International Relations
India-Philippines Relations Elevated to Strategic Partnership
- 07 Aug 2025
- 9 min read
For Prelims: Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty, BrahMos missile, Information Fusion Centre–Indian Ocean Region, ASEAN
For Mains: India’s Act East Policy and its strategic outreach in Southeast Asia, India’s role in promoting a rules-based order in the Indo-Pacific, India-ASEAN Relations
Why in News?
In 2025, India and the Philippines elevated their relationship to a Strategic Partnership during the Philippines President's state visit to India.
- The visit reaffirmed the 1952 Treaty of Friendship and aims to enhance cooperation in defense, trade, maritime security, technology, and people-to-people ties.
What are the Key Outcomes of the Philippines President Visit to India?
- Strategic Partnership Declaration: India and the Philippines officially established a Strategic Partnership, strengthening bilateral ties and cooperation across various sectors.
- Plan of Action (2025-2029): A detailed Plan of Action was adopted to guide the partnership, focusing on key areas such as defense, trade, technology, maritime cooperation, connectivity, and climate change.
- Consular & Legal Cooperation: Philippines grants visa-free access to Indian tourists. India has extended gratis e-tourist visas to Filipino nationals for one year starting August 2025.
- Two nations finalized the Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty (MLAT) and Treaty on Transfer of Sentenced Persons.
- The MLATs in criminal matters are the bilateral treaties, entered between the countries for providing international cooperation and assistance.
- The Treaty on Transfer of Sentenced Persons will allow Indian prisoners in the Philippines, and vice versa, to serve the remainder of their sentence near their families, aiding their social rehabilitation.
- Two nations finalized the Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty (MLAT) and Treaty on Transfer of Sentenced Persons.
- Infrastructure and Investment Cooperation: The Philippines invited India to participate in large infrastructure projects, with India offering to share the Gatishakti platform for coordinated development.
- India will support the Philippines in setting up its Sovereign Data Cloud infrastructure and invited the country to join the Information Fusion Centre–Indian Ocean Region (IFC-IOR) for enhanced maritime cooperation.
How India-Philippines Relations Evolved Over Time?
- Political & Diplomatic Engagement: The two countries established diplomatic ties in 1949. The Philippines is the ASEAN-India Dialogue Coordinator for 2024–27, reflecting trust and alignment in regional cooperation.
- Economic & Trade Cooperation: Bilateral trade, supported by the ASEAN–India Free Trade Agreement, has steadily increased from USD 2.03 billion in 2020–21 to USD 3.53 billion in 2023–24, with India maintaining a trade surplus.
- India exports pharmaceuticals, engineering goods, rice, and auto parts, while importing semiconductors, copper, and food-related inputs.
- India is a key pharma supplier to the Philippines, contributing about 12% of its total pharmaceutical imports.
- Defence: A Defence MoU in 2006 led to the formation of a Joint Defence Cooperation Committee.
- In 2022, India signed a deal to supply BrahMos missiles to the Philippine Navy, marking India’s first major defense export to Southeast Asia.
- In July 2025, India and the Philippines staged their first joint naval exercises in the disputed South China Sea.
- Support at International Forums: The Philippines has backed India’s bid for a permanent UN Security Council seat and supported its non-permanent membership bids. India, in return, supports the Philippines’ candidature for 2027–28.
What is the Significance of India-Philippines Relations?
- Strategic Alignment:The Philippines lies at the crossroads of the South China Sea, a region critical for Indo-Pacific security and global trade routes.
- As part of India's Act East Policy and Mutual and Holistic Advancement for Security and Growth Across Regions (MAHASAGAR) Vision, the Philippines is a key partner for maintaining a free, open, and rules-based maritime order.
- India and the Philippines, both Indo-Pacific democracies, share concerns over China’s actions in the South China Sea. India supports United Nations Convention of the Law of the Seas, 1982 and backs the Philippines against China’s Nine-Dash Line claims.
- ASEAN Engagement: The Philippines is an influential ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) member. Deepening bilateral ties strengthens India's presence in Southeast Asia.
- Economic Potential: India offers a large market, investment opportunities in IT, pharma, fintech, and partnerships in infrastructure and energy.
- India is supporting a pilot Sovereign Data Cloud Infrastructure for the Philippines boosting its digital autonomy and cyber capabilities.
- Special Technologies and Products: The Philippines is recognized for its expertise in seaweed cultivation, which India is looking to adopt for nutritional purposes in the future.
What are the Challenges in India-Philippines Relations?
- China’s Sensitivities and Regional Tensions: India’s naval ties with the Philippines in the South China Sea, amid China’s opposition.
- Beijing sees such moves as direct interference, which raises the risk of geopolitical friction and could test the Philippines' balancing act between India, the US, and China.
- Limited Economic Integration: India-Philippines trade is growing but remains underwhelming due to slow Preferential Trade Agreement negotiations, low investment, and weak connectivity.
- Implementation Gaps in Cooperation: Despite agreements on digital, and maritime, progress may be slow due to capacity gaps, differing priorities, and regional instability.
What Can be Done to Strengthen India-Philippines Relations?
- Prioritise Defence Capacity-Building: Expand Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) collaboration and pursue joint development of naval assets tailored to Philippine needs to foster durable strategic interdependence.
- Accelerate PTA Negotiations: Fast-tracking the PTA with a focus on pharma, electronics, digital services, and processed food can unlock real economic depth.
- Expand People-to-People Links: India should offer more university scholarships, especially in STEM, medicine, where India has soft power advantages.
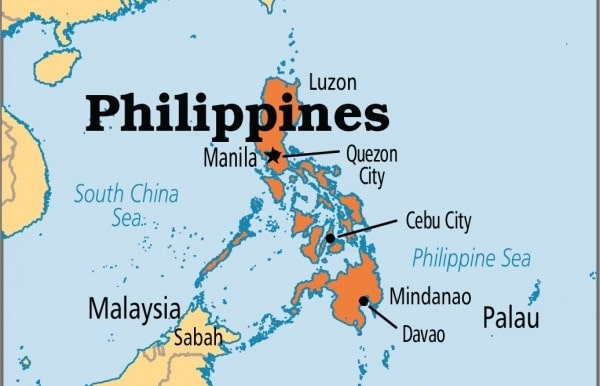
Philippines
- The Philippines, an archipelago in Southeast Asia, has 7,641 islands bordered by the Philippine Sea (east), South China Sea (west), and Celebes Sea (south).
- Luzon and Mindanao are the largest islands, with Manila as the capital.
- Mount Apo (2,954 m) on Mindanao is the highest peak and an active volcano.
- The Philippines is located in the Pacific Ring of Fire. The country has a tropical climate and is among the world’s top biodiversity hotspots.
Conclusion
India–Philippines ties will only grow if India is seen not as an alternative to China or the US but as a country that delivers relevant, reliable, and respectful solutions. That shift requires focus, speed, and sustained engagement.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. India and the Philippines recently elevated their bilateral ties to a Strategic Partnership. Discuss the significance of this move in the context of India's Indo-Pacific strategy |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.Consider the following countries: (2018)
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- USA
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN?
(a) 1, 2, 4 and 5
(b) 3, 4, 5 and 6
(c) 1, 3, 4 and 5
(d) 2, 3, 4 and 6
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. Evaluate the economic and strategic dimensions of India’s Look East Policy in the context of the post-Cold War international scenario. (2016)