Important Facts For Prelims
India's Air Pollution Crisis
- 01 Jul 2025
- 6 min read
Why in News?
A recent study revealed that secondary pollutants, particularly ammonium sulphate (sulphur dioxide (SO₂) + ammonia (NH₃)), contribute to nearly one-third of India’s PM2.5 pollution highlighting the urgent need for air pollution controls.
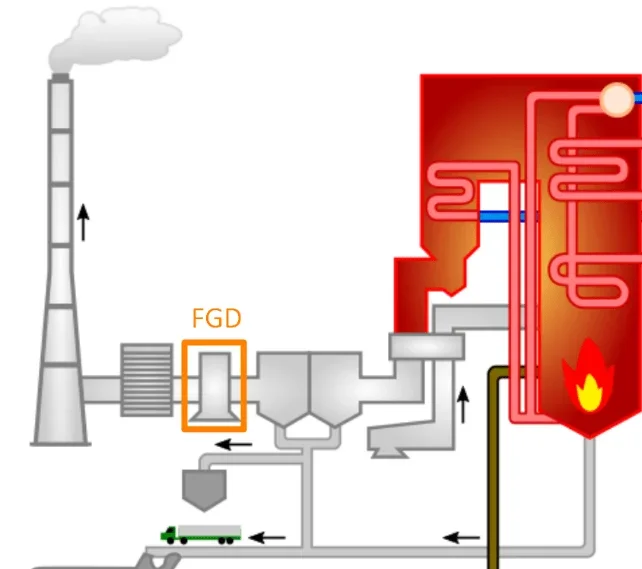
- Over 60% of SO₂ emissions in India come from coal-fired power plants, yet only 8% have installed mandatory Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD) systems, key to controlling secondary PM2.5 pollution.
What are Key Facts Regarding Air Pollution?
- About: Air pollution is caused by chemical, physical, or biological substances including noise that disturb the air’s natural composition, mainly from combustion, vehicles, industries, and fires.
- Key pollutants like PM, CO, O₃, NO₂, and SO₂ are associated with serious respiratory diseases and higher mortality rates.
- Types of Pollutants: They are divided into two types based on how they exist in the environment after being released.
- Primary Pollutants: They remain in the same form as they were released into the environment, such as DDT, plastic, carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO₂), and oxides of nitrogen and sulphur.
- Secondary Pollutants: They are produced through reactions between primary pollutants. For instance, peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) is formed by the interaction of nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons.
- Particulate Pollutants: Particulate pollutants (also called particulate matter or PM) are tiny solid or liquid particles suspended in the air that can be harmful to human health and the environment.
- PM10: Particles with a diameter of 10 micrometers or less. E.g., dust, pollen, mold etc.
- PM2.5: Particles with a diameter of 2.5 micrometers or less. E.g., Vehicle emissions, industrial processes, power plants etc.
- Measures Taken to Control Air Pollution:
What is Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD)?
- About: Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD) is a process that removes sulphur dioxide (SO₂) from flue gas emitted during the combustion of fossil fuels like coal and oil.
- It is mainly used in coal-fired power plants, using reagents such as limestone (CaCO₃), lime (CaO), and ammonia (NH₃).
- Purpose: Coal contains sulphur, and its combustion releases SO₂, causing acid rain. FGD cleans exhaust gases, preventing acid rain and protecting crops, infrastructure, soil, and aquatic ecosystems.
- Types: FGD systems are mainly of three main types:
- Dry Sorbent Injection: It involves using limestone to remove SO₂ before it reaches dust control systems and is known for its simplicity and dry operation.
- Wet Limestone System: It is ideal for large-scale applications, offering high SO₂ removal efficiency and producing useful gypsum as a byproduct.
- Seawater-Based System: It uses alkaline seawater to cut SO₂ emissions by 70–95%, suitable where emission standards are relaxed and initial costs are low.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following are the reasons/factors for exposure to benzene pollution? (2020)
- Automobile exhaust
- Tobacco smoke
- Wood burning
- Using varnished wooden furniture
- Using products made of polyurethane
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (a)
Q. In the context of solving pollution problems, what is/are the advantage/advantages of bioremediation techniques? (2017)
- It is a technique for cleaning up pollution by enhancing the same biodegradation process that occurs in nature.
- Any contaminant with heavy metals such as cadmium and lead can be readily and completely treated by bioremediation using microorganisms.
- Genetic engineering can be used to create microorganisms specifically designed for bioremediation.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)