora?
- Economic Vulnerability of Low-skilled Workers: Indian migrant workers in Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries face significant job insecurity due to volatile oil prices and evolving labour regulations.
- For example, the oil price dip in 2024 led to layoffs and non-renewal of contracts for many low-wage workers in Saudi Arabia and the UAE, disrupting remittance flows temporarily.
- The “Kafala” system in Gulf countries still exposes workers to exploitative practices like confiscation of passports, restricting their movement and livelihood security.
- Brain Drain and Talent Loss: India continues to witness a steady outflow of skilled professionals, as a significant number of medical graduates and engineering postgraduates migrate abroad in pursuit of better remuneration, research opportunities, and advanced career prospects.
- According to the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA), as of January 1, 2024, over 11.6 lakh Indian students were enrolled in higher education institutions abroad, highlighting India’s growing global academic footprint and educational mobility.
- While recent years have seen a modest rise in return migration due to changing global economic conditions and immigration norms, the continued outflow of skilled professionals poses a long-term challenge to India’s innovation ecosystem, particularly in high-tech sectors like biotechnology and information technology.
- Racism and Xenophobia: Recent years have witnessed a surge in hate crimes against Indians, particularly in countries like Australia, the US, and parts of Europe.
- In 2024, multiple attacks on Indian students in Australian universities raised concerns about safety and social inclusion.
- These incidents dampen diaspora morale and raise challenges for Indian consulates to manage community welfare abroad effectively.
- Restrictive Immigration and Visa Policies: Countries including the US, UK, and Canada tightened visa norms in 2023-25, restricting skilled worker and student visas, impacting Indian professionals’ mobility.
- The US has raised the H-1B visa fee to $100,000 from $1,000–$5,000 (effective 21 Sept 2025) to curb misuse and prioritise high-skilled, high-paid workers, impacting Indian tech professionals, who made up 71% of recipients in 2024, in terms of costs, mobility, and earnings.
- Limited Political Participation and Voting Rights: NRIs remain constrained by the requirement of physical presence in India for voting, despite repeated calls for postal or online voting alternatives, which have been delayed.
- This limits diaspora influence on Indian elections and policy formulation, affecting their interests, causing a democratic deficit for millions of Indians living overseas.
- Gaps in Policy Framework and Data Management: The absence of a unified and updated database on overseas Indians hampers targeted welfare and diplomatic engagement.
- Though portals like e-Migrate exist, their scattered nature and bureaucratic red tape deter effective grievance redressal.
What Key Initiatives has the Indian Government implemented for the Indian Diaspora Globally?
- Overseas Citizenship of India (OCI) Scheme, 2005: Provides lifelong visa-free travel to India for Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs), allowing them to live, work, own property, and invest in India without restrictions.
- This scheme strengthens ties by facilitating ease of access to India for the diaspora.
- Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD): An annual event since 2003, it celebrates the contributions of the Indian diaspora to India’s development.
- The biennial convention, such as the 18th PBD held in Odisha in 2025, themed “Diaspora’s Contribution to a Viksit Bharat,” offers a platform for dialogue, cultural exchange, and showcasing investment opportunities in Indian states.
- Pravasi Bharatiya Samman Award: The highest honour conferred on outstanding NRIs, PIOs, or diaspora organisations for exemplary contributions in various fields, encouraging further engagement with India.
- Pravasi Bharatiya Bima Yojana (PBBY), 2006: A mandatory insurance scheme for Indian migrant workers under the Emigration Check Required (ECR) category, providing coverage against accidental death or disability during overseas employment.
- Know India Programme (KIP): A flagship initiative aimed at young diaspora members (aged 18-30), familiarising them with India’s culture, development, and opportunities through a three-week orientation and immersion program.
- Visiting Advanced Joint Research (VAJRA) Faculty Scheme: Invites overseas scientists to collaborate with Indian institutions, promoting high-quality research in cutting-edge scientific fields.
- Promotion of Cultural Ties with Diaspora (PCTD) Scheme: Supports Indian missions abroad to organise cultural programs promoting India’s heritage and strengthening the diaspora’s cultural identity overseas.
- Voting Rights for NRIs: Through the Representation of the People (Amendment) Act, 2010, NRIs are allowed to vote in Indian elections, enhancing their political participation in India’s democratic process.
- Madad Portal: Provides a grievance redressal mechanism for Indians abroad, offering legal assistance, emergency repatriation, and timely support to distressed citizens.
- Recent Evacuation Programs :
- Operation Sindhu (2025): Successfully evacuated over 4,400 nationals from Iran and Israel amid escalating hostilities, including 3,500 from Iran and 800 from Israel.
- Operation Kaveri (2023, Sudan): Evacuated more than 3,000 Indians during Sudan’s conflict, including professionals and families, leveraging Indian Navy and Air Force support.
- Operation Ajay (2023, Israel): Over 1,300 Indians evacuated in response to intensified violence, showcasing rapid crisis response capabilities.
