Important Facts For Prelims
Amazon Rainforest
- 03 Oct 2025
- 6 min read
Why in News?
A Nature study shows Amazon Rainforest trees are growing larger as rising atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) levels triggers the carbon fertilisation effect, enhancing photosynthesis and plant growth, which increases carbon storage and may help offset climate change.
What is the Carbon Fertilisation Effect?
- It is the process where higher levels of CO2 in the atmosphere boost plant growth.
- CO2 is a key ingredient for photosynthesis, so when plants have more of it, they can grow faster, produce more biomass, and often use water more efficiently.
- This effect is seen naturally in forests and crops, and it’s also used artificially in greenhouses to improve yields of vegetables, fruits, and ornamental plants.
- However, this effect is not limitless and depends on other factors like water availability, soil nutrients (especially nitrogen), and temperature, which can constrain or even reverse the benefits
What are the Key Facts About the Amazon Rainforest?
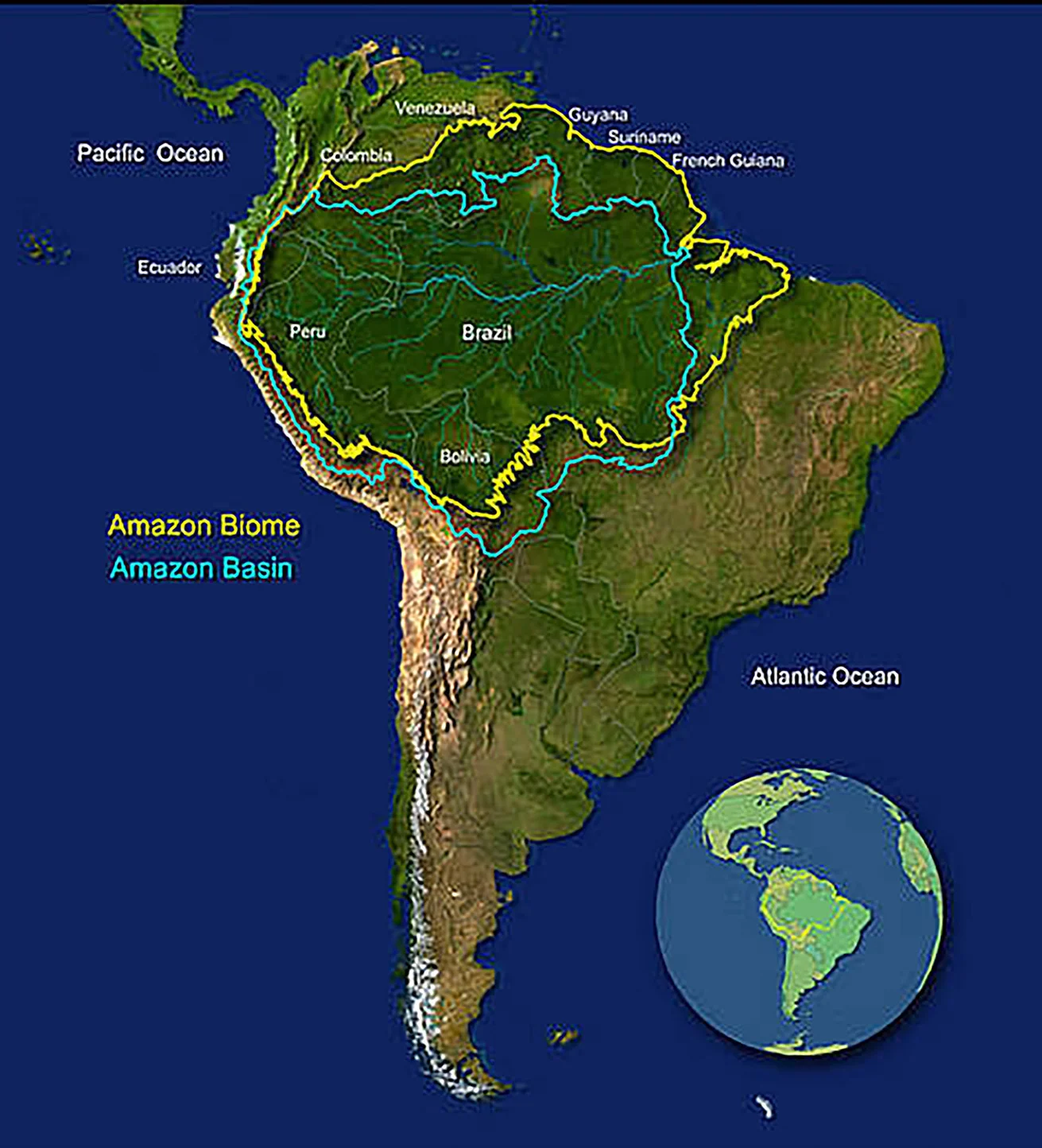
- Location & Size: The Amazon Rainforest, located in South America, is the largest tropical rainforest in the world, covering approximately 6 million sq. km, which is twice the size of India.
- It spans the Amazon River Basin, the largest river basin globally. Around 60% of the rainforest lies in Brazil, with the remainder spread across Peru, Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Bolivia, Guyana, Suriname, and French Guiana.
- Natural Boundaries: The Amazon is naturally bounded by the Guiana Highlands (North), Andes Mountains (West), Brazilian Plateau (South), and the Atlantic Ocean (East).
- Climate Characteristics: The region experiences high rainfall, intense humidity, and uniformly warm temperatures, creating ideal conditions for a dense and continuous rainforest canopy.
- Biodiversity Hotspot: The Amazon is one of the world’s richest biological reservoirs, hosting about 10% of all known wildlife species, many of which are still undocumented.
- Flora: Prominent plant species include myrtle, laurel, palm, acacia, rosewood, Brazil nut tree, rubber tree, mahogany, and cedar.
- Fauna: Iconic wildlife includes jaguar, manatee, tapir, capybara, red deer, monkeys, sloths, caimans, anacondas, tarantulas, toucans, and macaws.
- Protected Areas: The Amazon hosts several key protected areas, including Yasuni National Park (Ecuador), Tumucumaque National Park (Brazil), Jau National Park (Brazil), Pico de Neblina National Park (Brazil), Amacayacu National Natural Park (Colombia), Manu National Park (Peru), and Pacaya-Samiria National Reserve (Peru).
- Global Importance: Amazon Rainforest often called the “Lungs of the Earth”, the Amazon produces about 20% of the world’s oxygen and acts as a crucial carbon sink, moderating global climate change.
- Amazon River: The world’s largest river by discharge and second-longest after the Nile, the Amazon originates in the Peruvian Andes mountains and flows into the Atlantic Ocean.
- Major tributaries include Rio Negro, Madeira, and Xingu. Its watershed spans Brazil, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, Venezuela, and Bolivia.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the carbon fertilisation effect observed in the Amazon Rainforest?
It is the process where rising atmospheric CO2 boosts photosynthesis and plant growth, increasing biomass and carbon storage, which may help mitigate climate change.
2. Where is the Amazon Rainforest located, and what is its size?
Located in South America, the Amazon Rainforest spans about 6 million sq. km, covering 60% of Brazil and spreading across Peru, Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Bolivia, Guyana, Suriname, and French Guiana.
3. Why is the Amazon Rainforest called the “Lungs of the Earth”?
It produces around 20% of the world’s oxygen and acts as a major carbon sink, regulating global climate and supporting biodiversity.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2023)
Statement-I: The soil in tropical rain forests is rich in nutrients.
Statement-II: The high temperature and moisture of tropical rain forests cause dead organic matter in the soil to decompose quickly.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
(c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
(d) statement I is incorrect but statement II is correct.
Ans: d