Haryana Switch to Hindi
New Leave Policy: Promoting Workforce Participation for Female Employees
Why in News?
The Haryana government has revised its leave policy, under which female employees, including those working under the Haryana Kaushal Rozgar Nigam Limited (HKRN), will now be entitled to two additional days of casual leave per month, up to a maximum of 22 days per year.
- This initiative not only reflects progressive governance but also aims to encourage more women to join and sustain their participation in the workforce.
Key Points
- Impact on Women’s Workforce Participation:
- Improved Work-Life Balance: The extra leave provisions will provide female employees with the flexibility to balance their personal and professional lives better, which is crucial in improving work-life balance.
- This is particularly important in a society where women often face greater familial responsibilities.
- Support for Health and Well-being: The additional leave can be used for personal health issues, family care, or other needs, supporting a healthier and more productive workforce.
- This is in line with global best practices that promote the physical and mental well-being of workers.
- Gender Inclusivity: This policy is a step forward in promoting gender equality in the workplace by encouraging a more inclusive work environment.
- Improved Work-Life Balance: The extra leave provisions will provide female employees with the flexibility to balance their personal and professional lives better, which is crucial in improving work-life balance.
- About Haryana Kaushal Rozgar Nigam Limited (HKRN):
- HKRN was incorporated under the Companies Act, 2013 on 13th October 2021.
- It has been established to supply contractual manpower to government departments and agencies across Haryana.
- The Nigam aims to carry out recruitment in a transparent, efficient, and equitable manner.
- HKRN serves as the officially designated agency for deploying contractual manpower in the state.
- Focus Areas:
- Prioritises candidates from socio-economically disadvantaged backgrounds in the recruitment process.
- Ensures timely disbursement of salaries and benefits to all deployed personnel.
- Strictly adheres to the State Reservation Policy while selecting candidates.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
India’s First Equine Disease-Free Compartment (EDFC)
Why in News?
The World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH) has officially recognized India’s first Equine Disease-Free Compartment (EDFC) at the Remount Veterinary Corps (RVC) Centre and College in Meerut, Uttar Pradesh.
Key Points
- Equine Disease-Free Compartment (EDFC):
- Definition:
- An EDFC is a specially designated, biosecure zone for horses that ensures protection from serious equine diseases, enabling safe movement for sports, breeding, or trade.
- It is established under the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying.
- Features:
- The EDFC is part of a wider initiative to establish disease-free zones across sectors.
- India is also working on creating Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI)-Free Compartments for the safe export of poultry products.
- The EDFC follows detailed SOPs covering disease prevention, pest control, security, hygiene, health monitoring, waste management, and constant surveillance, in line with global best practices.
- The approval aligns with WOAH’s Terrestrial Animal Health Code, which outlines science-based guidelines for managing disease-free animal sub-populations through strict biosecurity and care practices.
- The EDFC is part of a wider initiative to establish disease-free zones across sectors.
- Certified Disease-Free:
- The EDFC has been declared free from major equine diseases such as Equine Infectious Anemia, Equine Influenza, Equine Piroplasmosis, Glanders, and Surra.
- India has also remained free from African Horse Sickness since 2014.
- The EDFC has been declared free from major equine diseases such as Equine Infectious Anemia, Equine Influenza, Equine Piroplasmosis, Glanders, and Surra.
- Definition:
- Significance:
- International Participation: Indian sport horses can now compete in international equestrian events, enhancing India's visibility and participation in the global equestrian arena.
- Boost to Equine Trade and Breeding: The EDFC will strengthen India’s position in the equine trade and breeding sectors, opening up global markets for Indian horses.
- Animal Health Excellence: India’s commitment to strengthening animal health systems with globally accepted practices positions it as a leader in veterinary excellence.
World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH)
- WOAH is the leading international body dedicated to animal health and welfare.
- Established in 1924 as the Office International des Epizooties (OIE), the organisation adopted its current name in May 2003.
- It operates as an intergovernmental organisation, with members from around the world collaborating on shared goals in animal health.
