Facts for UPSC Mains
Jal Jeevan Mission
- 21 Aug 2025
- 5 min read
Why in News?
On 15th August 2025, the 6th anniversary of the Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) was observed, showcasing its impact on 15 crore households with tap water access.
What is the Jal Jeevan Mission?
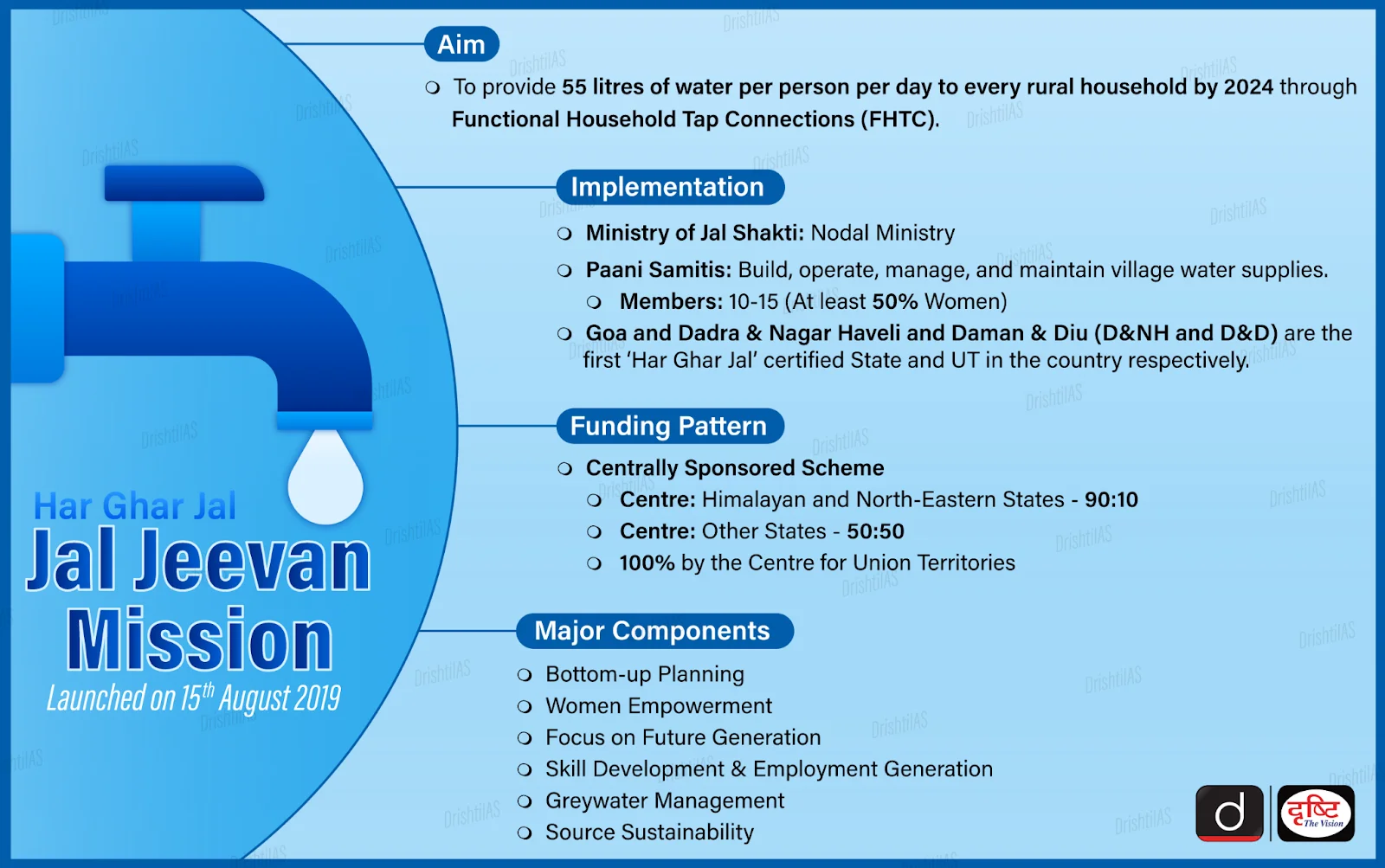
About:
- Launched on 15th August 2019, the Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) aims to provide tap water to every rural household by 2024 (extended till 2028), targeting 55 liters per person per day. It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme, implemented by the Ministry of Jal Shakti.
