Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Madhya Pradesh Ranks 3rd in India in Flower Production
Why in News?
Madhya Pradesh has gained a strong foothold in India's floriculture sector, becoming the third-largest flower producer in the country.
Key Points
About Key Developments in MP’s Floriculture Sector
- Rising Area and Production: In 2024–25, Madhya Pradesh cultivated 42,978 hectares of flowers, producing 5.12 lakh metric tonnes of flowers, a record figure.
- The area under flower cultivation increased from 37,647 hectares in 2021–22 to 42,976 hectares, with production rising by 86,294 tonnes.
- Productivity: Madhya Pradesh's per hectare flower productivity stands at 15.01 metric tonnes, a remarkable achievement in the floriculture industry.
- Key Flowers and Varieties:
- Primary Flowers: Marigold, rose, chrysanthemum, gladiolus, tuberose, and medicinal flowers like isabgol, ashwagandha, and safed musli.
- Marigold: Covers the largest area, grown on 24,214 hectares.
- Rose: Grown over 4,502 hectares.
- Other Varieties: Chrysanthemum (1,709 ha), gladiolus (1,058 ha), tuberose (263 ha), and other varieties on 11,227 hectares.
- Primary Flowers: Marigold, rose, chrysanthemum, gladiolus, tuberose, and medicinal flowers like isabgol, ashwagandha, and safed musli.
- Government Initiatives and Investments: Both the state and central governments are promoting floriculture through various schemes, aiming to double farmer incomes and make agriculture profitable.
- Farmers, even with small landholdings (1–3 acres), are benefiting from floriculture.
- The state’s Horticulture and Food Processing Department is consistently working to improve flower quality and boost marketing initiatives.
- In 2024–25, flower cultivation saw an expansion of 5,329 hectares, with government initiatives facilitating over 33% of this growth.
- Initiatives such as technical training and high-tech nurseries are playing a crucial role in the sector’s expansion.
- A ₹13 crore, centrally supported hi-tech floriculture nursery is being developed in Gwalior to further enhance the sector.
- Farmers, even with small landholdings (1–3 acres), are benefiting from floriculture.
- Market Expansion:
- Domestic Demand: Madhya Pradesh-grown flowers are in high demand across metro cities like Jaipur, Delhi, and Mumbai.
- International Reach: Roses from Guna district are now reaching global markets, including Paris and London.
- Significance: With favorable climate, improved irrigation, and expanding government support, Madhya Pradesh is set to become a national leader in floriculture, driving rural economic development and contributing significantly to India's agricultural growth.
About Floriculture Sector
- About:
- The government of India has identified floriculture as a sunrise industry and accorded it 100% export-oriented status.
- A sunrise industry is a new and rapidly growing sector or business that is in its infancy stage and shows strong potential for rapid expansion and significant economic impact in the future.
- It has been found that commercial floriculture has higher potential per unit area than most field crops and is, therefore, a lucrative business.
- The liberalized economy has given an impetus to the Indian entrepreneurs for establishing export-oriented floriculture units under controlled climatic conditions.
- Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) is responsible for export promotion and development of floriculture in India.
- The government of India has identified floriculture as a sunrise industry and accorded it 100% export-oriented status.
- Varieties:
- These mainly consist of cut flowers, pot plants, cut foliage, seeds, bulbs, tubers, rooted cuttings, and dried flowers or leaves.
- The important floricultural crops in the international cut flower trade are Rose, Carnation, Chrysanthemum, Gargera, Gladiolus, Gypsophila, Liatris, Nerine, Orchids, Archilea, Anthurium, Tulip, and Lilies.
- Floriculture crops like Gerberas, Carnations, etc., are grown in greenhouses.
- The open field crops are Chrysanthemum, Roses, Gaillardia, Lily Marygold, Aster, Tuberose, etc.
- Areas of Cultivation:
- Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, West Bengal, Chhattisgarh, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, Assam, and Maharashtra have emerged as major floriculture centers.
