Important Facts For Prelims
India Rolls Over USD 50 Million Treasury Bill to Support Maldives
- 03 Jun 2025
- 5 min read
Why in News?
India has extended financial support to the Maldives by rolling over (renewing) a USD 50 million Treasury Bill, under a special government-to-government (G2G) framework that began in 2019.
What are the Significant Dimensions of India-Maldives Bilateral Relations?
- Historical Ties: India recognized Maldives in 1965 and established its mission in Malé in 1972. Both are founding members of SAARC and signatories to SAFTA.
- Trade and Economy: India and Maldives signed a trade agreement in 1981, boosting bilateral trade.
- In 2024, India extended USD 400 million in support and a bilateral currency swap of Rs 3,000 crore to the Maldives, reinforcing its economic assistance.
- Additionally, the SBI rolled over USD 100 million of Treasury Bills for the Maldives.
- India became the Maldives' 2nd largest trade partner in 2022 and the largest in 2023.
- Visa-free entry for Indian business travelers in 2022 further enhanced commercial relations.
- In 2024, India and the Maldives have finalized a framework to promote the use of local currencies for cross-border trade.
- Tourism & Culture: Tourism forms 25% of Maldives’ GDP and 70% of employment, with India as the top tourist source since 2020. The 2022 open skies agreement enhanced air connectivity.
- Defence Partner: Under India’s Neighborhood First policy and SAGAR (now MAHASAGAR) initiatives, India has provided critical defence support including Operation Cactus (1988).
Note
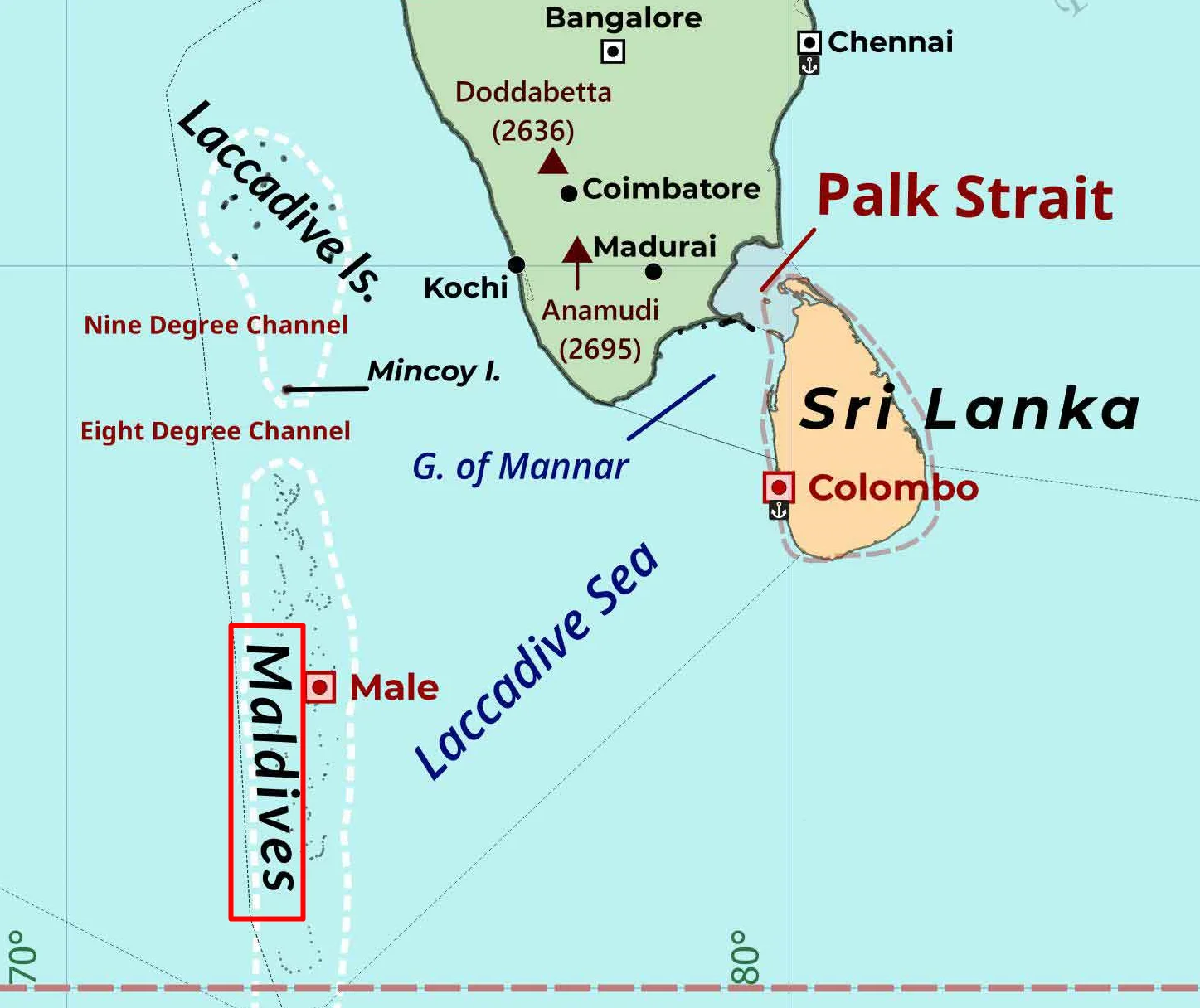
- Eight Degree Channel separates Indian Minicoy (part of Lakshadweep Islands) from that of Maldives.
