International Relations
China’s Presence in the Horn of Africa
- 30 Jun 2022
- 11 min read
For Prelims: Horn of Africa, Middle East, Red Sea, East Africa Community
Foe Mains: Significance of Horn of Africa for India and Way Forward, China’s Presence in Horn of Africa Region
Why in News?
Recently, first “China-Horn of Africa Peace, Governance and Development Conference.” was held.
- This is the first time China aims “to play a role in the area of security”.
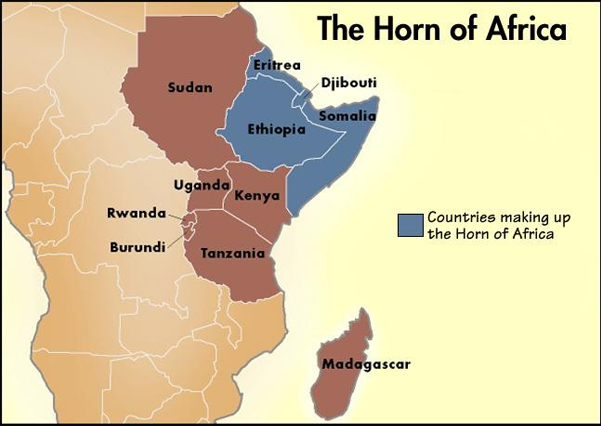
What is Horn of Africa?
- The Horn of Africa is a peninsula in Northeast Africa.
- Located on the easternmost part of the African mainland, it is the fourth largest peninsula in the world.
- It lies along the southern boundary of the Red Sea and extends hundreds of kilometres into the Guardafui Channel, Gulf of Aden, and Indian Ocean.
- The Horn of Africa is equidistant from the equator and the Tropic of Cancer.
- The Horn contains such diverse areas as the highlands of the Ethiopian Plateau, the Ogaden desert, and the Eritrean and Somalian coasts.
- The Horn of Africa denotes the region containing the countries of Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia.
- The area has experienced imperialism, neo-colonialism, Cold War, ethnic strife, intra-African conflict, poverty, disease, famine and much else.
What are the Recent Chinese Projects?
- In January 2022, China asserted its three objectives in Africa: controlling the pandemic, implementing a Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC) outcomes, and upholding common interests while fighting hegemonic politics.
- In the 2021 forum, the entire region of the Horn participated, and four resolutions were adopted:
- The Dakar Action Plan:
- The two sides commend the development of relations between China and Africa, and believe that over the past 21 years since its inception, the Forum has strongly promoted the development of relations between China and Africa, and become an important benchmark for international cooperation with Africa.
- China-Africa Cooperation Vision 2035:
- It was formulated to determine the directions and objectives of mid- and long-term cooperation and promote a closer community with a shared future for China and Africa.
- Sino-African Declaration on Climate Change:
- It is aimed at enhancing coordination and cooperation in the multilateral process on climate, and jointly safeguard the legitimate rights and interests of China, Africa and other developing countries.
- Declaration of the Eighth Ministerial Conference of FOCAC:
- Under the theme "Deepen China-Africa Partnership and Promote Sustainable Development to Build a China-Africa Community with a Shared Future in the New Era" and committed to the development of FOCAC and to the deepening of the China-Africa comprehensive strategic and cooperative partnership, both adopted by consensus the Dakar Declaration of the Eighth Ministerial Conference of FOCAC.
- The FOCAC promotes China’s role in the infrastructural and societal development of the Horn.
- The Dakar Action Plan:
- During the Covid-19 pandemic, China donated over 3,00,000 vaccines to Ethiopia and Uganda, and 2,00,000 vaccines to Kenya and Somalia. Sudan and Eritrea have also benefited from China’s vaccine diplomacy.
What are China’s Primary Interests in the Region?
- Infrastructure:
- One of its landmark projects was fully funding the USD 200 million African Union headquarters in Addis Ababa.
- China has also invested in the Mombasa-Nairobi rail link in Kenya, and has already delivered on railway projects in Sudan.
- It also has a viable military hardware market in Ethiopia and has built over 80 infrastructural projects in Somalia, including hospitals, roads, schools and stadiums.
- In Djibouti, 14 infrastructural projects are funded by China.