- India Facts and Figures:
- As per the economic survey 2024-25, during 2023-24, approximately 297,000 hectares were dedicated to floriculture, yielding an estimated 22,84,000 tonnes of loose flowers and 947,000 tonnes of cut flowers.
- During the same period, India exported 19,678 metric tonnes of floriculture products, earning ₹717.83 crore.
- Major Export Destinations (2023-24):
- Key export destinations included the USA, Netherlands, UAE, UK, Canada, and Malaysia.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
UP Government Launches HRMS Portal for Udyami Mitras
Why in News?
The Uttar Pradesh Government has launched the Human Resource Management System (HRMS) portal for 'Udyami Mitras' to enhance investor facilitation and internal efficiency.
- This cloud-based platform, integrated with the state's Nivesh Sarathi platform, aims to digitize and streamline essential administrative functions.
Key Points
About Key Features of the HRMS Portal
- Automation of HR Functions: The HRMS portal is designed to automate key human resource operations like attendance, leave management, payroll processing, and Form-16 generation.
- Real-time Access to Records: The portal provides real-time access to employee records, promoting transparency and reinforcing administrative oversight at both district and state levels.
- Digitization of Workflows: The transition from manual to system-based workflows enhances the speed and accuracy of HR processes, ensuring smoother operations across the board.
- Integration with Nivesh Sarathi: By integrating with Nivesh Sarathi, the portal ensures seamless coordination between Udyami Mitras and other government platforms, enhancing communication and operational efficiency.
About the Role of Udyami Mitras
- Under the Mukhyamantri Udyami Mitra Yojana (launched in 2023), more than 110 trained Udyami Mitras have been deployed across districts and industrial authorities.
- These Mitras play a pivotal role as facilitators between investors and the government.
- Their responsibilities include:
- Land Identification: Assisting investors in identifying suitable land for their projects.
- MoU Tracking: Ensuring the smooth execution and monitoring of Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs).
- Investment Proposal Verification: Verifying and validating investment proposals to ensure alignment with government policies.
- Industrial Interactions: Facilitating smooth interactions between industrialists and government authorities.
- Resolving Bottlenecks: Addressing and resolving obstacles faced by investors through platforms like Nivesh Mitra, Nivesh Sarathi, and OIMS (Online Industrial Management System).
Other Investor-Friendly Initiatives of Uttar Pradesh Government
- Nivesh Sarathi: Nivesh Sarathi in Uttar Pradesh is a comprehensive online platform launched by the UP government in November 2022 to facilitate and streamline the investment process in the state.
- It acts as a single-window clearance system for investors, significantly simplifying interactions with over 50 government departments by integrating their services on one digital portal.
- Invest UP: The state’s dedicated nodal agency supporting prospective and existing investors through policy advocacy, project facilitation, and aftercare services. It organizes major events like the UP Global Investors Summit to mobilize investment proposals and foster industry engagement.
- Extensive Land Bank Development: UP has created a 30,000-acre land bank, especially along expressways, with 4,000 acres already allocated for industrial development.
- Special Sectoral Policies:
- UP Industrial Investment & Employment Promotion Policy 2022
- GCC Policy 2024 (Global Capability Center): Incentives for global firms to establish centers in both metro and non-metro cities, including land subsidies up to 50%, capital subsidies, and salary support for local talent.
- SAF Manufacturing Promotion Policy 2025: First-of-its-kind in India, offers incentives, streamlined support, and a focus on sustainable aviation fuel industries, benefiting both investors and local farmers.
- Electronics Manufacturing Cluster (EMC 2.0): A ₹417 crore project in Gautam Buddha Nagar expected to draw ₹2,500 crore in investments and generate 15,000 jobs by 2028, boosting the electronics ecosystem in line with Make in India.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Justice KR Shriram Sworn in as Chief Justice of Rajasthan HC
Why in News?
Justice Kalpathi Rajendran Shriram was sworn in as the new Chief Justice of Rajasthan High Court by Governor Haribhau Bagde at a ceremony held at Raj Bhavan.
