Important Facts For Prelims
NISAR Satellite
- 31 Jul 2025
- 5 min read
Why in News?
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) - Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) satellite, an Earth observation mission, was launched by ISRO from Sriharikota.
What are the Key Facts About NISAR Satellite?
- About: NISAR, jointly developed by ISRO and NASA, is the first satellite mission to use dual-frequency radar (L-band and S-band) from a single platform, with advanced microwave imaging capabilities including polarimetric and interferometric data.
- Technical Features:
- Dual-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR):
- L-band SAR (by NASA): Penetrates forest canopy, ice, and soil, useful for biomass and deformation studies.
- S-band SAR (by ISRO): Better for monitoring crops, wetlands, and other surface-level features.
- Launch Vehicle: Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark II (GSLV Mk II) (specifically the GSLV-F16 variant), India’s largest rocket, is an expendable three-stage launch vehicle.
- The NISAR mission marks the first time ISRO is using a GSLV to place a satellite in sun-synchronous polar orbit.
- Mission Life: 5 Years.
- Phases: The mission includes four phases- launch, deployment, commissioning, and science operations.
- The deployment phase extends a 12-meter antenna 9 meters from the satellite, with commissioning in the first 90 days, followed by science operations for the rest of the mission.
- Dual-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR):
- Mission Objectives and Coverage: The NISAR mission will provide high-resolution data every 12 days to monitor land changes across Earth.
- It will track ground deformation caused by earthquakes, landslides, and volcanic activity.
- Measure forest biomass and carbon stock by observing woody vegetation.
- It monitors agricultural patterns such as crop extent and growth cycles, and assesses changes in wetlands driven by seasonal and climatic variations.
- Study cryosphere dynamics, including glacier and sea ice melt in the Arctic and Antarctic regions.
- Significance for India: NISAR marks as a key step in Indo-US space ties, the launch reflects India’s rise as a global science partner or ‘Vishwa Bandhu’.
- It supports disaster management, agriculture, and climate monitoring.
- Furthermore, India has joined the Artemis Accords and collaborated with NASA on human spaceflight, marking a deeper partnership in space exploration.
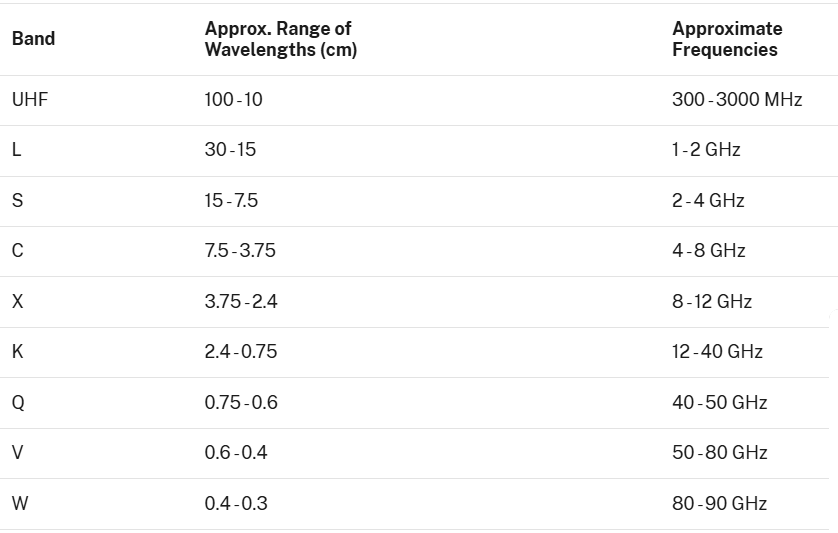
What is a Radar Band?
- About: Electromagnetic radiation with frequencies between about 10 kHz and 100 GHz are referred to as radio frequencies (RF).
- The RFs are divided into groups that have similar characteristics, called "bands," such as "S-band," "L-band," etc.
- Common Radar Bands:
- Significance:
- Lower frequency bands (L, S) can penetrate through rain, clouds, vegetation useful for mapping and Earth observation.
- Higher frequency bands (X, Q, V, W) give sharper images and better resolution, but are more affected by weather and atmospheric conditions.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements: (2018)
- PSLVs launch the satellites useful for Earth resources monitoring whereas GSLVs are designed mainly to launch communication satellites.
- Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the same position in the sky, as viewed from a particular location on Earth.
- GSLV Mk III is a four-staged launch vehicle with the first and third stages using solid rocket motors, and the second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 3 only
Ans: (a)
Q. Which of the following pairs is/are correctly matched? (2014)
Spacecraft Purpose
- Cassini-Huygens : Orbiting the Venus and transmitting data to the Earth
- Messenger : Mapping and investigating the Mercury
- Voyager 1 and 2 : Exploring the outer solar system
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)




.png)