Indian Economy
India's First National Policy on Geothermal Energy
- 27 Oct 2025
- 8 min read
For Prelims: Renewable Energy, Geothermal Power, 500-Gw Non-Fossil, Solar Power, Small Hydro Power, Biomass Energy, Grid Infrastructure, Green Hydrogen , Transmission Lines
For Mains: Significance of Boosting Renewable Energy Capacity, Significance of Geothermal Energy for India
Why in News?
The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has launched India’s first National Policy on Geothermal Energy 2025, aiming to tap India’s vast but underutilized geothermal potential to advance the nation’s Net Zero 2070 commitment, ensure energy security, and diversify its renewable energy mix.
What are the Key Features of the National Geothermal Energy Policy 2025?
- Broad Scope of Application: The policy encompasses all major aspects of geothermal energy development including:
- Geothermal Resource Assessment
- Power Production Systems
- Direct-use Applications
- Ground (Geothermal) Source Heat Pumps (GSHP)
- Utilization of abandoned oil and gas wells for geothermal energy extraction is encouraged.
- Extraction of valuable mineral by-products like silica, borax, cesium, and lithium will be regulated under the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act (MMDR Act),1957 with applicable royalties.
- Promotion of Emerging Tech: It also promotes emerging and innovative technologies such as:
- Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS)
- Advanced Geothermal Systems (AGS)
- Geothermal energy storage
- Offshore geothermal wells
- Geothermal Resource Data Repository: Establishment of a comprehensive geothermal resource data repository through inter-ministerial collaboration with agencies such as the Ministry of Mines, Ministry of Earth Sciences, Geological Survey of India (GSI), and National Data Repository (NDR).
- Permission for resource assessment surveys will be granted to developers for R&D and feasibility studies.
- Fiscal & Financial Support: Under the Renewable Energy Research and Technology Development Programme (RE-RTD):
- Up to 100% financial support for government and non-profit research institutions.
- Up to 70% support for private sector entities including start-ups and manufacturing units.
- Additional support mechanisms:
- Inclusion under the Indian Carbon Credit Trading Scheme.
- Waiver of open access charges.
- Eligibility under Renewable Purchase Obligations (RPOs).
- State-Level Guidelines: State/UT governments will have the authority to issue:
- Exploration leases (valid for 3–5 years)
- Development leases for power generation or direct-use (valid for up to 30 years)
- Establishment of a single-window clearance mechanism through designated state nodal agencies.
What is Geothermal Energy?
- About: Geothermal energy refers to the heat derived from the Earth’s interior, which can be used for heating buildings, and generating electricity.
- It is considered a renewable energy source because the Earth continuously produces heat within its core.
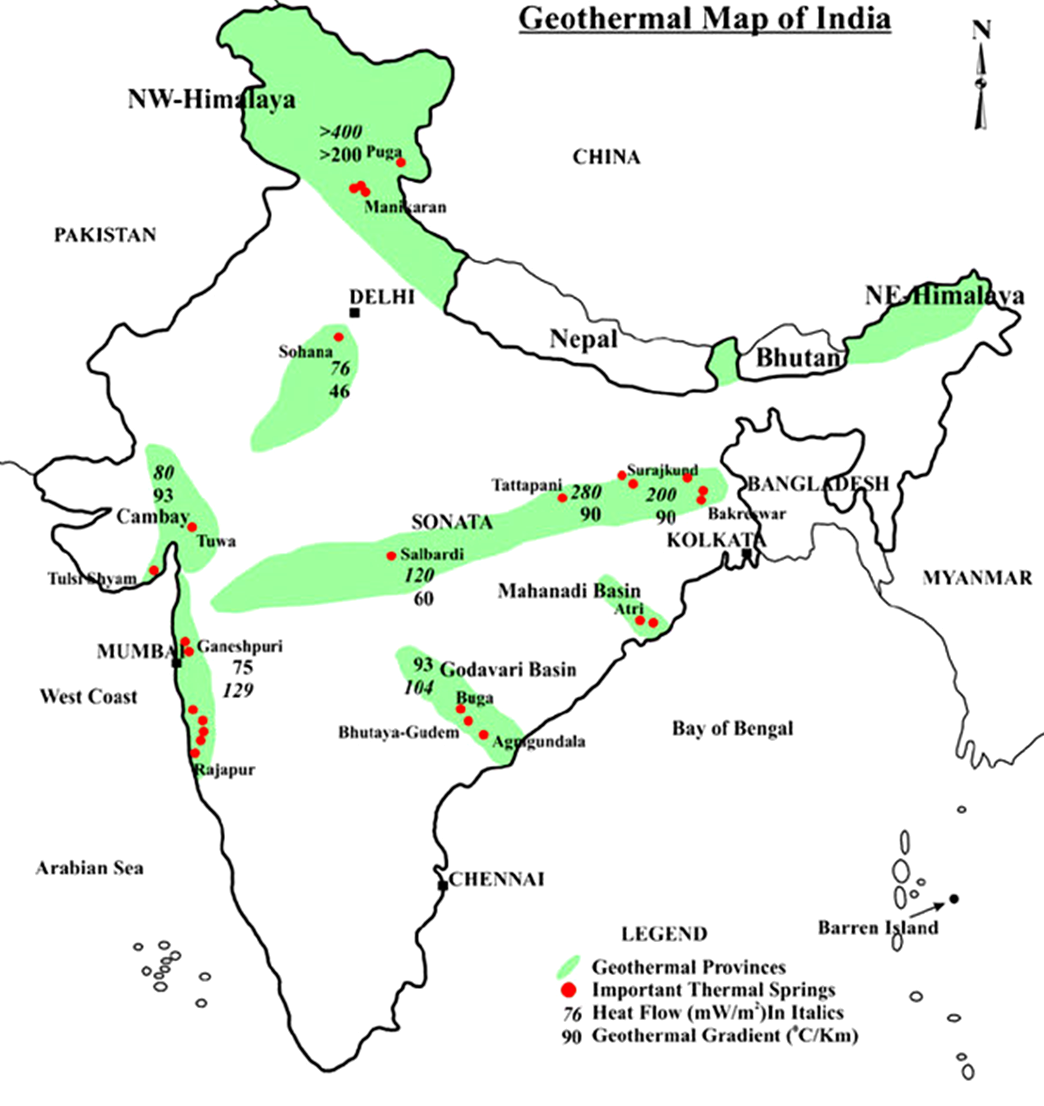
- India’s Geothermal Potential:
- India’s geothermal potential-spread across 381 hot springs and 10 geothermal provinces including Ladakh(Puga valley), Himachal Pradesh, Gujarat, Odisha, and Chhattisgarh.
- A potential of about 10,600 MW of geothermal power has been estimated in the country.
- Globally, geothermal energy contributes 15.4 GW (2019), led by the U.S., Indonesia, and the Philippines.
- Sources:
- Deep reservoirs: Hot water or steam found deep within the Earth is accessed through drilling.
- Surface reservoirs: Geothermal reservoirs located near the surface, especially in western U.S., Alaska, and Hawaii, are more easily accessible.
