Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
Poshan Maah Campaign in Jharkhand
Why in News?
The 8th Poshan Maah 2025 was launched in Jharkhand, focusing on reducing oil and sugar consumption and promoting the “Paanch Sutra – Golden 1000 Days” initiative to improve maternal and child nutrition.
Key Points
- About: The initiative is part of the Poshan Abhiyan to improve maternal and child nutrition across the state. Aimed at tackling malnutrition, the campaign also focused on reducing excessive consumption of unhealthy oils and sugars.
- Reduction in Oil & Sugar Consumption: During the launch event, campaign materials were unveiled, focusing on raising awareness about the need to reduce oil and sugar consumption in daily diets.
- These posters will be distributed across Anganwadi Centres (AWCs) statewide to ensure effective outreach.
- Paanch Sutra – Golden 1000 Days Initiative: This is a crucial step in improving maternal and child nutrition by promoting a healthy diet during the critical 1000 days of a child’s life (from pregnancy to the second birthday).
- The five key nutritional practices emphasized in the initiative will guide communities in enhancing their dietary habits, ensuring optimal growth and development for children.
Poshan Abhiyaan
- About:
- Poshan Abhiyaan was launched by the Prime Minister on 8th March, 2018, in Jhunjhunu district of Rajasthan.
- The focus of Abhiyaan is to emphasize the nutritional status of adolescent girls, pregnant women, lactating mothers, and children from 0 to 6 years old.
- Objectives
- Prevent and reduce stunting in children (0- 6 years)
- Prevent and reduce under-nutrition (underweight prevalence) in children (0-6 years)
- Reduce the prevalence of anaemia among young Children(6-59 months)
- Reduce the prevalence of anaemia among Women and Adolescent Girls in the age group of 15-49 years
- Reduce Low Birth Weight (LBW)
National Current Affairs Switch to Hindi
Mohanlal Honored with Dadasaheb Phalke Award
Why in News?
Veteran Malayalam actor Mohanlal will receive the prestigious Dadasaheb Phalke Award for 2023, as announced by the Union Ministry of Information and Broadcasting.
- The award will be conferred on Mohanlal on 23rd September 2025, during the 71st National Film Awards ceremony.
Key Points
- About: Born on 21st May 1960, in Pathanamthitta, Mohanlal began his acting career with Thiranottam (1978) and debuted as a villain in Manjil Virinja Pookkal (1980).
- By 1986, his role in Rajavinte Makan established him as Malayalam cinema's first modern superstar.
- With over 45 years and 400 films to his name, Mohanlal remains a defining figure in Mollywood, starring in notable films like Thanmathra, Iruvar, Drishyam, and Lucifer.
- He won the National Film Award for Best Actor in 1991 and received the Padma Shri in 2001 and the Padma Bhushan in 2019.
- Dadasaheb Phalke Award:
- It is the country’s highest film honour, introduced in 1969, conferred for “Outstanding contribution to the growth and development of Indian cinema”.
- It was awarded for the first time to Devika Rani, “the first lady of Indian cinema”.
- This award includes a 'Swarna Kamal,' a cash prize of INR 10 lakh, a certificate, a silk roll, and a shawl.
- The President of India presents it.
- Dhundiraj Govind Phalke:
- He was an Indian producer, director, and screenwriter who directed India's first feature film, Raja Harischandra (1913).
- He is known as the “Father of Indian Cinema”.
Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
Surajpur Becomes Model for Child Marriage Eradication
Why in News?
Surajpur district in Chhattisgarh has made a remarkable achievement by declaring 75 of its village panchayats as "Child Marriage-Free Panchayats" on 17th September 2025.
- This recognition marks a major victory for the district's relentless social reform efforts and public awareness campaigns under the "Healthy Women, Empowered Families" initiative.
Key Points
- About:
- The announcement of the 75 child marriage-free panchayats coincided with the launch of National Nutrition Month and the ongoing "Healthy Women, Empowered Families" campaign. These panchayats were recognized for having reported no cases of child marriage in the past two years.
- On 10th March 2024, Chief Minister Vishnu Deo Sai launched the “Child Marriage-Free Chhattisgarh Campaign” with the support of UNICEF. The initiative aims to make the entire state child marriage-free through active awareness, monitoring, and community participation.
- Implementation:
- The Women and Child Development Department led consistent awareness drives in the region.
- Anganwadi workers, panchayat representatives, and voluntary organizations played a crucial role in spreading awareness about the detrimental effects of child marriage.
- Educational dialogues emphasized the importance of child rights, education, and the necessity of delaying marriage to ensure better health and socio-economic outcomes for girls.
- This created a shift in mindset where parents began prioritizing education and self-reliance for their daughters over early marriage.
Child Marriage
- UNICEF categorizes child marriage as a human rights violation due to its adverse impacts on the development of both girls and boys.
