Place In News
US Response on Nigeria Violence
- 15 Nov 2025
- 2 min read
The US President criticised Nigeria for failing to protect Christians from violence (Plateau, Benue, and Kaduna states), warning of possible aid cuts and military action, triggering diplomatic and political debate.
- Insecurity in Nigeria stems from terrorist insurgencies like Boko Haram, communal land–water conflicts, and criminal banditry, all intensified by poverty, weak governance, and climate change.
- This mirrors wider Sahel instability—in Mali, Burkina Faso, Niger, and Chad—where Islamist groups, ethnic tensions, and climate stress drive conflict and weaken state authority.
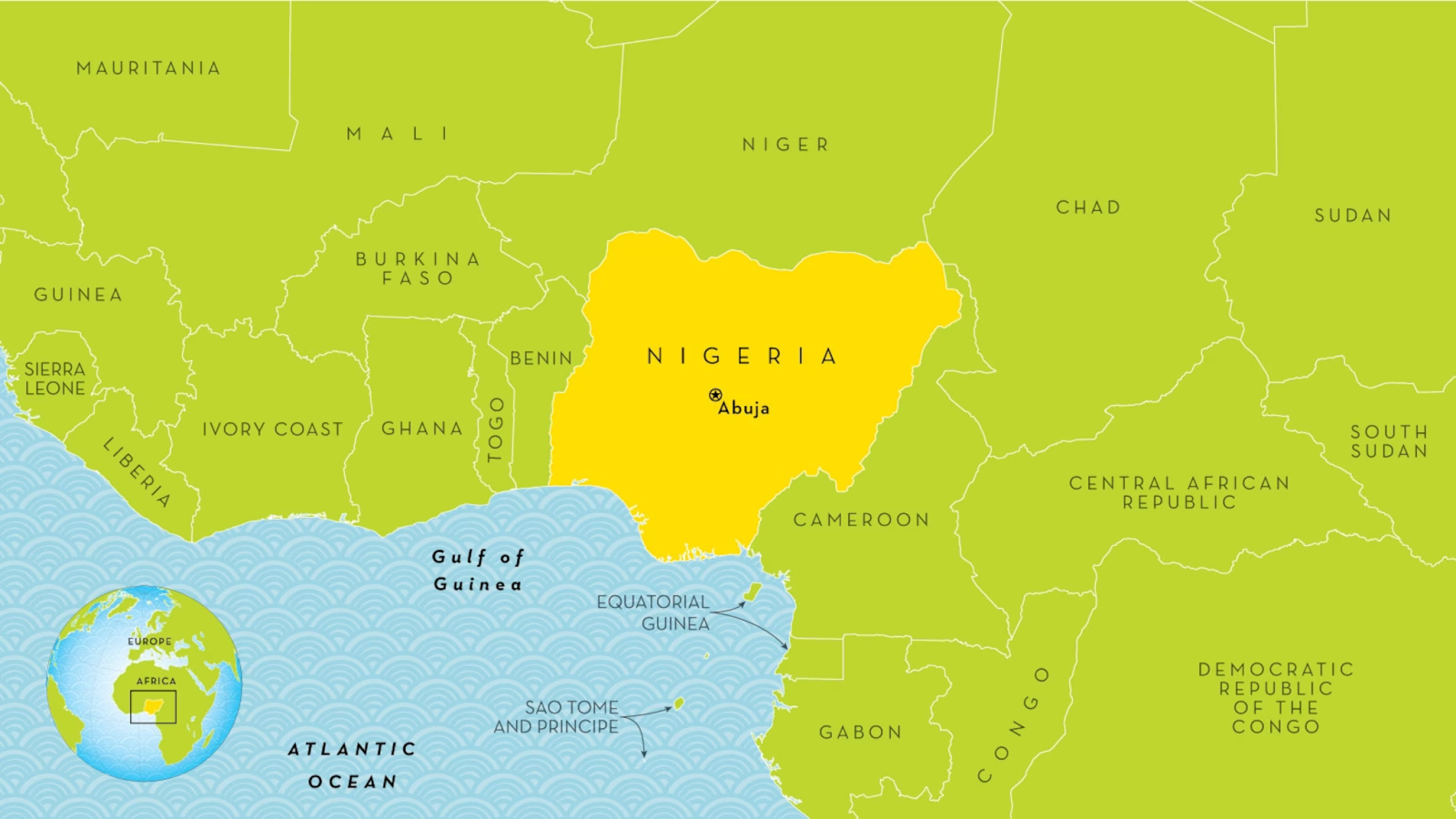
Nigeria
- Location: Nigeria is located on the western coast of Africa and is often called the Giant of Africa because of its size, population, and economic influence on the continent.
- It shares borders with Niger to the north, Chad and Cameroon to the east, the Gulf of Guinea to the south, and Benin to the west.
- Population and Economy: Nigeria has the world’s 6th largest population and Africa’s largest, and it ranks as the 4th largest economy in Africa.
- Rivers and Drainage: Nigeria’s main drainage basins are the Niger–Benue, Lake Chad, and the Gulf of Guinea. The Niger River and its major tributary, the Benue River, are the country’s most important rivers.
- Global Engagement: Nigeria recently became the 9th BRICS partner country (without membership or decision-making power), joining Belarus, Bolivia, Cuba, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Thailand, Uganda, and Uzbekistan.
- Nigeria, Africa's largest recipient of US aid, is shifting its focus to strengthen ties with China, India, and the EU to reduce its reliance on the US.
| Read More: PM's Visit to Nigeria, Brazil and Guyana |