Science & Technology
Antimicrobial Resistance and One Health
- 07 Jul 2023
- 6 min read
For Prelims: UN Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), UN Environment Programme (UNEP), World Health Organization (WHO), World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH), One Health approach, Antimicrobial resistance, Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis, National Health Policy 2017, National Action Plan on AMR.
For Mains: Causes of Antimicrobial Resistance, One Health Approach, Measures to Address Antimicrobial Resistance.
Why in News?
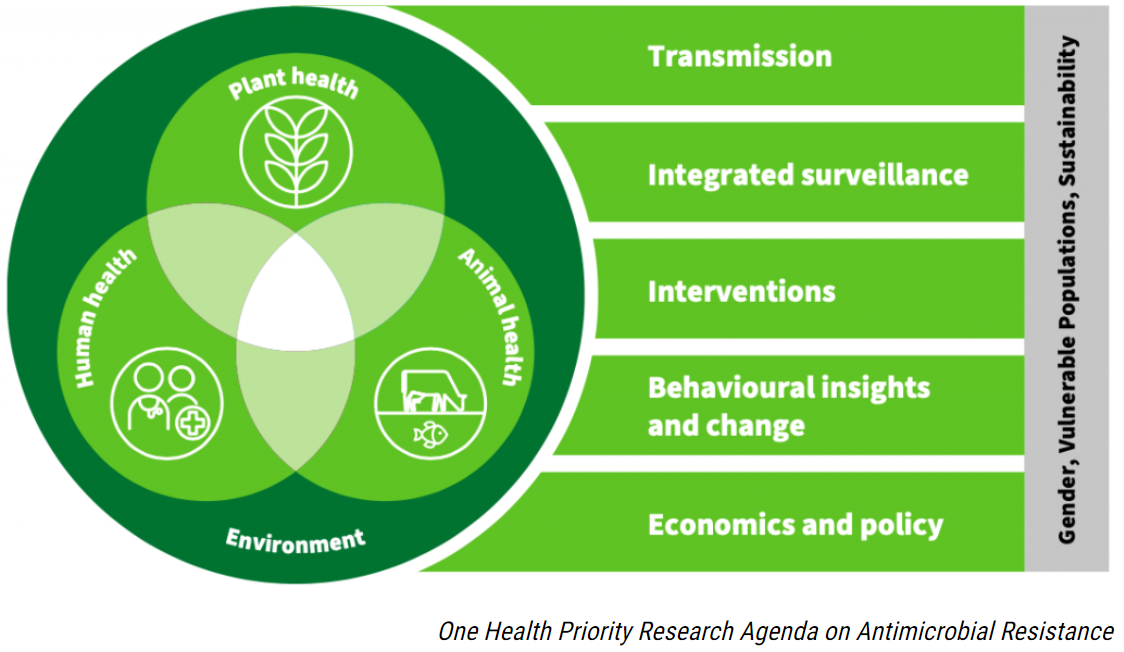
Recently, four major multilateral agencies - Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), UN Environment Programme (UNEP), World Health Organization (WHO), and World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH), announced the launch of a priority research agenda to address the critical issue of antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
- The research agenda is based on the One Health approach.
What are the Major Focus Areas of the Research Agenda?
- Major Objectives:
- To find out drivers and pathways of AMR transmission across different sectors and environment.
- To assess and evaluate the impact of AMR on various aspects of health, economy and society.
- To focus on innovation and development of new or improved diagnostics, therapeutics or vaccines to combat infections caused by resistant microorganisms.
- Cross Cutting Themes:
- The research agenda identifies 3 cross-cutting themes that need to be considered in One Health AMR research, namely gender, vulnerable populations and sustainability.
- Gender influences how people access and use antimicrobials, how they are exposed to and affected by AMR, and how they participate in and benefit from AMR research.
- Vulnerable populations refer to groups of people who are at higher risk of exposure to or infection by resistant microorganisms due to various factors such as age, poverty, malnutrition, displacement, marginalization or lack of access to quality healthcare.
- Sustainability implies balancing the environmental, economic and social dimensions of development while ensuring human rights and well-being.
- It also requires taking into account the intergenerational equity and justice implications of AMR.
- The research agenda identifies 3 cross-cutting themes that need to be considered in One Health AMR research, namely gender, vulnerable populations and sustainability.
What is Antimicrobial Resistance?
What Measures can be Taken to Address Antimicrobial Resistance?
- Enhanced Surveillance and Monitoring: Establish robust systems for monitoring and tracking the emergence and spread of resistant organisms.
- This includes tracking patterns of resistance, collecting data on antibiotic usage, and sharing information internationally to identify hotspots and take timely actions.
- Rational Use of Antibiotics: Promote responsible use of antibiotics in human and animal health, ensuring they are prescribed and used only when necessary.
- Encourage healthcare providers to follow appropriate guidelines for antibiotic prescription and educate the public about the risks of unnecessary antibiotic use.
- Infection Prevention and Control: Implement effective infection prevention and control practices in healthcare settings (hand hygiene, proper sanitation, and adherence to standard precautions).
- Preventing infections reduces the need for antibiotics, consequently preventing AMR.
- Vaccination Programs: Strengthen vaccination programs to prevent the occurrence of infectious diseases and reduce the need for antibiotic treatment.
What is 'One Health' Approach?
- About:
- 'One Health' is an integrated, unifying approach to balance and optimize the health of people, animals and the environment.
- It is particularly important to prevent, predict, detect, and respond to global health threats.
- The One Health approach is particularly relevant for food and water safety, nutrition, the control of zoonoses (diseases that can spread between animals and humans, such as flu, rabies and Rift Valley fever), pollution management, and combatting antimicrobial resistance.
- 'One Health' is an integrated, unifying approach to balance and optimize the health of people, animals and the environment.
- Recognition:
- In May 2021, The One Health High-Level Expert Panel (OHHLEP) was formed to advise FAO, UNEP, WHO and WOAH on One Health issues.
- This includes recommendations for research on emerging disease threats, and the development of a long-term global plan of action to avert outbreaks of diseases like H5N1 avian influenza, Zika and Ebola.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following are the reasons for the occurrence of multi-drug resistance in microbial pathogens in India? (2019)
- Genetic predisposition of some people
- Taking incorrect doses of antibiotics to cure diseases
- Using antibiotics in livestock farming
- Multiple chronic diseases in some people
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Can overuse and free availability of antibiotics without Doctor’s prescription, be contributors to the emergence of drug-resistant diseases in India? What are the available mechanisms for monitoring and control? Critically discuss the various issues involved. (2014)