Important Facts For Prelims
RBI’s Recommendations on Liquidity Management Framework
- 09 Aug 2025
- 6 min read
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) Internal Working Group (IWG) has submitted its recommendations to improve the efficiency and predictability of the Liquidity Management Framework (LMF), which has been in operation since February 2020.
What is RBI's Liquidity Management Framework (LMF)?
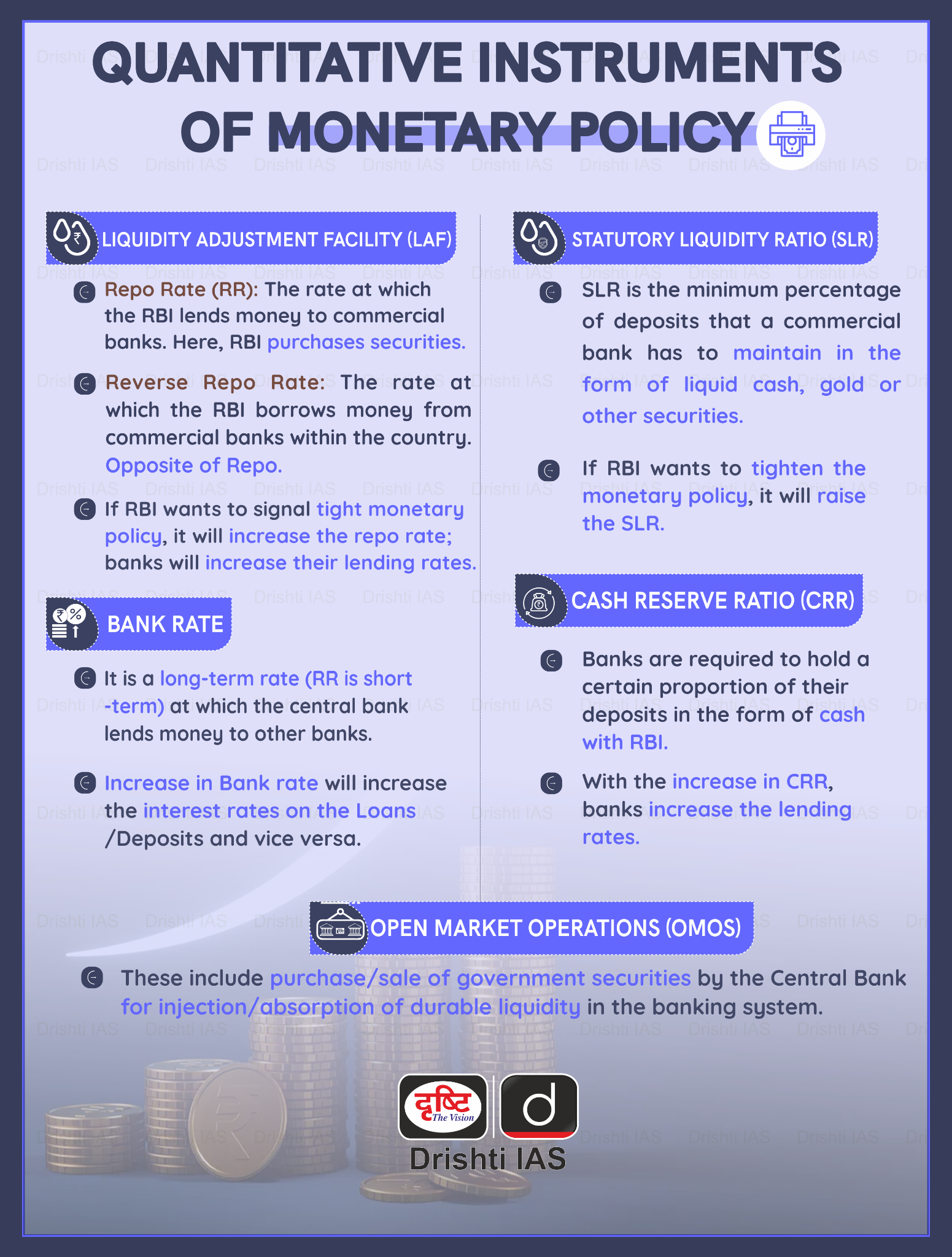
- About: The LMF is essentially the toolkit the RBI uses to manage the amount of cash in the banking system, helping steer short-term interest rates and ensuring smooth monetary policy transmission.