- Operation Ganga (2022): During the Russia-Ukraine war, India airlifted over 18,000 nationals, mostly students, through neighbouring countries using military and commercial flights.
What Additional Measures Should be Adopted to Empower the Indian Diaspora?
- Establish a Unified, Updated Diaspora Database: To address data inconsistencies, the government should create a unified, real-time diaspora database linking the Ministry of External Affairs, immigration, tax, and consular data.
- This would ensure better targeting and implementation of welfare schemes.
- The Standing Committee’s 2025 report advocated for a national migration database and streamlined policy measures to better integrate the diaspora’s aspirations and protect vulnerable groups.
- Enact a Diaspora Protection Act: Codify rights of OCIs and NRIs to create a legal framework ensuring their welfare and grievance redressal.
- This would resolve current legal fragmentation and eligibility ambiguities noted in recent reports.
- The Act could draw from diaspora protection laws in countries like Israel or China.
- Facilitate Political Inclusion through Voting Reforms: Implement postal or online voting for NRIs, as recommended by the Election Commission and parliamentary committees.
- This would enhance democratic participation without the physical presence barrier.
- Expand Skill Development and Pre-Departure Orientation: Scale up training under the Pravasi Kaushal Vikas Yojana and Pre-Departure Orientation Training.
- Equip overseas Indian workers with skills attuned to host country workplace norms, reducing vulnerability and exploitation.
- Enhance Consular and Legal Support Services: Indian embassies should establish multi-lingual legal aid desks and robust grievance redressal mechanisms.
- This addresses language barriers and improves protection for vulnerable diaspora members, especially in the Gulf.
- Promote Diaspora Investment with Tax Incentives and Simplified Processes: Offer targeted tax benefits, green bonds, and easier compliance for diaspora investments.
- Showcase investment opportunities during Pravasi Bharatiya Divas and state-specific diaspora programs.
- This fosters economic linkage and supports India’s growth goals.
- Institutionalise Regular Impact Audits and Policy Reviews: Conduct annual audits of migration MoUs, diaspora schemes, and consular services.
- Use transparent metrics to evaluate outcomes and refine strategies, following recommendations from the 2025 Lok Sabha Report.
- Fostering Retention, Return, and Growth of Talent: India needs a comprehensive strategy to counter brain drain and shift towards talent retention and attraction by transforming systemic weaknesses into attractive opportunities for its global talent.
- This involves not merely welcoming back the diaspora, but proactively upgrading the domestic ecosystem with global-standard research infrastructure and competitive incentives.
- Targeted re-entry schemes, combined with a focus on improving the quality of life and minimising bureaucratic hurdles, aim to foster a dynamic environment where India's brightest minds can find fulfilling growth and contribute directly to the nation's development goals.
Conclusion:
Prime Minister Modi describes the Indian diaspora as “India’s ambassadors,” emphasising their unique role in advancing both soft power and hard power. Through contributions to democracy promotion, social harmony, and economic development, the diaspora serves as a vital bridge between India and the world. Embracing this community with robust engagement, guided by the Ministry of External Affairs’ 4Cs framework of Care, Connect, Celebrate, and Contribute, will accelerate India’s journey toward becoming a truly global and developed nation.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Across the globe, India’s diaspora serves as a bridge linking domestic goals with international influence. How can India harness its diaspora to boost economy, diplomacy, and soft power while bridging policy gaps? |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the Indian Diaspora and its key categories?
Ans: Indians living abroad with ties to India, including NRIs (retain citizenship), PIOs (foreign citizens of Indian ancestry), and OCIs (special residency, lifelong visa-free travel).
2. How does the Indian Diaspora contribute to India’s economy?
Ans: Through remittances, investments, and entrepreneurship, supporting GDP, regional economies, and macro-economic stability. FY25 remittances: $135.46 billion.
3. What challenges currently affect the Indian Diaspora?
Ans: Economic vulnerability, brain drain, cultural identity issues, racism, restrictive immigration, and policy/data gaps.
4. What major government initiatives support the Indian Diaspora?
Ans: OCI Scheme, Pravasi Bharatiya Divas, Samman Award, PBBY, Swarna Pravas, Know India Programme, PCTD, NRI voting rights, evacuation operations (Sindhu, Ganga, Kaveri, Ajay).
5. What measures are suggested to further empower the Indian Diaspora?
Ans: Unified database, Diaspora Protection Act, postal/online voting, skill training, consular support, investment incentives, policy audits, guided by MEA’s 4Cs.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. In the context of India, which of the following factors is/are contributor/contributors to reducing the risk of a currency crisis? (2019)
- The foreign currency earnings of India’s IT sector
- Increasing the government expenditure
- Remittances from Indians abroad
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. 'The Indian diaspora has a decisive role to play in the politics and economy of America and European Countries’. Comment with examples. (2020)