Key Points
About Justice Kalpathi Rajendran Shriram
- His tenure at Rajasthan HC is likely to be 69 days, as 27 Sept 2025 is his retirement date.
- Justice Shriram succeeds Chief Justice MM Srivastava, who has been transferred to the Madras High Court.
- Justice Shriram served on the Bombay High Court bench from 2013 until 26 September 2024, before becoming the Chief Justice of the Madras High Court on 27 September 2024, until his transfer to the Rajasthan High Court.
About Appointment of High Court Judges
- Article 217 of the Constitution: It states that the Judge of a High Court shall be appointed by the President in consultation with the Chief Justice of India (CJI), the Governor of the State.
- In the case of appointment of a Judge other than the Chief Justice, the Chief Justice of the High Court is consulted.
- Consultation Process: High Court judges are recommended by a Collegium comprising the CJI and two senior-most judges.
- The proposal, however, is initiated by the Chief Justice of the High Court concerned in consultation with two senior-most colleagues.
- The recommendation is sent to the Chief Minister, who advises the Governor to send the proposal to the Union Law Minister.
- The Chief Justice of the High Court is appointed as per the policy of having Chief Justices from outside the respective States.
- The Collegium takes the call on the elevation.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
FIDE World Cup 2025 to be Hosted in India
Why in news?
India will host the Chess World Cup 2025 from 30 October 2025 to 27 November 2025, with the host city announcement to be made later by the International Chess Federation (FIDE).
Key Points
About the Tournament
- Tournament Format:
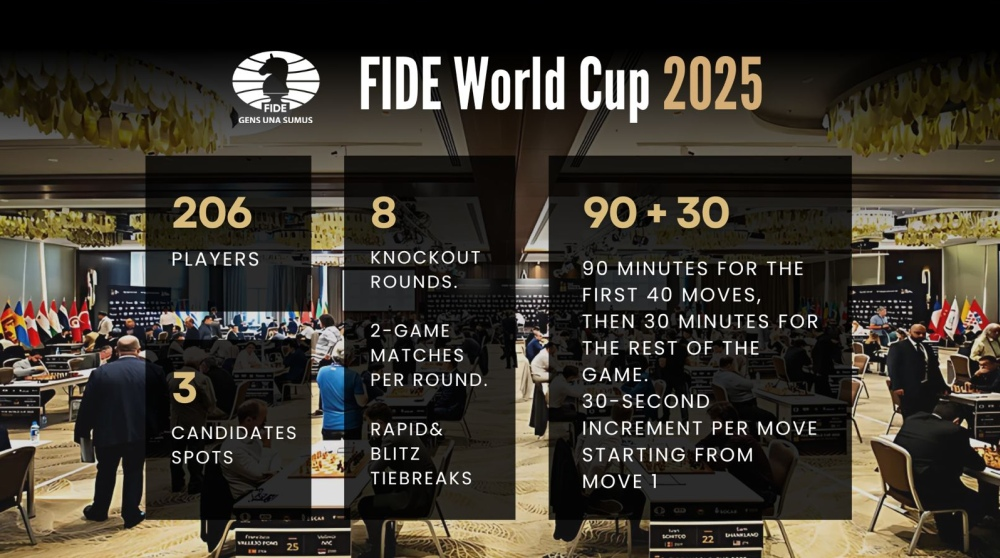
- The FIDE World Cup 2025 will follow a knockout format, with 206 players competing.
- The tournament has a dynamic elimination system where the losing player is eliminated after each round.
- Each round spans three days: two classical games on the first two days, followed by tie-breaks on the third day if necessary.
- The top 50 players will receive byes in the first round, while the rest will compete based on a principle where the top half faces the reversed lower half.
- Qualification Pathways:
- Direct qualification: The top three finishers of the 2025 World Cup will earn direct entry to the 2026 Candidates Tournament.
- Players eligible: Reigning World Champion, top four finishers from the 2023 World Cup, Women’s World Champion, 2024 World Junior Champion (U-20), and other continental qualifiers.
- Continental spots: 80 spots will be granted to players through Continental events, with each continent receiving a different allocation (Africa: 3, Asia: 35, Europe: 30, Americas: 3).
- Top-rated players: The highest-rated players from the June 2025 FIDE rating list will also receive invitations, along with players from the top 100 national federations from the 2024 Chess Olympiad.
About India’s Contribution to Chess
- India’s Major Achievements:
- India’s has produced some of the world’s most celebrated chess players, most notably Viswanathan Anand, a five-time World Champion and current FIDE Deputy President, who has helped elevate India’s status as a global chess hub.
- The emergence of young talents like Gukesh Dommaraju, Praggnanandhaa R, and Arjun Erigaisi, have transformed the nation’s chess landscape.
- In 2024, India made history by winning its first-ever gold medals in both the Open and Women’s Chess Olympiad teams.
- The 2024 FIDE World Chess Championship was won by Gukesh Dommaraju, who became the youngest Chess World Champion in history at age 18.
- He defeated the reigning champion Ding Liren (China) in a 14-game classical match held in Singapore.
- The FIDE World Championship 2024 match was also the first in 138 years to feature two contestants from Asia.
- Praggnanandhaa R also finished as the runner-up in the 2023 World Cup.
- Major Chess Events in India: India’s success in hosting international chess events is well established. Notable recent events include:
- FIDE Chess Olympiad 2022: Held in Mamallapuram, this event was a major organizational success.
- Tata Steel Chess India: A key event in the global chess calendar.
- FIDE World Junior U20 Championship 2024: Hosted by India, showcasing the country’s growing reputation as a destination for high-level chess.
- FIDE Women’s Grand Prix (2025): A part of the global chess series highlighting women’s participation in the sport.
Bihar Switch to Hindi
Bihar Polling Station Rationalisation
Why in News?
Bihar has become the first Indian state to ensure all polling stations have fewer than 1,200 electors, marking a major reform to enhance voter convenience and electoral accessibility.
- This move aligns with a broader push by the Election Commission of India (ECI) to rationalize polling stations nationwide, particularly in the context of upcoming Assembly elections and the proposed ‘One Nation, One Election’ plan.
Key Points
About Polling Station Rationalisation
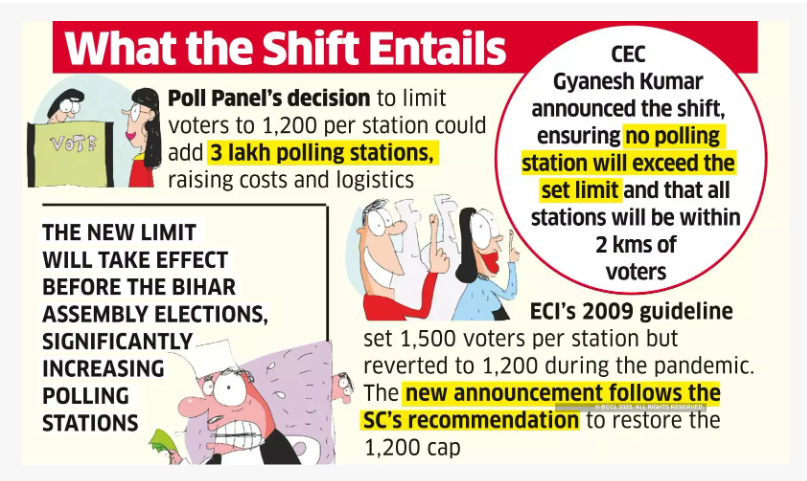
- Revised Elector Cap per Booth: The State Instructional Representation (SIR) Order of June 2025 revised the maximum number of electors per polling station from 1,500 to 1,200, reversing the 2009 standard to reduce voter congestion.
- Increase in Polling Stations: Bihar added 12,817 new polling stations, raising the total to 90,712, up from 77,895. This effort places all booths within 2 km of voters, improving accessibility in rural areas.
- Inclusive Voter Registration Drive: Electoral officers conducted widespread consultations with 12 political parties and shared lists of:
- 29.62 lakh electors whose forms were pending,
- 43.93 lakh electors not found at their registered addresses.
- Draft Electoral Roll Timeline: The Draft Rolls will be published on 1 August 2025, after which voters can submit claims, objections, or corrections for a month, as per the SIR Order.
Implications for Electoral Management
- Impact on One Nation, One Election (ONOE): The voter cap rationalisation will influence the logistics of ONOE, especially the requirement for EVM-VVPATs and polling personnel.
- The ECI earlier projected over 13.57 lakh booths and a cost of ₹7,950 crore for a 2029 simultaneous poll.
- Judicial Intervention Prompted Reform: A December 2024 Supreme Court petition demanded reverting to the 1,200-voter cap, citing long queues and voter apathy.
- The EC’s reform aligns with the Court’s concerns about voter fatigue and inefficiencies under the 1,500-voter cap.
- Historical Evolution of Booth Size Norms:
- Pre-2009: 1,200 electors per station (standard).
- Post-EVMs (2009): Raised to 1,500.
- During COVID: Reduced to 1,000–1,200.
- 2024 General Elections: Returned to 1,500.
- Post-2025 SIR: Back to 1,200 nationwide, starting with Bihar.
Significance of the Reform
- Template for Other States: The ECI called Bihar’s initiative a model for other States and UTs. Over 3 lakh new booths may be needed nationwide to implement this cap before upcoming elections.
- Administrative and Financial Burden: The change will increase election infrastructure costs, with higher demand for EVMs, VVPATs, and personnel.
- Strengthening Electoral Democracy: These changes aim to enhance the quality of voter participation, reduce disenfranchisement, and ensure every eligible voter is registered and conveniently able to vote.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Youth Spiritual Summit Adopts Kashi Declaration
Why in News?
The Youth Spiritual Summit held at the Rudraksh International Convention Centre in Varanasi concluded with the formal adoption of the Kashi Declaration, marking a significant milestone in India's journey towards a drug-free society by 2047.
About Youth Spiritual Summit
- Summit Overview:
- The summit, organized by the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports, brought together over 600 youth leaders and representatives from 120 spiritual and socio-cultural organizations.
- The summit provided a platform for in-depth discussions on the psychological and societal impacts of drug abuse, the mechanics of drug trafficking, and strategies for grassroots awareness.
- Four plenary sessions were conducted, culminating in the Kashi Declaration. Key themes discussed during the sessions include:
- The psychological impacts of addiction.
- Understanding the drug supply chains and trafficking mechanisms.
- Effective grassroots campaigns for drug awareness.
- The role of spiritual and cultural institutions in rehabilitation.
- The Kashi Declaration:
- The Kashi Declaration reflects the consensus to tackle drug abuse as a public health crisis and societal challenge.
- It calls for a whole-of-government and whole-of-society approach, integrating efforts from spiritual, educational, and technological sectors.
- The declaration proposes the establishment of a Joint National Committee for multi-ministerial coordination, ensuring accountability and progress tracking.
- The Declaration also calls for annual progress reports and a national platform to connect individuals struggling with addiction to support services.
- Youth-Led Campaigns and MY Bharat Framework:
- MY Bharat will take the lead in mobilizing youth-led efforts to combat drug abuse across the nation.
- Youth clubs and volunteers affiliated with MY Bharat will spearhead awareness drives, pledge campaigns, and community outreach efforts, ensuring the sustainability of this movement.
- The Kashi Declaration will serve as the guiding document, directing the efforts of youth groups and policymakers, and will be reviewed during the Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Dialogue 2026 for progress and accountability.
- MY Bharat will take the lead in mobilizing youth-led efforts to combat drug abuse across the nation.
Note
- My Bharat Portal, officially known as Mera Yuva Bharat (MY Bharat), is a comprehensive youth-centric platform established by the Government of India, launched on National Unity Day, 31 October 2023, by Prime Minister.
- It is operated by the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports as an autonomous body, designed specifically for youth aged 15 to 29 (with some activities for those aged 10–19), aligning with the National Youth Policy, 2014.





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan