Economy
2025 World Economic Outlook Report
- 10 May 2025
- 10 min read
For Prelims: International Monetary Fund, World Economic Outlook, Inflation, Demographic dividend, Make in India
For Mains: India’s macroeconomic stability and fiscal policy, Drivers of economic growth in emerging markets
Why in News?
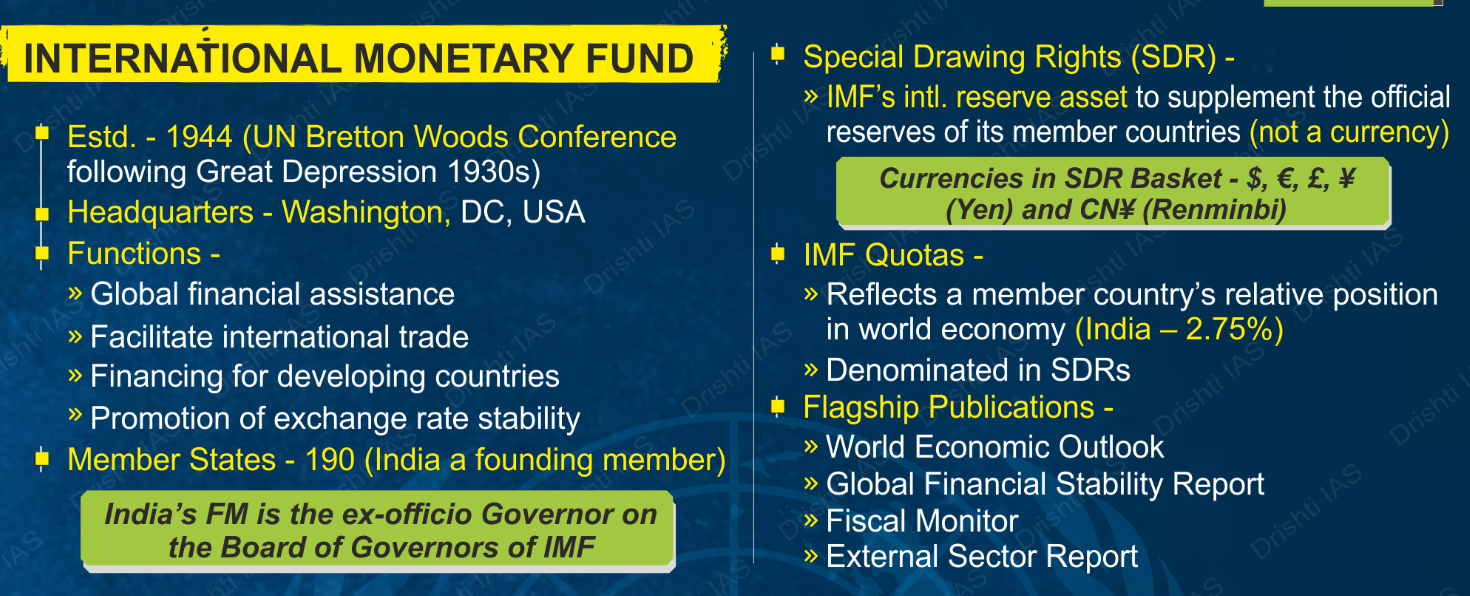
The International Monetary Fund (IMF)'s April 2025 World Economic Outlook (WEO) projects that India will surpass Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in 2025.
What are the Key Highlights of the World Economic Outlook Report 2025?
Global:
- Global Growth Forecast: The IMF revised global growth down to 2.8% for 2025, and projected 3.0% growth for 2026.
- The world's largest economy, the US, is projected to grow by just 1.8%, significantly lower than last year’s expectations due to policy uncertainty and trade tensions.
- Emerging Markets: Growth in emerging markets and developing economies is projected to slow, with a 3.7% growth rate forecast for 2025, though still above the global average.
- Global Inflation: Inflation rates are expected to decline but at a slower pace than anticipated, and downside risks remain, particularly from trade tensions and volatile financial markets.
- Aging Economies: Global economies are experiencing rapid aging, driven by declining fertility rates and rising life expectancy.
- This shift from a demographic dividend to a demographic drag presents challenges for economic growth. The average age of the world’s population is projected to increase by 11 years between 2020 and the end of the century.
- However, improvements in health and longevity have significantly enhanced the quality of life in older age.
- A 70-year-old in 2022 had cognitive abilities similar to those of a 53-year-old in 2000. Healthy aging is projected to add 0.4% to global GDP growth between 2025 and 2050.
India
- Growth forecast: While India’s growth forecast has been slightly revised down from 6.5% to 6.2% for 2025, it remains the fastest-growing major economy among its global counterparts.
