Important Facts For Prelims
DNA Identification Techniques
- 16 Jun 2025
- 5 min read
Why in News?
After the Air India Boeing 787 Dreamliner crash in Ahmedabad, authorities used DNA identification to confirm the identities of the victims.
- With body remains severely damaged, DNA analysis has become the gold standard for identifying individuals in mass fatality events, such as this one.
What is DNA Analysis Techniques and its Application in Disaster Victim Identification?
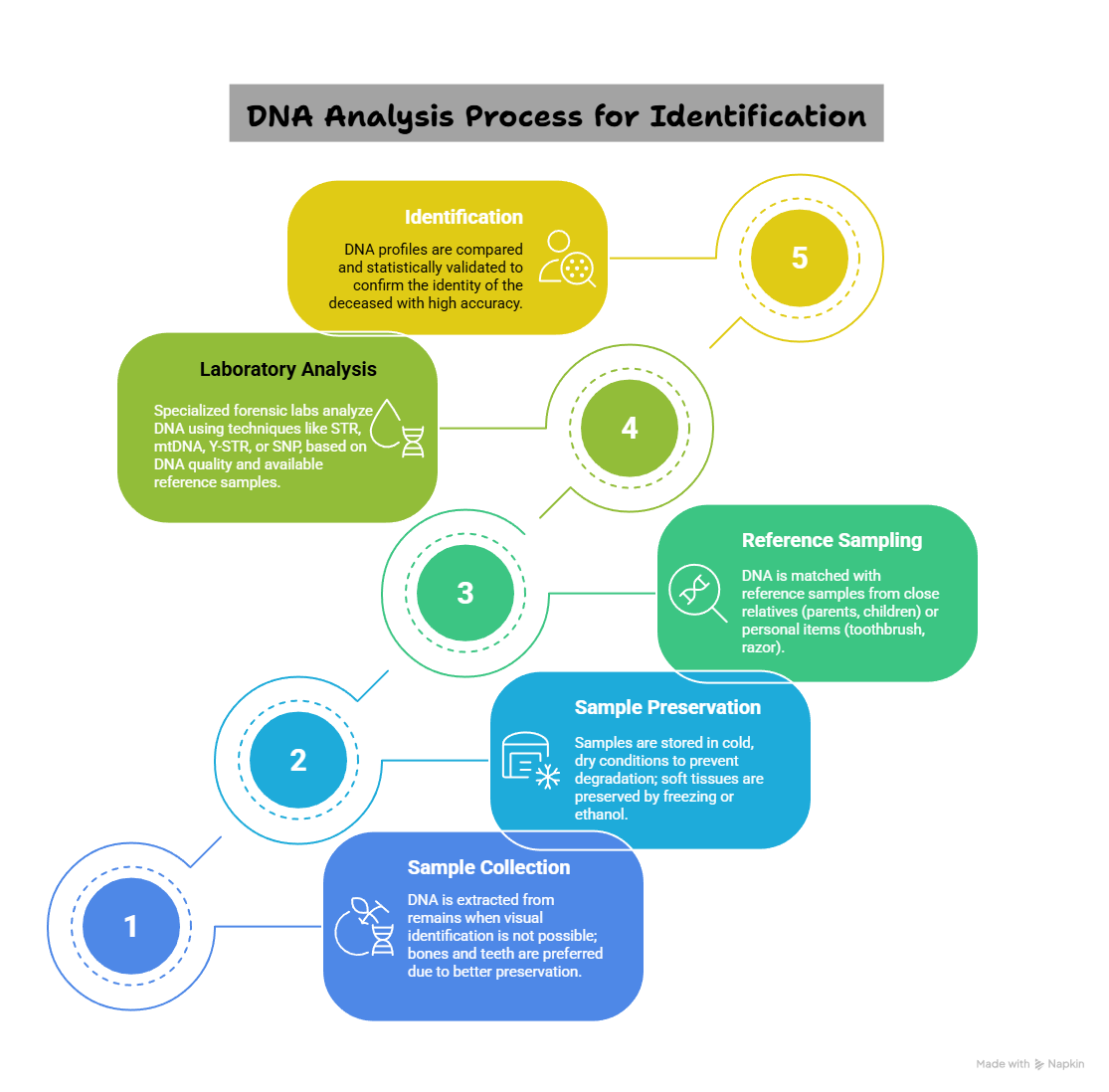
- About: DNA Analysis Techniques refer to scientific methods used to examine an individual’s genetic material (DNA) for the purpose of identification, relationship testing, or detecting genetic traits.
- DNA profiling is used to identify individuals by examining specific regions of their DNA.
- DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is the hereditary material found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells.
- It is a genetic blueprint unique to each individual, except identical twins, and is present in almost every cell of the human body.
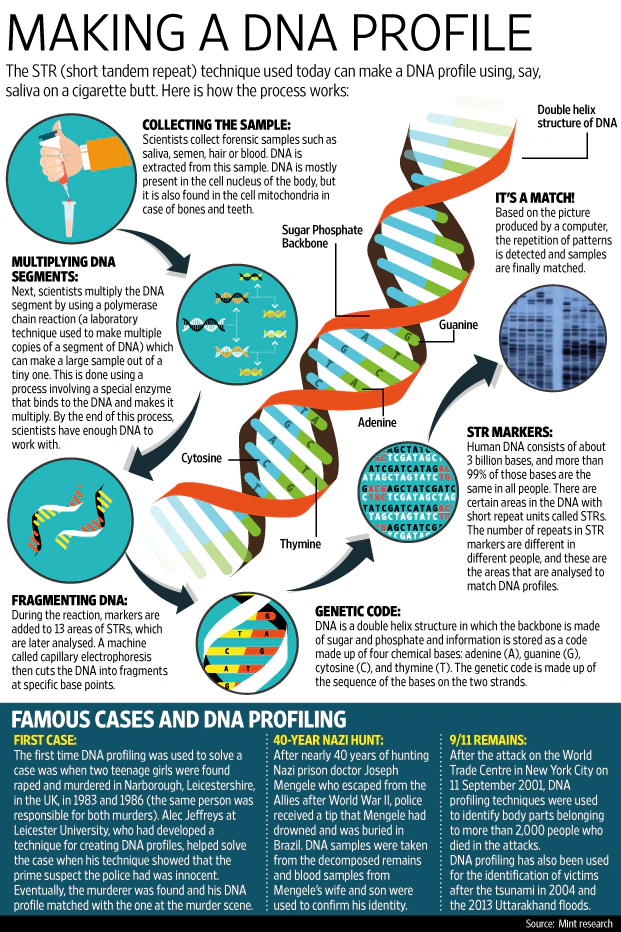
- While 99.9% of human DNA is identical across individuals, the remaining 0.1% contains variations, particularly in regions called Short Tandem Repeats (STRs), that make each person’s DNA profile unique.
- Techniques of DNA Analysis:
- Short Tandem Repeat (STR) Analysis: STR analysis is the most commonly used method in forensic DNA identification. It examines short, repeating sequences in nuclear DNA that differ significantly among individuals.
- Analyzing 15 or more STR loci can confirm identity with high accuracy. However, its reliability decreases if the nuclear DNA is badly degraded.
- Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) Analysis: Used when nuclear DNA is absent or degraded, mtDNA analysis focuses on maternally inherited genetic material.
- Since mtDNA exists in multiple copies per cell, it has higher survivability in degraded remains.
- Identification is done by matching with maternal relatives such as the mother, maternal siblings, or maternal uncles and aunts.
- Y-Chromosome STR Analysis: This method examines STRs on the Y chromosome, which is inherited along the paternal line from father to son.
- It is particularly useful for identifying male victims by comparing their DNA with that of paternal male relatives. It is also effective when only distant male relatives are available for reference.
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) Analysis: SNP analysis is used when DNA is highly degraded and other methods are not viable.
- It identifies variations at single base pairs in the genome. Though less discriminatory than STR analysis, SNPs are useful when only limited reference material or personal items are available for identification.
- Short Tandem Repeat (STR) Analysis: STR analysis is the most commonly used method in forensic DNA identification. It examines short, repeating sequences in nuclear DNA that differ significantly among individuals.
|
More on DNA Profiling: What are the Legal Provisions Regarding DNA Profiling in India?Click Here to Read: Legal Provisions Regarding DNA Profiling in India What are the Limitations of DNA Profiling?Click Here to Read: Limitations of DNA Profiling |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: DNA Barcoding can be a tool to:(2022)
- assess the age of a plant or animal.
- distinguish among species that look alike.
- identify undesirable animal or plant materials in processed foods.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 2 and 3
Ans: (B)
Q: With reference to the recent developments in science, which one of the following statements is not correct? (2019)
(a) Functional chromosomes can be created by joining segments of DNA taken from cells of different species.
(b) Pieces of artificial functional DNA can be created in laboratories.
(c) A piece of DNA taken out from an animal cell can be made to replicate outside a living cell in a laboratory.
(d) Cells taken out from plants and animals can be made to undergo cell division in laboratory petri dishes.
Ans: (A)