- It works to improve global animal health and is headquartered in Paris, France.
- As of 2025, WOAH had 183 member countries, including India.
- It creates guidelines, such as the Terrestrial Animal Health Code, to help countries prevent disease entry.
- The World Trade Organization (WTO) acknowledges WOAH standards as international sanitary guidelines.
Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
Chhattisgarh Celebrates Water Conservation Week
Why in News?
The Chhattisgarh Government celebrated Water Conservation Week under the ‘More Villages, More Water’ campaign.
Key Points
- ‘More Villages, More Water’ Campaign:
- It aims to promote water conservation practices at the village level, emphasizing community participation and sustainable water management.
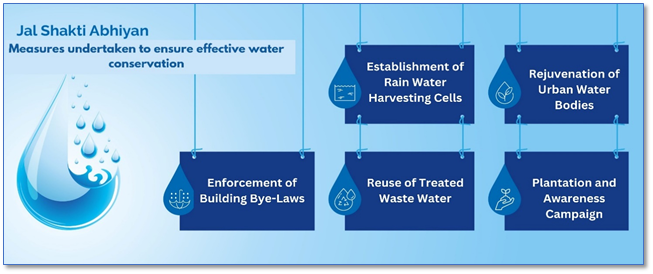
- The campaign is linked to the broader Jal Shakti Abhiyan and encourages activities like rainwater harvesting, groundwater recharge, and efficient irrigation methods.
- Other Water Conservation Initiatives:
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan (JSA):
- "Catch the Rain" Campaign:
- In 2021, the government launched Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Catch the Rain (JSA: CTR) with the theme "Catch the Rain – Where it Falls, When it Falls."
- This phase expanded the campaign to all blocks in both rural and urban areas across the country.
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Catch the Rain 2025
- On World Water Day (22nd March 2025), Jal Shakti Ministry launched JSA: Catch the Rain 2025.
- Theme: “Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari – Jan Jagrukta Ki Or” (Water Conservation through People's Participation and Public Awareness).
- The campaign will be implemented from 22nd March to 30th November 2025, with a focused emphasis on the pre-monsoon and monsoon seasons.
- The campaign targets 148 districts identified by the Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) as critical for water conservation.
- The 2025 edition emphasises deeper grassroots participation, inter-sectoral convergence and innovative financing mechanisms.
- Khandwa in Madhya Pradesh has emerged as the model district for the initiative.
- Key focus areas:
- Water Conservation & Rainwater Harvesting
- Geo-tagging & Inventory of Water Bodies; Scientific Planning
- Establishing Jal Shakti Kendras in All Districts
- Intensive Afforestation
- Public Awareness & Outreach Campaigns
World Water Day
- It aims to raise awareness about water conservation and its sustainable management.
- It was conceptualized at the 1992 Rio Summit and officially designated to be observed annually by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) in 1993.
- The day aligns with UN SDG-6: Ensuring water and sanitation for all by 2030.
- Theme (2025): ‘Glacier Preservation’
Central Ground Water Board (CGWB)
- About: The CGWB, established under the Ministry of Water Resource (now Ministry of Jal Shakti), is the apex body for managing, exploring, monitoring, assessing, and regulating groundwater resources in India.
- Established in 1970, CGWB was initially formed by renaming the Exploratory Tube Wells Organization and was later merged with the Ground Water Wing of the Geological Survey of India in 1972.
- The Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA), constituted under the Environmental Protection Act, 1986, regulates groundwater development to ensure its sustainability.
- Key Functions and Responsibilities: CGWB provides scientific expertise for groundwater management, including exploration, monitoring, and water quality assessments.
- It also implements schemes for artificial recharge and rainwater harvesting to augment groundwater levels.
- Scientific Reports: CGWB releases State and District hydrogeological reports, groundwater year books and Atlases.
Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
Niyad Nella Nar Initiative
Why in News?
Irkabhatti, located in Narayanpur district in Bastar division, was previously a village where basic needs, especially education, were unattainable due to the Maoist insurgency.