- The IMF projects India's nominal gross domestic product (GDP) to reach USD 4.187 trillion in 2025, surpassing Japan's estimated USD 4.186 trillion.
- Comparisons to competitors: Despite this slight downtrend, India continues to outperform most global and regional competitors, including China, which is projected to grow at a slower rate.
- China’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth forecast for 2025 has been downgraded to 4.0% from 4.6%, making India’s growth trajectory stand out.
- Private consumption: A key driver of India’s growth is private consumption, particularly in rural areas, which is expected to remain strong, even amid global economic uncertainty.
IMF’s World Economic Outlook
- The WEO, published biannually in April and October, provides analysis and projections for the global economy and individual countries.
- It aims to assess economic developments, identify trends, and offer policy recommendations.
- Key components WEO include forecasts for global and regional economic performance, insights into inflation trends, and an evaluation of financial stability risks.
- The WEO serves as an essential tool for policymakers, researchers, and investors to understand and navigate the economic landscape.
What are the Key Drivers of India’s Economic Resilience?
- Private Consumption: The Private Consumption is a significant driver, especially in rural areas, ensuring steady domestic demand despite global economic challenges.
- India’s private consumption has nearly doubled to Rs. 1.83 lakh crore in 2024, growing at a 7.2% Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR), surpassing the US, China, and Germany.
- The country is on track to become the world’s third-largest consumer market by 2026, with the middle class expanding rapidly.
- By 2030, the number of individuals earning over Rs. 8.73 lakh annually is expected to nearly triple.
- India’s per capita income is projected to exceed Rs. 3.49 lakh by 2030, driving consumption growth.
- Macroeconomic Fundamentals: India’s robust fiscal management, with a lower debt-to-GDP ratio of 56.8% in FY25 compared to its competitors like the US, which has a debt-to-GDP ratio of 124.0%, along with structural reforms, helps maintain stability.
- Infrastructure Development: Investment in infrastructure and digitalization boosts productivity and job creation, enhancing long-term growth prospects.
- India’s digital economy has become a significant contributor to its economic growth, accounting for 11.74% of GDP in 2022-23.
- Government Reforms: Initiatives like the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana for financial inclusion, and Make in India along with Production-Linked Incentive schemes to boost manufacturing have strengthened India’s economic dynamism.
- Additionally, schemes like Bharatmala Pariyojana for road infrastructure, Sagarmala Project for port development, and Smart Cities Mission have significantly improved physical infrastructure, supporting long-term growth.
- Demographics and Labor Force: India benefits from a young, growing workforce, with policies aimed at increasing female labor participation (from 23.3% in 2017-18 to 41.7% in 2023-24) and addressing global aging workforce challenges.
- A ServiceNow report projects India’s workforce will grow from 423.73 million in 2023 to 457.62 million by 2028, adding 33.89 million jobs, particularly in sectors like retail, tech, manufacturing, education, and healthcare.
- Technological Innovation: The growing adoption of digital technologies, including Artificial Intelligence and renewable energy solutions, supports higher productivity and resilience in economic activities.
- Indian startups are likely to create 50 million new jobs and add USD 1 trillion to the economy by 2029-30 (FY30).
- India's technology sector is witnessing rapid growth and is projected to reach USD 300-350 billion over the next five years.
- External Demand and Trade Diversification: India's increased integration into global value chains and trade agreements provides growth opportunities and buffers against global volatility. India’s share in global services exports has doubled from 1.9% in 2005 to 4.3% in 2023.
Conclusion
India’s resilient economic growth, driven by robust private consumption, structural reforms, and strategic investments, positions it as a global leader amidst economic uncertainties. With demographics supporting its trajectory, India’s outlook remains positive. The country’s ability to leverage these factors ensures it will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the global economic landscape.
|
Drishti Mains Question: India is projected to remain the fastest-growing major economy despite global uncertainties. Discuss the key factors contributing to this resilience. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. "Rapid Financing Instrument" and "Rapid Credit Facility" are related to the provisions of lending by which one of the following? (2022)
(a) Asian Development Bank
(b) International Monetary Fund
(c) United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative
(d) World Bank
Ans: (b)
Q2. ‘Global Financial Stability Report’ is prepared by the (2016)
(a) European Central Bank
(b) International Monetary Fund
(c) International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
(d) Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. The World Bank and the IMF, collectively known as the Bretton Woods Institutions, are the two inter-governmental pillars supporting the structure of the world’s economic and financial order. Superficially, the World Bank and the IMF exhibit many common characteristics, yet their role, functions and mandate are distinctly different. Elucidate. (2013)