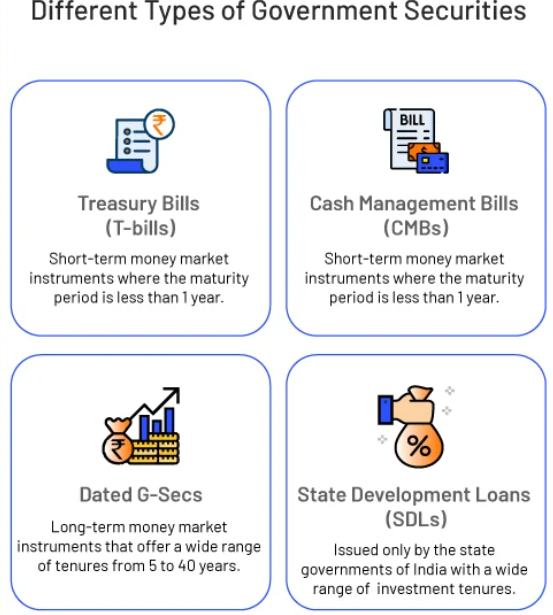
What are Treasury Bills (T-Bills)?
- T-Bills are short-term debt instruments issued by the Government of India through the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- They form part of Government Securities (G-Secs) and help raise short-term funds.
- These are zero-coupon securities, meaning they do not pay periodic interest. Instead, they are issued at a discount and redeemed at face value on maturity.
- G-Secs are tradable debt instruments issued by the Central or State Governments to borrow funds from the public with a contractual obligation to repay the principal on a specified date.
- They are issued with maturities of 91, 182, and 364 days and are sold at a discount from their face value. Investors earn returns from the difference between the purchase price and maturity amount.
- They are issued through RBI auctions via competitive and non-competitive bidding and offer high liquidity due to their short tenure.
- Gains from T-Bills are taxable as short-term capital gains, and their fixed returns may be eroded by inflation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. In the context of Indian economy, ‘Open Market Operations’ refers to (2013)
(a) borrowing by scheduled banks from the RBI
(b) lending by commercial banks to industry and trade
(c) purchase and sale of government securities by the RBI
(d) None of the above
Ans: (c)
Q2. In the context of the Indian economy, non-financial debt includes which of the following? (2020)
- Housing loans owed by households
- Amounts outstanding on credit cards
- Treasury bills
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)