- Core Mechanism: At LMF core, it relies on the Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) that is the repo and reverse repo mechanism through which RBI injects or absorbs liquidity as needed.
- This framework typically operates with a "corridor system," where the policy repo rate sits in the middle. The overnight Weighted Average Call Rate (WACR) serves as the key operating target for monetary policy.
- Other Tools in LMF: The LMF also includes other tools like Open Market Operations (OMO), Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR), and Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) for longer-term and structural liquidity adjustments.
Recommendations of RBI on Liquidity Management Framework (LMF)
- WACR as the Operating Target: IWG recommends continuing to use the overnight WACR as the operating target for monetary policy.
- Rationale: WACR has shown a high correlation with other overnight collateralized money market rates, making it an effective tool for transmitting monetary policy signals.
- It remains a reliable instrument for ensuring smooth transmission of rates across different segments of the money market.
- Rationale: WACR has shown a high correlation with other overnight collateralized money market rates, making it an effective tool for transmitting monetary policy signals.
- Discontinue the 14-day VRR/VRRR Auctions: 14-day Variable Rate Repo (VRR) and Variable Rate Reverse Repo (VRRR) auctions should no longer be the primary operations for managing transient liquidity.
- Instead, the RBI should manage transient liquidity primarily through 7-day repo/reverse repo operations and other operations with tenors ranging from overnight to 14 days.
- Rationale: 14-day VRR/VRRR auctions have seen lower participation, with banks preferring shorter-term tools like the Standing Deposit Facility (SDF).
- Shorter-term operations are more effective in managing liquidity needs without causing dislocations in the market.
- Advance Notice for Repo/Reverse Repo Operations: The RBI should provide at least one day’s advance notice for conducting repo/reverse repo operations.
- IWG recommends, if required, the RBI may conduct same-day repo/reverse repo operations in response to evolving liquidity conditions.
- Rationale: Advance notice reduces market uncertainty and helps smooth money market rates.
- Minimum CRR Requirement: The RBI should continue to enforce the 90% daily minimum requirement for maintaining the CRR.
- Rationale: This requirement ensures that banks maintain sufficient reserves, thereby preventing liquidity shortfalls.
Key Terms Related to RBI's LMF
- Weighted Average Call Rate (WACR): It is the average interest rate at which banks borrow and lend money to each other for one day (overnight) in the call money market, weighted by the volume of transactions.
- It’s the RBI’s main operating target for monetary policy to signal short-term interest rates.
- Variable Rate Repo (VRR): It is an RBI tool used to manage short-term liquidity. Unlike the fixed repo, where the rate is pre-set, VRR uses an auction mechanism to determine the lending rate based on market demand.
- Variable Rate Reverse Repo (VRRR): It is a monetary policy tool used by the RBI to absorb excess liquidity through auctions, where banks bid at variable interest rates to place short-term deposits with the RBI and earn interest in return.
- Unlike the fixed reverse repo, VRRR rates are set via auctions, letting market forces decide and helping RBI absorb excess liquidity more effectively.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. If the RBI decides to adopt an expansionist monetary policy, which of the following would it not do? (2020)
- Cut and optimize the Statutory Liquidity Ratio
- Increase the Marginal Standing Facility Rate
- Cut the Bank Rate and Repo Rate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q.Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)? (2017)
- It decides the RBI’s benchmark interest rates.
- It is a 12-member body including the Governor of RBI and is reconstituted every year.
- It functions under the chairmanship of the Union Finance Minister.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Ans: (a)