Important Facts For Prelims
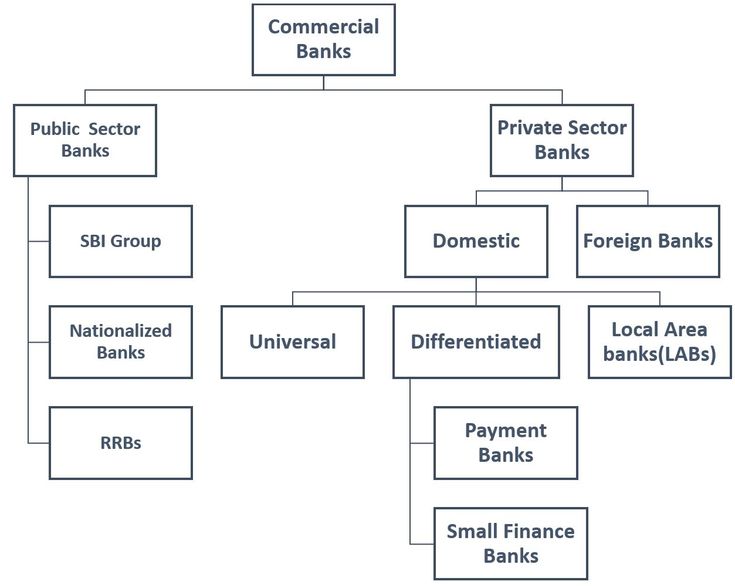
Small Finance Banks (SFBs)
- 31 Oct 2025
- 5 min read
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has returned Jana Small Finance Bank’s (SFB) application for transition into a universal bank, citing non-fulfilment of eligibility criteria outlined under its 2024 guidelines for SFBs.
What is a Small Finance Bank?
- About: SFBs are private institutions created to enhance financial inclusion in India. They offer basic banking facilities, including deposits and credit, to unserved and underserved groups like small farmers, micro industries, and informal sector enterprises.
- Origin: Announced in Union Budget 2014–15 to boost financial inclusion, the idea stems from the 2009 Raghuram Rajan Committee’s A Hundred Small Steps report.
- Eligibility Criteria: Resident individuals/professionals with 10 years of experience in banking and finance.
- NBFCs, Micro Finance Institutions (MFIs), and Local Area Banks (LABs) owned and controlled by residents can convert into SFBs.
- Only resident-controlled entities can promote SFBs.
- Capital Requirements: For Primary (Urban) Co-operative Banks transiting into SFBs, initial requirement of net worth shall be ₹100 crore, which will have to be increased to ₹200 crore.
- Minimum paid-up voting equity capital / net worth requirement shall be ₹200 crore.
- Promoter’s initial contribution: 40%, to be reduced to 26% within 12 years.
- Foreign investment permitted as in other private sector banks.
- Regulatory and Prudential Norms: SFBs are full-fledged banks, unlike Payments Banks, and follow RBI’s prudential norms such as CRR and SLR maintenance.
- Regulated under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 and supervised by the RBI.
- Operational Mandates: Must allocate 75% of Adjusted Net Bank Credit (ANBC) to Priority Sector Lending (PSL).
- At least 50% of loans should be of value up to Rs 25 lakh.
- No geographical restrictions, but 25% of branches must be in unbanked rural centres.
- Preference to banks setting up in under-banked states/districts.
- Permissible Activities: It can distribute mutual fund units, insurance, and pension products with RBI and sectoral regulator approval.
- May become a Category II Authorised Dealer in foreign exchange.
- Cannot establish subsidiaries for non-banking financial activities.
RBI's 2024 Guidelines for Converting SFBs into Universal Banks
- Eligible Applicants: Only listed Small Finance Banks (SFBs) are eligible to apply for conversion into a Universal Bank.
- Financial Requirements: Must have a minimum net worth of Rs 1,000 crore, scheduled bank status, and a profitable operational record for at least five years.
- Asset Quality Criteria: Must maintain gross NPAs below 3% and net NPAs below 1% consistently for the previous two years.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a Small Finance Bank?
SFBs are private institutions created to enhance financial inclusion in India. They offer basic banking facilities, including deposits and credit, to unserved and underserved groups like small farmers, micro industries, and informal sector enterprises.
2. When were SFBs introduced and under whose recommendation?
Introduced in Union Budget 2014–15, based on the 2009 Raghuram Rajan Committee Report – “A Hundred Small Steps.”
3. What are the key eligibility criteria for an SFB to convert into a universal bank as per RBI's 2024 guidelines?
The SFB must be listed, have a minimum net worth of ₹1,000 crore, a profitable track record of 5 years, and maintain gross NPAs <3% and net NPAs <1% for two consecutive years.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. What is the purpose of setting up of Small Finance Banks (SFBs) in India? (2017)
- To supply credit to small business units
- To supply credit to small and marginal farmers
- To encourage young entrepreneurs to set up business particularly in rural areas.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)