Important Facts For Prelims
National Commission for Minorities
- 07 Jul 2025
- 5 min read
Why in News?
The National Commission for Minorities (NCM) has been functioning without a Chairperson and several members since April 2025, following the retirement of its previous leadership.
What is the National Commission for Minorities?
- About: It is a statutory body established under the National Commission for Minorities Act, 1992, with the vision to safeguard and protect the interests of minority communities.
- The first statutory Commission was constituted on 17th May 1993.
- Genesis: The Minorities Commission (MC) was established in 1978 through a Ministry of Home Affairs Resolution and was moved to the newly created Ministry of Welfare in 1984.
- In 1988, the Ministry of Welfare excluded linguistic minorities from the Commission’s jurisdiction.
- Composition: It consists of a Chairperson, a Vice-Chairperson, and five Members, all nominated by the Central Government but absence of a full body has led to concerns over inefficiency.
- Each member must belong to one of the six notified minority communities: Muslim, Christian, Sikh, Buddhist, Parsi, and Jain.
- Powers and Tenure: It has quasi-judicial powers and each member serves a three-year term from the date they assume office.
- Removal: The Central Government may remove the Chairperson or any Member of the NCM if they:
- Are adjudged insolvent,
- Take up paid employment outside their duties,
- Refuse or become incapable of acting,
- Are declared of unsound mind by a court,
- Abuse their office, or
- Are convicted of an offence involving moral turpitude.
Who are Minorities in India and what are their Constitutional Safeguards?
- About Minorities: The Constitution of India does not provide a definition for the term ‘Minority’, but the Constitution recognises religious and linguistic minorities.
- The NCM Act, 1992 defines a minority as “a community notified as such by the Central government.
- Minority Communities: As per a 1993 notification by the Ministry of Welfare, the Government of India initially recognized five religious communities—Muslims, Christians, Sikhs, Buddhists, and Zoroastrians (Parsis)—as minority communities.
- Later, in 2014, Jains were also notified as a minority community.
- Minorities Population: According to the 2001 Census, these six communities together constitute 18.80% of India’s population.
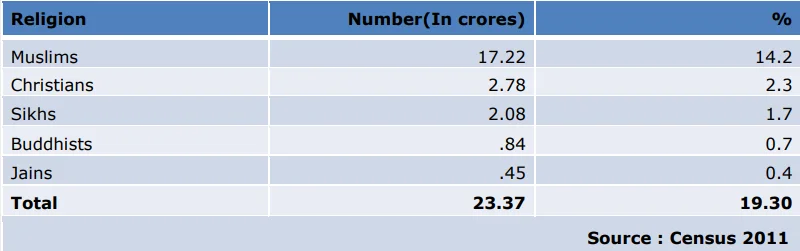
- While the 2011 Census does not mention the Parsi population, it is estimated at around 57,000.
- Safeguards Related to Minorities:
- Article 29: Right of any section of citizens to conserve their distinct language, script, or culture.
- Article 30: Right of minorities to establish and administer educational institutions.
- Article 347: Special provision relating to the language spoken by a section of the population of any State.
- Article 350-A: Provision for facilities for instruction in mother-tongue at the primary stage.
- Article 350-B: Provision for a Special Officer for Linguistic Minorities and his duties.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. What was the exact constitutional status of India on 26th January, 1950? (2021)
(a) A Democratic Republic
(b) A Sovereign Democratic Republic
(c) A Sovereign Secular Democratic Republic
(d) A Sovereign Socialist Secular Democratic Republic
Ans: (b)
Q. The Preamble to the Constitution of India is (2020)
(a) a part of the Constitution but has no legal effect
(b) not a part of the Constitution and has no legal effect either
(c) a part of the Constitution and has the same legal effect as any other part
(d) a part of the Constitution but has no legal effect independently of other parts
Ans: (d)