- However, through the state government’s ‘Niyad Nella Nar’ scheme, focused efforts have been made to improve education, connectivity, and infrastructure.
Key Points
- ‘Niyad Nella Nar’ Scheme:
- The Niyad Nellanar scheme is a Chhattisgarh government initiative focused on providing basic amenities and welfare benefits to Naxal-affected villages in the state.
- Niyad Nellanar, meaning “aapka achcha gaon” or “your good village” is the local Dandami dialect (spoken in south Bastar).
- The scheme aims to improve living standards by offering services for Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs).
- It focuses on delivering essential facilities like housing, healthcare, water, electricity, roads, and education within a kilometer radius of security camps.
- Families in these villages will receive free gas cylinders under the Ujjwala scheme, ration cards, irrigation pumps, free electricity, Anganwadi, and certificates of forest rights.
- The Niyad Nellanar scheme is a Chhattisgarh government initiative focused on providing basic amenities and welfare benefits to Naxal-affected villages in the state.
Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY)
- The Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY) is a flagship initiative aimed at providing clean cooking fuel (LPG) to rural and economically disadvantaged households.
- It was launched on 1st May 2016 in Ballia, Uttar Pradesh.
- The scheme targets families that previously relied on traditional fuels such as firewood, coal, and cow-dung cakes for cooking.
- Health and Environmental Impact:
- The use of traditional fuels posed serious health risks, especially for rural women exposed to indoor air pollution.
- It also contributed to environmental degradation due to deforestation and carbon emissions.
- Ujjwala 2.0 was launched in August 2021 as the second phase of the scheme.
Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs)
- About:
- A PVTG is a sub-classification of a Scheduled Tribe or section of a Scheduled Tribe that is considered more vulnerable than a regular Scheduled Tribe. The Indian Government created the PVTG list to improve their living.
- State-wise Distribution:
- There are 75 PVTGs in India, with the highest number—13—in Odisha, followed by 12 in Andhra Pradesh.
- There are 7 PVTGs in Chhattisgarh, who live in 17 of the state’s 33 districts.
- These are Kamar, Baiga, Pahadi Korba, Abujhmadiya, Birhor, Pando and Bhujia.
- While the first five tribes have been declared PVTG by the central government, the remaining two, Pando and Bhujia, have been given the tag by the state government.
- Article 342(1): The President with respect to any State/UT (after consultation with the Governor in case of state) may specify the tribes/tribal communities/part of or groups within tribes/ tribal communities as a Scheduled Tribe in that State/UT.
- Parliament may by law include in or exclude from the list of STs specified in a notification issued under article 342(1) any tribe or tribal community or part of or group within any tribe or tribal community, but save as aforesaid a notification issued under the said clause shall not be varied by any subsequent notification.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Accelerating Solar Power Growth in Rajasthan
Why in News?
A high-level meeting reviewed issues affecting 18 major infrastructure projects worth over Rs 36,296 crore in Gujarat and Rajasthan, focusing on resolving bottlenecks through the Project Monitoring Group (PMG) mechanism.
Key Points
- Key Focus of the Meeting:
- The meeting reviewed the Transmission System Strengthening Scheme aimed at evacuating solar power from renewable energy zones in Rajasthan and Gujarat.
- With a projected investment of Rs 14,147 crore, the scheme focuses on developing high-capacity transmission lines and substations to integrate solar energy into the national grid.
- In Rajasthan, the project covers Jaisalmer, Bikaner, and Barmer; in Gujarat, it focuses on Surendranagar, Patan, and Kutch—regions rich in solar potential.
- These projects are vital to ensuring reliable power transmission from generation zones to consumption centres across India.
- The meeting prioritised resolving key implementation challenges such as right-of-way (RoW) and land acquisition to fast-track progress on transmission infrastructure.
- State Government officials focused on expediting forest-related clearances critical to the rollout of telecom infrastructure in remote areas.