- Sustainable Development Goal 5.3 states that Child marriage elimination is pivotal in achieving Sustainable Development Goal 5, aiming for gender equality and empowerment of women and girls by 2030.
- According to the UN, 1 in 5 young women worldwide (19%) were married in childhood in 2022.
Legislative Framework
- India enacted the Prohibition of Child Marriage Act in 2006, establishing the legal age for marriage at 21 for men and 18 for women.
- Section 16 of the Prohibition of Child Marriage Act allows State Governments to appoint 'Child Marriage Prohibition Officers (CMPO)' for specific areas.
- CMPOs are responsible for preventing child marriages, collecting evidence for prosecutions, counseling against promoting or aiding such marriages, raising awareness about their harmful effects, and sensitizing communities
- The government has introduced a bill, namely 'the Prohibition of Child Marriage (Amendment) Bill, 2021 for raising the age of marriage of women to 21 years to make it at par with men.
- Section 16 of the Prohibition of Child Marriage Act allows State Governments to appoint 'Child Marriage Prohibition Officers (CMPO)' for specific areas.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
PM Lays Foundation of India’s 1st Freight Village
Why in News?
The Prime Minister laid the foundation for key infrastructure projects in Varanasi, including a ship repair facility and India’s first freight village, under the 'Prosperity from the Sea' initiative, aimed at boosting water transport and creating employment.
- He emphasized the role of waterways in strengthening the economy and creating jobs, aligning with the vision of 'Make in India.'
Key Points.
- First Freight Village in India: The freight village is located over 100 hectares in Milkipur, Chandauli district, and will serve as a logistics hub, connecting different transport modes for smoother and more affordable goods movement.
- It will link Haldia, Patna, Kolkata, and Kashi with eco-friendly freighters that cut transport costs by approximately 50% compared to road and rail.
- India’s First Dry-Dock Facility: Located in Ramnagar, Varanasi, this dry-dock, India’s first along the Ganga River, will be capable of repairing four vessels simultaneously, reducing both repair times and costs.
- This will enhance regional development and provide sustainable employment opportunities for the youth in the Purvanchal region.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
UP Emerges as Leading Revenue Surplus State
Why in News?
The Comptroller and Auditor-General of India (CAG) decadal study on state finances reveals that 16 states are in revenue surplus, with Uttar Pradesh leading the pack.
Key Points
- Revenue Surplus States: The CAG report reveals that 16 states reported a revenue surplus in the fiscal year 2023, marking a significant turnaround for states once considered economically weaker.
- Leading the charge is Uttar Pradesh, with a surplus of ₹37,000 crore, a stark contrast to its previous standing as part of the BIMARU states.
- BIMARU is an acronym for Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh, a grouping of states that have historically lagged in economic and social indicators.
- Leading the charge is Uttar Pradesh, with a surplus of ₹37,000 crore, a stark contrast to its previous standing as part of the BIMARU states.
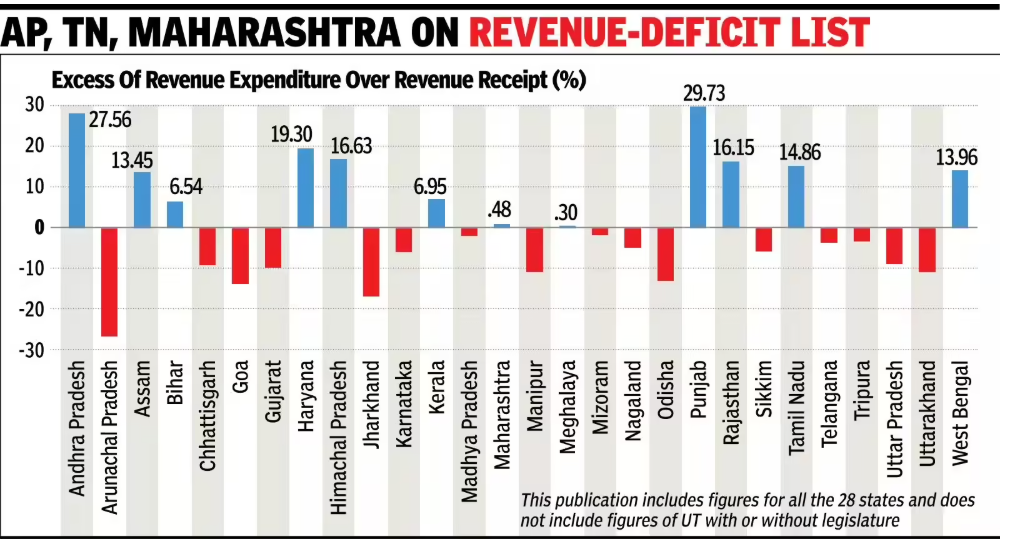
- Revenue Deficit States: Conversely, at least 12 states were found to be in revenue deficit in 2022-23, indicating significant fiscal distress.