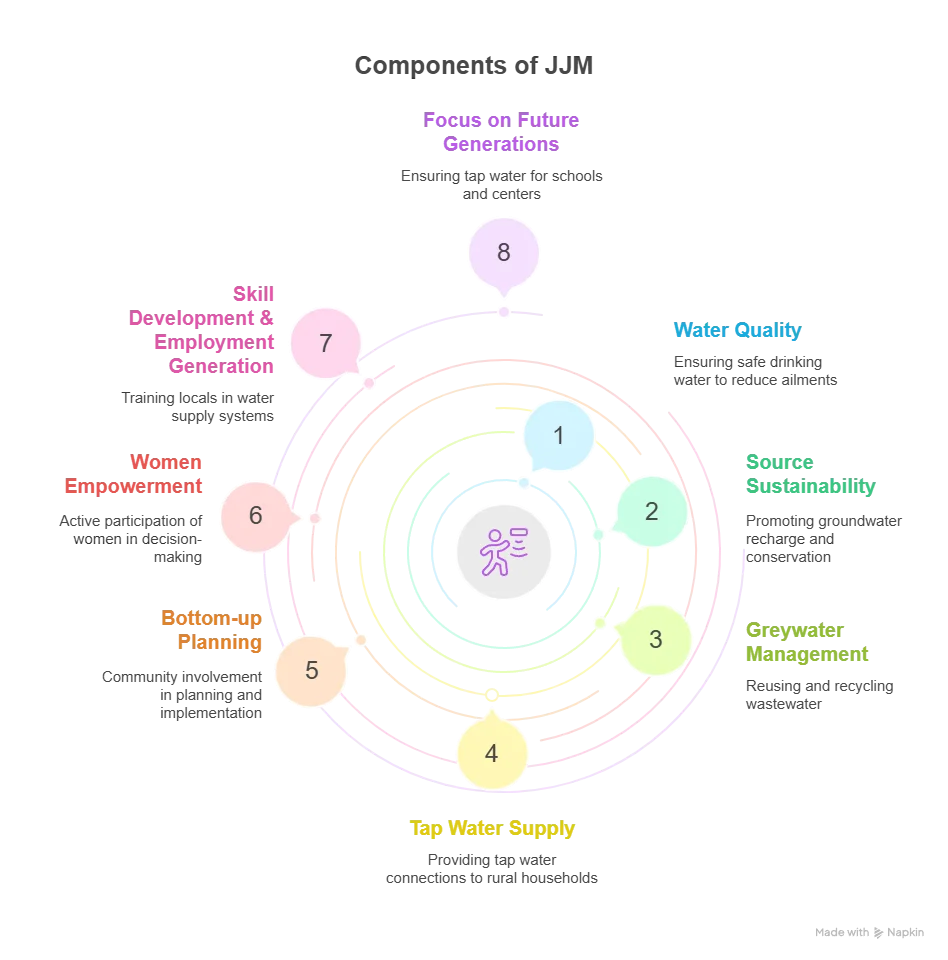
Objectives:
Mnemonic: TAP
- T – Target Every Rural Household: Provide Functional Household Tap Connections (FHTC) to all rural households.
- A – Areas of Priority: Focus on quality-affected, drought-prone, desert regions, and Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana (SAGY) villages.
- P – Public Places: Ensure taps in schools, Anganwadi centers, gram panchayats, and community buildings.
Features:
Mnemonic: WATER
- W- Women and Weaker Sections: Ensure 50% representation of women in committees like VWSC (Village Water And Sanitation Committee) and Pani Samitis.
- A- Awareness and Stakeholder Involvement: Janandolan for water, encouraging voluntary contributions like shramdaan.
- T - Technological Interventions: JJM-IMIS (Integrated Management Information System), real-time Dashboards, IoT-based sensor solutions for water supply.
- E - Empowerment through Education: Train 5 individuals, preferably women, per village on water quality testing.
- R - Rural Focus: Shift from ‘habitations’ to ‘households’ for decentralized, demand-driven, community-managed water supply.
What are the Key Challenges Affecting the Functioning of the JJM?
Mnemonic: GAPS
- G- Gaps in Data: Concerns over unreliable data making it difficult to address rural water supply issues. Over 12,000 rural habitations face contamination from iron, nitrate, salinity, and heavy metals.
- A- Absence of Infrastructure Quality: A parliamentary standing committee highlighted that post-pipeline public infrastructure restoration is substandard in many States and UTs.
- P- Poor Maintenance Planning: Only 20 states have comprehensive repair and maintenance policies by mid-2025.
- S- Sluggish Execution: Slow implementation of critical actions and projects, affecting the mission’s progress.
What Key Actions Can Enhance the Functioning of the JJM?
Mnemonic: REPAIR
- R- Revise Infrastructure Quality: Enforce restoration clauses, link contractor payments to verified quality, and adopt integrated planning. Ensure high-quality infrastructure and accountability in water supply projects.
- E- Ensure Data Authenticity: Mandate third-party audits, use geotagging, and create a public dashboard for transparency. Improve data credibility and ensure effective tracking of JJM progress.
- P- Performance-based Funding: Deploy task forces in lagging states, link funding to performance. Tie funding to states' progress to enhance accountability and speed up execution.
- A- Awareness & Testing: Ensure safe piped water, mandatory testing by gram panchayats, and launch an awareness drive. Raise public awareness on water safety while ensuring regular testing.
- I- Integrate Financial Reforms: Revise Rs 12,000 SBM-G incentive and integrate JJM with rainwater harvesting & Atal Bhujal Yojana. Strengthen financial support and integrate water conservation initiatives.
- R- Repair & Maintenance Planning: Ensure a nationwide repair and maintenance policy, with regular reviews. Prevent disruptions and ensure long-term sustainability of water systems.
Did You Know?
- Drinking water is a state subject and the power to plan, approve and implement drinking water supply schemes is vested in the State Government.
- In 2019, only 3.23 crore rural households (17%) had tap water; by 2025, coverage rose to 15+ crore households (80%).
|
Drishti Mains Question: Examine the financial and social implications of inadequate rural water supply and suggest measures to address them. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. What are the salient features of the Jal Shakti Abhiyan launched by the Government of India for water conservation and water security? (2020)
Q. What is water stress? How and why does it differ regionally in India? (2019)