- Shallow ground: The shallow layers of the Earth maintain a constant temperature (50–60°F), which can be used for direct heating and cooling applications.
- Benefits:
- Renewable Source: With proper management, the rate of energy extraction can be balanced with the natural heat recharge rate of the reservoir.
- Continuous Supply: Geothermal power plants can operate 24×7, providing a consistent energy supply unaffected by weather conditions.
- Small Land Footprint: Geothermal plants occupy less land area per GWh compared to coal, solar, or wind energy installations.
- Less Water Consumption: Additionally, geothermal systems consume less water than most conventional energy sources.
- Disadvantages/issues of Geothermal Energy:
- If improperly harnessed, geothermal projects can lead to pollutant release.
- Incorrect drilling may release hazardous gases and minerals trapped deep inside the Earth.
- Higher capital costs, techno-economic viability issue due to remote location.
What is the Significance of the National Geothermal Energy Policy 2025?
- Facilitates baseload renewable power generation, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- The policy significantly boosts geothermal energy adoption by offering long-term concessional loans, Sovereign Green Bonds, and Viability Gap Funding (VGF), alongside fiscal incentives like GST/import duty exemptions and tax holidays, thereby enhancing project viability and attracting private investment.
- Supports remote Himalayan and Northeastern regions with clean heating and power.
- Encourages industrial decarbonization by reusing existing oil infrastructure.
- Strengthens India’s position in global renewable innovation alongside nations like Germany and Iceland.
- Complements national initiatives such as the National Green Hydrogen Mission and the RE-RTD Programme for renewable R&D.
|
Drishti Mains Question Q. Discuss the significance of India’s National Geothermal Energy Policy (2025) in advancing the country’s Net Zero 2070 goals and ensuring energy security. |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. What is the main objective of India’s National Geothermal Energy Policy (2025)?
The policy aims to harness geothermal potential to achieve Net Zero 2070, enhance energy security, and diversify India’s renewable energy mix.
Q. Which sectors will benefit from the geothermal policy?
It covers electricity generation, heating/cooling for buildings, industrial use, agriculture, aquaculture, and tourism, making it a multi-sectoral renewable initiative.
Q. Why is geothermal energy important for India’s energy future?
Geothermal provides 24×7 baseload renewable power with low CO₂ emissions, and reduced fossil fuel dependence.
UPSC Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Consider the following: (2013)
- Electromagnetic radiation
- Geothermal energy
- Gravitational force
- Plate movements
- Rotation of the earth
- Revolution of the earth
Which of the above are responsible for bringing dynamic changes on the surface of the earth?
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 4 only
(b) 1, 3, 5 and 6 only
(c) 2, 4, 5 and 6 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. Explain briefly the ecological and economic benefits of solar energy generation in India with suitable examples. (2025)
Q. How can India achieve energy independence through clean technology by 2047? How can biotechnology can play a crucial role in this endeavour? (2025)
Q. Examine the potential of wind energy in India and explain the reasons for their limited spatial spread. (2022)