- States like Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and Rajasthan reported the highest deficits, pointing to a growing reliance on central grants.
- States Relying on Central Grants: Several states are heavily dependent on central financial support, with West Bengal receiving the largest share of 16% in FY 2023.
- These grants help bridge the gap between their revenue receipts and expenditure.
- Revenue from Own Sources: Some states have successfully boosted their revenue generation through both tax and non-tax means.
- Haryana leads with over 80% of its revenue coming from its own sources, followed by Telangana and Maharashtra with over 70% and 60% respectively.
- State's Own Tax Revenue (SOTR): The CAG report also highlights the reliance of certain states on States' Own Tax Revenue (SOTR), with six states (Haryana, Maharashtra, Telangana, Karnataka, Gujarat, and Tamil Nadu) deriving over 60% of their revenue from SOTR.
- Low SOTR States: On the other hand, some northeastern states and smaller regions like Arunachal, Manipur, Nagaland, and Sikkim report very low SOTR, with contributions from their own tax revenue falling below 20%.
West Bengal Switch to Hindi
Bengal Maps India's First Wolf Corridors
Why in News?
West Bengal has recently made a remarkable stride in wildlife conservation with the successful mapping of two wolf corridors near the industrial town of Durgapur.
Key Points
- About: The pioneering initiative marks a first-of-its-kind initiative in India and contributes to the broader Indian Grey Wolf Conservation Project in West Burdwan.
- The corridors, located in the West and East Burdwan regions, span a combined area of approximately 20 kilometers and represent a crucial movement space for the Indian grey wolves.
- With the help of local experts and organizations like the Wildlife Information and Nature Guide Society (WINGS) and WWF-India, this corridor mapping seeks to understand and protect the movement patterns of urban wolves.
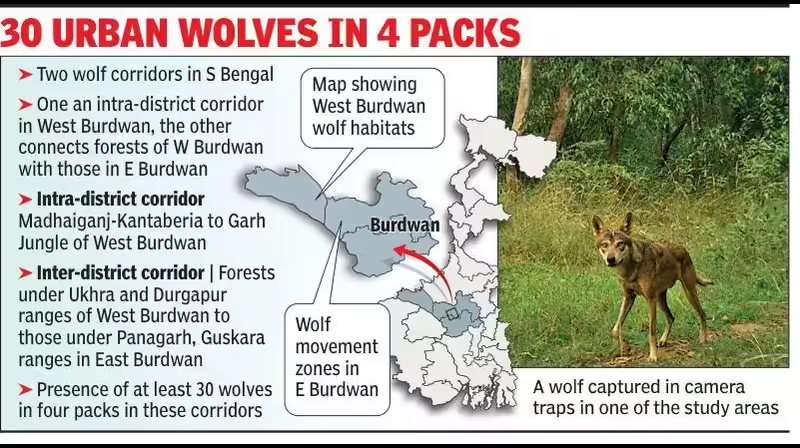
- Corridor Mapping: The mapping identifies two key corridors:
- Intra-District Corridor: Linking the forests of Madhaiganj-Kantaberia to Garh Jungle in West Burdwan.
- Inter-District Corridor: Connecting the forests under the Ukhra and Durgapur ranges of West Burdwan to those in East Burdwan (Panagarh, Durgapur, Guskara ranges).
- Findings on Wolf Population: Approximately 30 wolves have been recorded in the area, organized into four packs. The presence of at least 15-24 Indian wolves was also noted in a 2024 study conducted near Durgapur.
- Ecological Insights: These corridors are vital habitats for the species, with evidence pointing to the highest abundance of wolves found within the corridors over the last one and a half years. The study has also identified key breeding habitats and rendezvous sites, critical for the wolves' lifecycle.
- Dietary Habits: Through scat analysis, researchers have identified that the wolves' diet is primarily livestock-based (goats and sheep) but also includes scavenged cow, buffalo, rodent, and bird remains, which is essential for understanding the species' ecological role.
- Deterrent Measures: Fladry deterrent flags—brightly colored flags that create moving barriers—have been installed in conflict-prone areas to minimize human-wolf conflict.
Indian Grey Wolf
- About: The Indian grey wolf (Canis lupus pallipes) is a subspecies of grey wolf found across Southwest Asia and the Indian subcontinent.
- It lives in smaller packs and is less vocal compared to other wolf subspecies.
- It is primarily nocturnal, hunting from dusk to dawn.
- Habitat: It is an apex predator in India’s scrublands, grasslands, and semi-arid agro-ecosystems. Thrives in regions with warmer temperatures.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN: Endangered (population in India: 2,000 - 3,000 individuals).
- CITES: Appendix I.
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule I.





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan