Agriculture
Mission for Cotton Productivity
- 29 Jul 2025
- 10 min read
For Prelims: Mission for Cotton Productivity, Textile Vision 2030, "5F" approach, Bt (Bacillusthuringiensis) cotton, Bollgard-II,PM MITRA Scheme ,Cotton Corporation of India (CCI),Digital Agriculture Mission 2021–25,Cott-Ally Mobile App
For Mains: Need of the Mission for Cotton Productivity, Government initiatives for the Development of Cotton Sector.
Why in News?
To strengthen India’s textile value chain and enhance global competitiveness, the Government has launched the ‘Mission for Cotton Productivity’ in line with the Vision 2030 for the textile industry.
- Textile Vision 2030 for India aims at positioning India as a global textiles manufacturing hub by building a USD 250 billion textile industry and achieving USD 100 billion in global textile exports by 2030.
What is the Mission for Cotton Productivity?
- About: It is a five-year initiative launched by the Government of India in the Union Budget 2025-26 to significantly enhance cotton production in the country.
- It will provide scientific and technological support to cotton farmers, aligning with the Government's 5F vision- Farm to fibre, fibre to factory, factory to fashion, fashion to foreign for the textile sector.
- It seeks to increase farmers' incomes while ensuring a consistent supply of high-quality cotton, vital for revitalizing India's traditional textile industry.
- The Department of Agricultural Research & Education (DARE) is the nodal agency for implementing the mission, with the Ministry of Textiles as a key partner.
- Key Objectives:
- Enhance cotton productivity by adopting advanced scientific methods and developing climate-smart, pest-resistant, and high-yielding varieties, including Extra Long Staple (ELS) cotton.
- ELS cotton is known for its long fibers, superior strength, softness, and durability.
- Utilize advanced breeding techniques and biotechnology tools to improve fibre quality.
- Equip farmers with cutting-edge technology to build resilience against climatic and pest-related challenges.
- Enhance cotton productivity by adopting advanced scientific methods and developing climate-smart, pest-resistant, and high-yielding varieties, including Extra Long Staple (ELS) cotton.
What are the Reasons Driving the Need for Mission for Cotton Productivity?
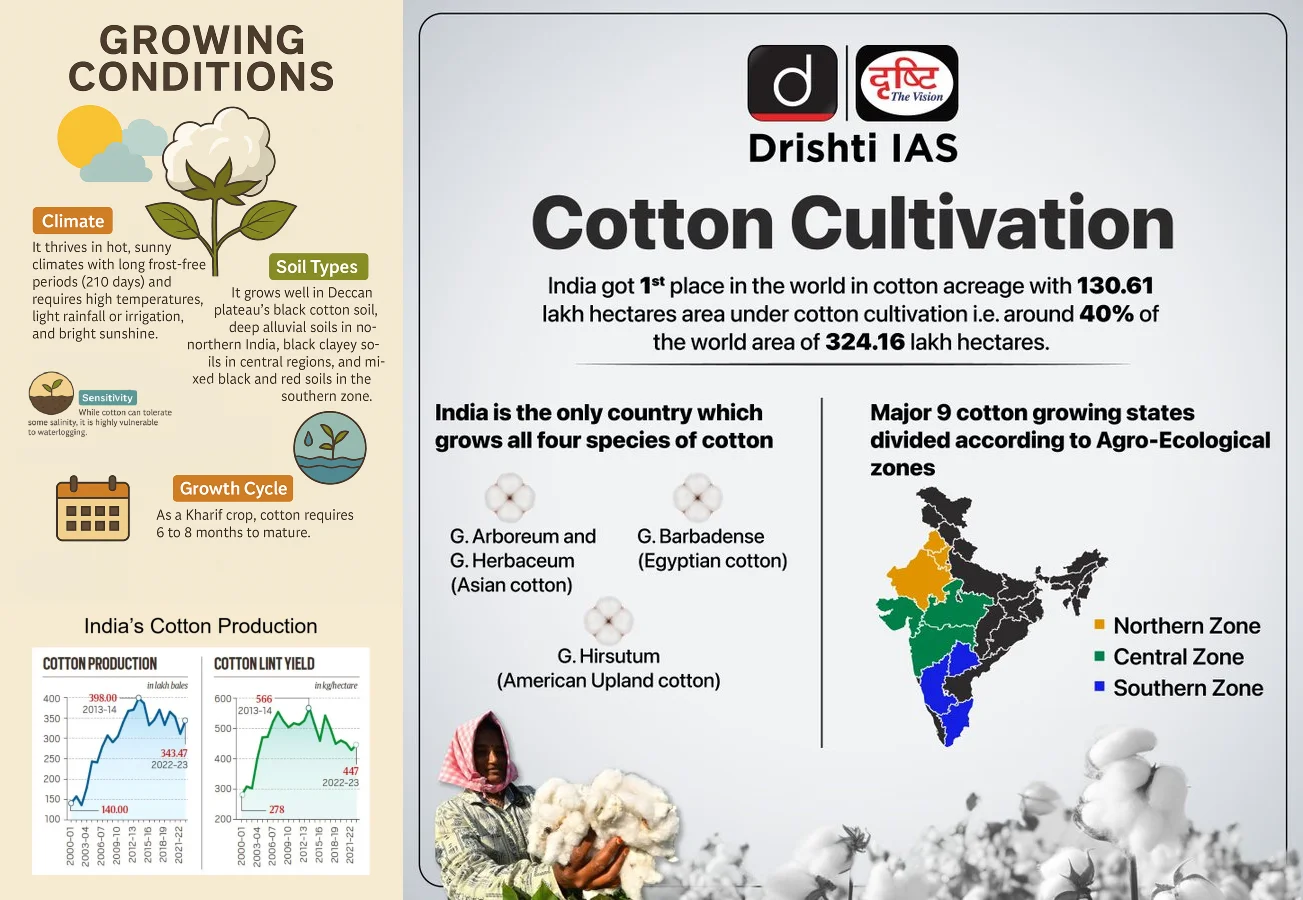
- Low Productivity: India ranks 1st globally in cotton acreage, with 130.61 lakh hectares under cultivation, accounting for 40% of the world’s total cotton area (324.16 lakh hectares).
- However, in terms of productivity, India stands 39th in the world, with an average yield of just 447 kg/ha.
- Rising Dependence on Imports: Cotton imports surged from USD 518.4 million in 2023–24 to USD 1.04 billion in 2024–25, while exports fell from USD 729.4 million to USD 660.5 million.
- Stagnation after Success: Despite the success of Bt (Bacillus thuringiensis) cotton and Bollgard-II technologies, India has not approved any new genetically modified (GM) cotton variants since 2006.
- Infestation: The decline in cotton production is mainly due to the increased infestation of pink bollworm (PBW).
- Initially, Bt cotton offered effective pest control, but over time, PBW developed resistance to Bt proteins.
- Missed Opportunities in Global Markets: Countries like the US and Brazil, with robust biotech adoption, are capturing the export space once dominated by India.
What are the Key Factors that Influence Cotton Cultivation in India?
- About Cotton: Cotton is a fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll around its seeds.
- In northern India, cotton is planted between April and May, while in the southern regions, the season is delayed due to monsoon patterns.
- Production: India leads the world in cotton acreage, accounting for around 40% of global cotton cultivation. The major cotton-producing regions in India are:
- India ranks second globally in cotton production, with an estimated output of 343.47 lakh bales (5.84 MMT) in 2022-23, contributing to 23.83% of global cotton production.
- India ranks 39th in global cotton yield, lagging behind countries like the USA, China, and Brazil.
- India is the second-largest cotton consumer globally, accounting for 22.24% of world consumption in 2023. Less than 10% of India’s cotton consumption is imported by the textile industry.
- Key Factors Influencing its Cultivation:
- Cotton can tolerate temperatures up to 43°C but temperatures below 21°C are detrimental.
- Cotton requires 210 frost-free days and 50 to 100 cm of rainfall for optimal growth.
- Warm days and cool nights with large diurnal temperature variations during the fruiting period promote better boll and fiber development.
- Cotton is grown in various soil types, including well-drained deep alluvial soils in the northern region, black clayey soils in the central region, and black and mixed soils in the southern zone.
- Cotton is semi-tolerant to salinity and sensitive to waterlogging, preferring light, well-drained soils that retain moisture.
India’s Initiatives For Development of the Cotton Sector
What Steps are Needed to Make India Self-reliant in Cotton?
- Accelerate R&D and Biotech Approvals : Fast-track approval of next-generation GM cotton (Bt 3.0, herbicide-tolerant traits, RNAi technology) to combat pink bollworm (PBW) resistance.
- Brazil and the US have adopted advanced biotech traits, boosting yields beyond 1,500 kg/ha.
- Promote Extra Long Staple (ELS) Cotton: Premium MSP, contract farming models, and cluster-based approaches are essential to boost ELS cotton adoption and enhance export competitiveness.
- Agricultural Export Policy (2018) emphasized production of export-oriented varieties.
- Integrated Pest and Farm Management : Scale up Integrated Pest Management (IPM) and area-wide PBW eradication using pheromone traps, sterile male techniques, and crop rotation.
- ICAR-CICR’s PBW management protocols have shown success in Maharashtra.
- Enhance Market and Export Competitiveness: Brand “Kasturi Cotton India” to promote premium quality and sustainability in global markets.
- Set up cotton quality testing hubs and encourage cluster-based textile parks (PM-MITRA).
- Digital Cotton Ecosystem : AI-driven pest alerts, remote sensing for yield monitoring, and blockchain for traceability can modernize the cotton value chain.
- Digital Agriculture Mission 2021–25 advocates the use of emerging technologies in agriculture.
- Climate-Smart Cotton Cultivation : Adopt micro-irrigation, organic farming, and precision nutrient management to improve yields and lower input costs.
- Ashok Dalwai Committee recommends climate-resilient practices to address water stress.
Conclusion:
If implemented with urgency and scientific rigour, the Mission can lift yields, cut import dependence, revive exports, raise farmer incomes, and green the cotton value chain, directly advancing SDG‑2 (Zero Hunger & productivity), SDG‑8 (Decent Work & growth), SDG‑9 (Innovation).
|
Drishti Mains Question: Mission for Cotton Productivity is a strategic initiative to boost India's textile value chain.Discuss the key objectives and implementation strategy of this mission in the context of Textile Vision 2030. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Which of the following activities constitute real sector in the economy? (2022)
- Farmers harvesting their crops
- Textile mills converting raw cotton into fabrics
- A commercial bank lending money to a trading company.
- A corporate body issuing Rupee Denominated Bonds overseas.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (a)
Mains:
Q. Analyse the factors for highly decentralized cotton textile industry in India. (2013)