- Financial Assistance:
- Ethiopia, is one of the top five African recipients of Chinese investments, and also has a debt of almost USD 14 billion.
- China accounts for 67% of Kenya’s bilateral debt.
- In 2022, China promised to provide USD 15.7 million assistance to Eritrea.
- Natural Resources (Oil and Coal):
- China is also interested in minerals such as gold, iron-ore, precious stones, chemicals, oil and natural gas in Ethiopia.
- South Sudan, a source for petroleum products, has had continued Beijing investment in the industry since the latter’s initial entry in 1995.
- Maritime Interests:
- China’s first and only military base outside its mainland is in Djibouti.
- In 2022, China hinted its willingness to develop Eritrea’s coast which would connect to China’s investments in land-locked Ethiopia.
- The U.S. has speculated that China wishes to build another military base in Kenya and Tanzania, thereby increasing its military presence in the region.
Does China shift from its Principle of Non-Intervention?
- For Africa, Chinese investments could lead to stable environments which could help the countries achieve their peace and development objectives. For China, conflict in the region comes at a heavy cost.
- In Ethiopia. when the conflict broke out, over 600 Chinese nationals, working on different projects, were evacuated, putting several investments at risk.
- From a trading perspective, the region plays a significant role in achieving the objectives of the China-Africa Cooperation Vision 2035.
- China’s move towards peace in Africa indicates a shift in its principle of non-intervention.
- It is China’s message that its presence in the continent has a larger objective and is not likely to be limited to the Horn of Africa.
- This includes an aim to project itself as a global leader and boost its international status.
- Further, the recent developments imply that China is focusing on a multifaceted growth in the continent for the long run.
- For Africa, China’s presence is an alternative to the European powers, many of whom are facing criticism from African governments.
- Further, African governments, which do not conform to Western standards of democracy, interact better with powers like China and Russia.
What is the Significance of Horn of Africa for India?
- Africa has been a Growing Interest:
- Africa has been of growing interest to India for political, economic and security reasons, especially the sub-region - the Horn of Africa.
- Proximity to Oil Producing Region:
- The Horn of Africa is strategically important since it is close to the oil-producing region of the Middle East.
- Approximately 40% of the oil produced in the Middle East crosses through the shipping lanes of Red Sea.
- Shipping Routes:
- Djibouti is the choke point on this shipping route. It is due to this reason that countries like the United States, France, and China have a military base in Djibouti.
- With the new reliance on the sea lines of communication for India’s economic growth, Delhi declared that its national interests were no longer limited to the Subcontinent but stretched from the “Aden to Malacca”.
What is India’s Concern over China’s presence?
- Dominance in the Indian Ocean:
- Situated on the north-western edge of the Indian Ocean, Djibouti could become another of China’s “string of pearls” of military alliances and assets ringing India, including Bangladesh, Myanmar and Sri Lanka.
- China has stepped up activity in the Indian Ocean, which India considers within its sphere of influence, in recent days, citing anti-piracy patrols and freedom of navigation. It has forced the Indian Navy to tighten surveillance of the strategic waters.
- China seeks to control over Vital Shipping Routes:
- The Indian Ocean shipping lanes carry 80% of the world’s oil and a third of the global bulk cargo. China is looking to secure its energy and trade transportation links along the vital shipping route.
- Influencing Indian Ocean Countries:
- The Indian Ocean is also emerging as the playground for countries eyeing a bigger role in world affairs. China is looking to generate goodwill and influence in the Indian Ocean countries by investing in projects such ports, roads and railways.
- China is looking to expand its presence in the Indian Ocean, and is building ports and other infrastructure in Sri Lanka, Bangladesh and Pakistan.
- Expanding through OBOR:
- The Indian Ocean figures prominently in China’s ambitious One Belt, One Road (OBOR) initiative to build a new Silk Route.
- India has kept away from OBOR as its centrepiece.
- The Indian Ocean figures prominently in China’s ambitious One Belt, One Road (OBOR) initiative to build a new Silk Route.
Way Forward
- What happens in the region has a direct bearing on India’s security and well-being and hence India should pay more attention to the prevailing conditions and power dynamics in the Horn of Africa.
- India would be well advised to become more active in examining and discussing the complex problem in-depth with the governments in Eastern Africa, the African Union and others concerned so as to be able to make a meaningful contribution to its resolution.