Facts for UPSC Mains
Skill Impact Bonds
- 06 Aug 2025
- 8 min read
Why in News?
As India strives for economic growth and inclusive development, innovative models like the Skill Impact Bond (SIB) are emerging to address key challenges in skilling and employment, especially among marginalized communities and women.
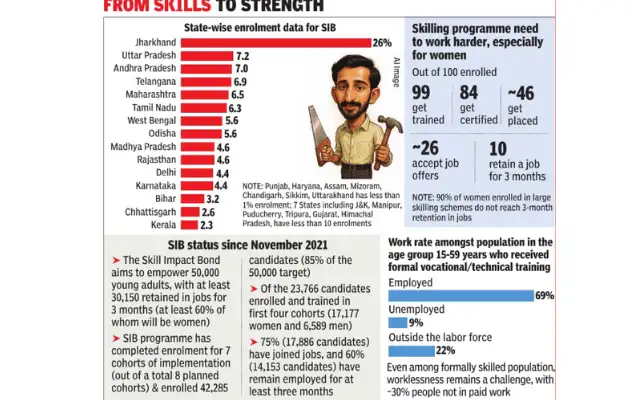
- The Skill Impact Bond (SIB) 2025 report reveals that Jharkhand has the highest share of enrolled trainees, with women continuing to dominate enrolment in the apparel sector; however, gender-based pay disparities persist, despite improvements in female retention and placement rates.
What is the Skill Impact Bond (SIB)?
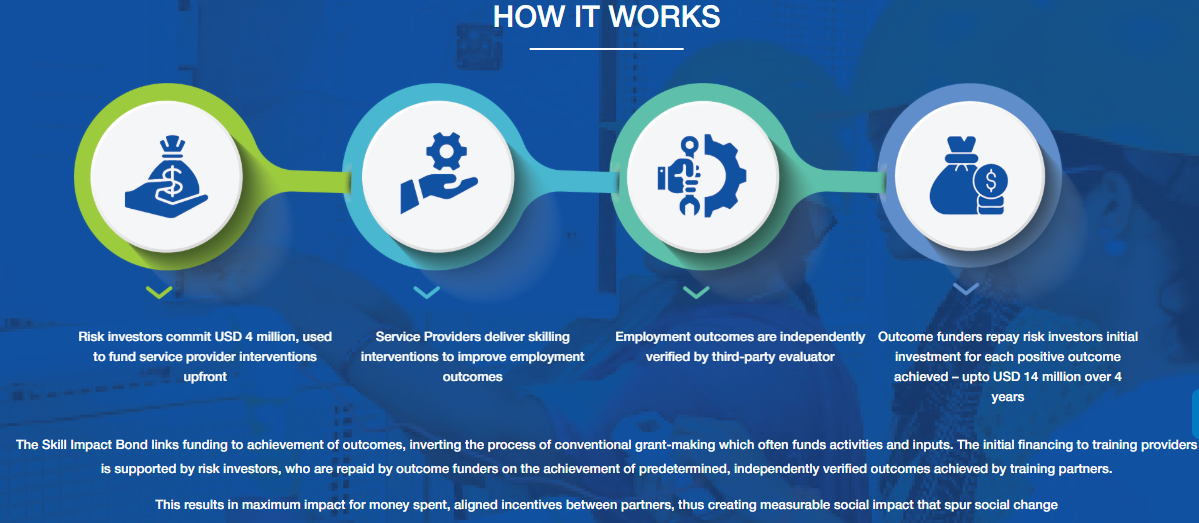
- About: SIB is India’s first Development Impact Bond (DIB), launched in 2021 focused on skills training and job placement.
- It shifts focus from enrollment to outcomes like placement and retention. It uses private-sector funding to address social and development challenges.
- Objective: To skill 50,000 youth, with 60% women, especially from marginalised and rural backgrounds, and ensure at least 30,150 retain jobs for 3+ months.
- Key Highlights of the SIB Report 2025:
- Top States: Jharkhand (27%), UP, Maharashtra, Odisha, and Telangana had highest enrollments.
- Popular Sectors:
- Women: Mainly trained in apparel, with rising numbers in retail, IT-enabled services (ITeS), and BFSI (banking, financial services, and insurance)
- Men: Moving from construction to sectors like automotive and telecom.
- Women-Led Skilling: Over 72% of 23,700+ trainees were women from vulnerable backgrounds. Female certification rate reached 92%, and job placement was 81%. Self-employment among women rose from 6% to 14%.
- Better Job Outcomes: 75% of all trainees got jobs, and 60% stayed employed for over 3 months—above national average. Female employment increased from 35% to 48%.
- Gender Pay Gap: Men earned more (Rs 12,400–15,700) than women (Rs 11,500–13,000) despite similar job outcomes.
What is the Status of Skill Development in India?
- Low Employability: As per India Skills Report 2024, only 51.25% of assessed young people in India possessed the necessary skills to be employable.
- Low Formal Training: As per the Economic Survey 2023–24, only 4.4% of youth are formally skilled, and 16.6% are informally trained.
- Skill Gaps in Industry: According to ManpowerGroup's (US-based MNC) 2025 Global Talent Shortage Survey, 75% of global employers are struggling to find skilled workers.
- India has a 60%-73% demand-supply gap in key roles such as ML engineer, data scientist, DevOps engineer, and data architect.
- Underemployment: As per Economic Survey 2024–25, over 50% of graduates and 44% of postgraduates are in low-skill jobs, indicating inefficient workforce utilisation.
- Limited Women Participation: In India, women constitute 40% of STEM students but only 14-27% of STEM professionals, according to the Ministry of Science and Technology.
What are the Key Challenges Hindering Skill Development in India?
- Inconsistent Quality & Infrastructure Gaps: Many ITIs, especially in rural areas, lack trained instructors and modern equipment, leading to low training quality and employability.
- Industry Disconnect & Skill Mismatch: Skilling schemes like PMKVY & Skill India focus on syllabus completion over practical relevance.
- Key sectors like AI, cybersecurity, and green energy are often underserved.
- Low Private Sector Role & Rural Exclusion: Limited private sector participation due to red tape, low incentives, and weak academia-industry links.
- Despite Skill India Digital Hub (SIDH), skilling remains urban-focused, sidelining the 90% informal workforce. Just 10% of rural workers receive formal skill training (WEF).
Key Skill Development Schemes and Initiatives
- Skill India Mission
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY)
- Pradhan Mantri National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (PM-NAPS)
- India Skills Accelerator (ISA)
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Kendras (PMKK)
- PM Vishwakarma Yojana
- SANKALP (Skills Acquisition and Knowledge Awareness for Livelihood Promotion)
- STRIVE (Skill Strengthening for Industrial Value Enhancement)
- Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDU-GKY)
- Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL)
What Measures Should be Taken to Reform India’s Skilling Ecosystem?
- Inclusive Rural Skilling: Launch a Rural Skilling and Livelihood Mission focused on agri-tech, food processing, and crafts. Use mobile centers, village hubs, and digital literacy programs.
- Future-Ready & Digital Skilling: Align curriculum with Industry 4.0, green jobs, and digital economy.
- Sector Skill Councils (SSCs) to co-design courses with MSMEs and gig platforms.
- Expand Skill India Digital Hub with AI-based multilingual content and 5G-enabled hubs in Tier-2/3 cities.
- Education Integration & Women’s Skilling: Introduce vocational training from school level under NEP 2020 and link with National Credit Framework.
- Promote women’s skilling in STEM, finance, and gig roles through flexible training, digital access, childcare, grants, and mentorship.
- Monitoring, Soft Skills & Accountability: Use AI-driven dashboards, outcome-based funding, geo-tagging, biometric attendance, and third-party audits to ensure accountability.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the significance of the Skill Impact Bond (SIB) initiative in reimagining India’s skilling ecosystem. How does it promote gender empowerment and innovation in outcome-based financing? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana, consider the following statements: (2018)
- It is the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- It, among other things, will also impart training in soft skills, entrepreneurship, and financial and digital literacy.
- It aims to align the competencies of the unregulated workforce of the country to the National Skill Qualification Framework.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. “Demographic Dividend in India will remain only theoretical unless our manpower becomes more educated, aware, skilled and creative.” What measures have been taken by the government to enhance the capacity of our population to be more productive and employable? (2016)
Q: “Earn while you learn" scheme needs to be strengthened to make vocational education and skill training meaningful.” Comment (2021)