- The meeting reviewed the Transmission System Strengthening Scheme aimed at evacuating solar power from renewable energy zones in Rajasthan and Gujarat.
- Solar Power Production in Rajasthan:
- Rajasthan ranks 1st in India in terms of solar energy, with an installed solar capacity of 22,860.73 MW.
- The state benefits from over 325 sunny days annually, making it ideal for solar power generation.
- Rajasthan recorded the highest annual growth rate of 18.63% in installed renewable energy capacity among all Indian states.
- In 2023, Rajasthan had the highest installed capacity of grid-connected renewable energy at 22,398 MW, followed by Gujarat with 19,436 MW.
- As of 2024, Rajasthan surpassed 18 GW of installed solar capacity, reinforcing its status as India’s top solar power-generating state.
- Rajasthan's Integrated Clean Energy Policy 2024 aims to significantly boost renewable energy, particularly solar power, to achieve a 125 GW renewable energy capacity by 2030.
- The policy focuses on leveraging the state's abundant natural resources and includes measures for both large-scale solar parks and rooftop solar installations.
- It also promotes wind, hybrid, and green hydrogen energy initiatives.
- Rajasthan ranks 1st in India in terms of solar energy, with an installed solar capacity of 22,860.73 MW.
Note: India became the world’s third-largest producer of electricity from wind and solar energy in 2024, overtaking Germany, as reported in April 2025.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Uttar Pradesh Targets Global Manufacturing Shift
Why in News?
Uttar Pradesh (UP) is intensifying its global outreach to attract multinational manufacturers, particularly through the China+1 strategy, as part of Chief Minister Yogi Adityanath’s vision to transform the state into a USD 1 trillion economy.
Key Points
- About China+1 Strategy:
- It refers to the global trend where companies diversify their manufacturing and supply chains by establishing operations in countries other than China.
- This approach aims to mitigate risks associated with over-reliance on a single country, especially in light of geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions.
- Global Outreach to Attract Investment:
- As part of its China+1 strategy, Invest UP, the state’s nodal investment promotion agency, is leading a global outreach initiative.
- The campaign includes roadshows and strategic business engagements across the United States, Europe, and the United Kingdom to attract Fortune 500 companies and global industrial leaders.
- The outreach will feature Business-to-Government (B2G) meetings and roundtable discussions in global business hubs such as New York, London, Paris, among others.
- These events are being organised in collaboration with Indian embassies and leading trade associations like US-India Business Council (USIBC), Confederation of Indian Industries CII, and Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce & Industry (FICCI).
- Sectoral Growth and Key Investments in UP:
- Electronics: Rs 3,700 crore HCL–Foxconn OSAT investment marks a milestone in the state’s semiconductor ambitions.
- Textiles: UP is strengthening its textile value chain through PM MITRA Mega Textile Park and mini parks focused on synthetic, defence, and medical textiles.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Under the EV Policy 2023, UP targets 36 Gigawatt hours (GWh) battery production capacity by 2028.
- Digital Infrastructure: Noida–Greater Noida is emerging as India’s leading data centre hub, with plans to develop an integrated AI City.
Invest UP
- About:
- Invest UP, formerly known as Udyog Bandhu, is the investment promotion and facilitation agency of the Government of Uttar Pradesh.
- It is dedicated to attracting new investments and resolving issues faced by existing and upcoming industries in the state.
- Vision:
- Invest UP envisions transforming UP into India’s most preferred investment destination.
- It aims to serve as an effective driver of investment policies and provide a world-class business environment and infrastructure, thereby fostering economic growth and enhancing the quality of life for the people of the state.
- Mission:
- As state’s Investment Promotion and Facilitation Agency, Invest UP aims at attracting investment in the state through proactive contribution in policy formulation for rapid development of industries and infrastructure in the State.
- The organization facilitates the resolution of problems of prospective and existing entrepreneurs by providing them the advisory services.




























.jpg)







.png)


.jpg)

 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan