Rapid Fire
Review of Project Elephant
- 28 Jun 2025
- 2 min read
The Union Environment Ministry reviewed key initiatives under Project Elephant (1992) , highlighting the completion of Phase-I of the synchronized elephant population estimation in Northeastern states.
- In another development, the National Board for Wildlife committee recommended the inclusion of the Sloth bear and Gharial in the Species Recovery Programme.
Key Highlights of Project Elephant Review
- Mortality Mitigation Measures: Railway tracks were surveyed to identify high-risk zones for mitigating elephant-train collisions, which have resulted in 73 elephant deaths between 2019 and 2024.
- Genetic Profiling & Conservation: Created a genetic profile of captive elephants.
- Conflict Management: Regional action plans to prevent human-elephant conflict in Southern and Northeastern India by protecting elephant corridors.
Elephants
- About: Elephants, India's National Heritage Animal, are matriarchal and live in female-led groups.
- As keystone species and ecosystem engineers, they maintain forest health by dispersing seeds and creating water access for other species.
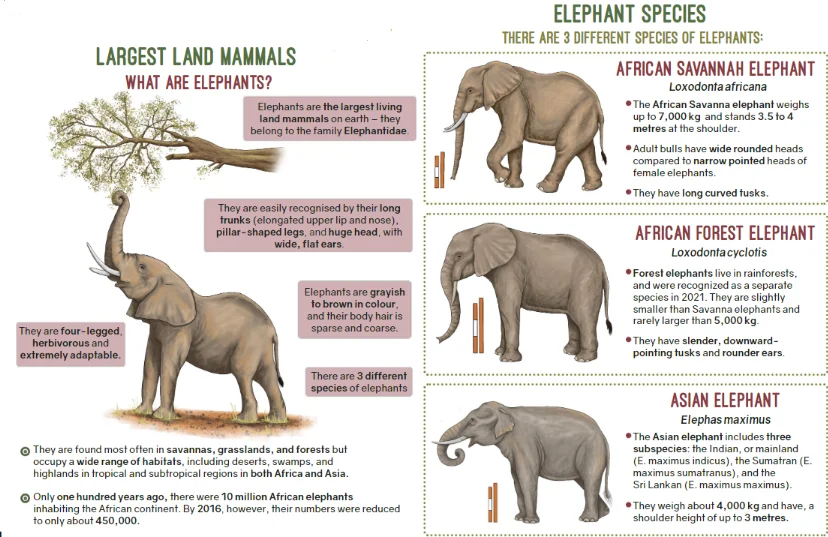
- Species:
- Asian Elephant (Elephas maximus)
- African Elephants:
- Savannah Elephant (Loxodonta africana)
- Forest Elephant (Loxodonta cyclotis)
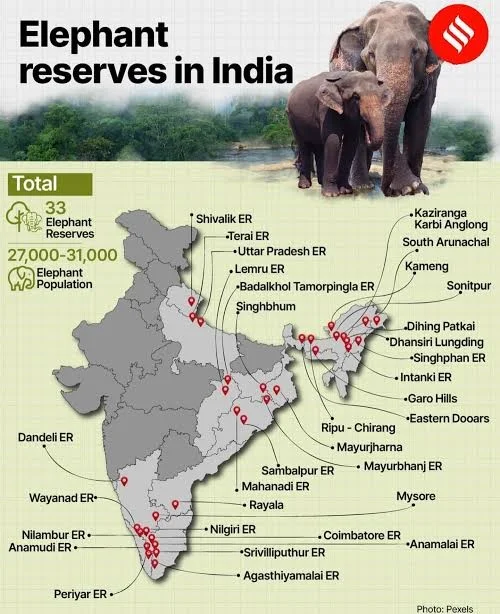
- Population in India: Indian elephants (Elephas maximus indicus), a subspecies of Asian elephants, account for around 60% of the global Asian elephant population.
- As per the 2017 census, India hosts approximately 29,964 elephants.
- Karnataka recorded the highest elephant population, followed by Assam and Kerala.
- In terms of protected areas, Sathyamangalam forest division has the highest number of elephants.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Endangered
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
- CITES: Appendix I
- Key Initiatives:
| Read More: Elephant Poaching in Tamil Nadu |