Indian Economy
MPC Keeps Repo Rate Unchanged
- 12 Apr 2024
- 7 min read
For Prelims: Reserve Bank of India, Banking sector & NBFC, Sovereign Green Bond, Monetary Policy Committee, Fiscal policy, Repo Rate, inflation,
For Mains: Significance of interest rate in fiscal policy and monetary policy
Why in News?
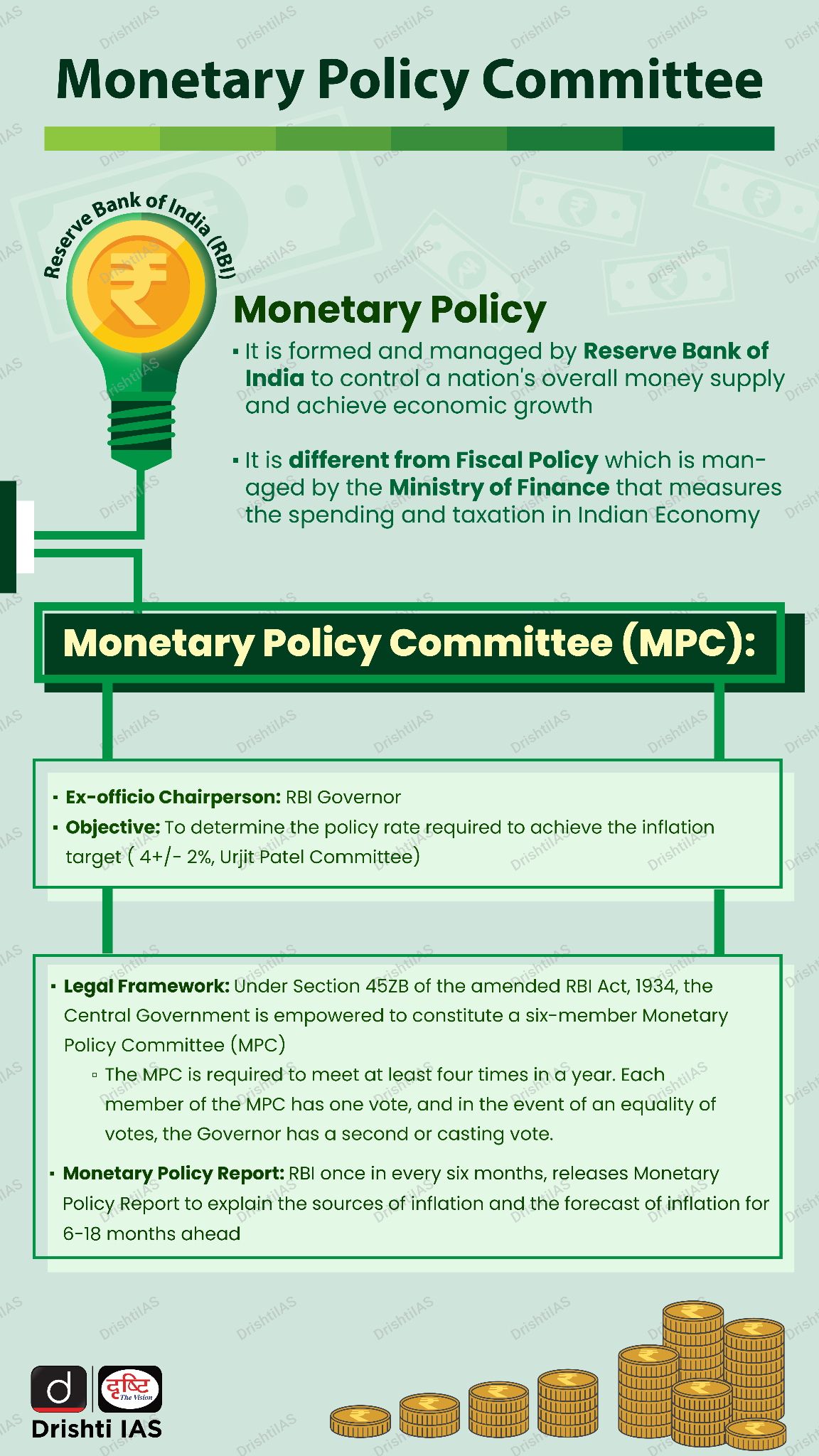
Recently, the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) voted in its meeting to keep interest rates unchanged. The repo rate stands at 6.5%.
- The committee also decided to remain focused on the withdrawal of accommodation.
Note:
- Accommodative Monetary Policy: An accommodative stance means the central bank is prepared to expand the money supply to boost economic growth.
- The withdrawal of accommodative policy means a reduction of the money supply in the system which will rein in inflation.
What are the Outcomes of the MPC Meeting?
- The RBI has retained the GDP growth forecast at 7% for FY25 as against the 7.6% growth projected by the National Statistical Office (NSO).
- It has projected a growth of 7.1% in the first quarter of FY25, 6.9 per cent in Q2, and 7% each in Q3 and Q4.
- The MPC decided to keep the policy repo rate under the liquidity adjustment facility (LAF) unchanged at 6.50% and the standing deposit facility (SDF) at 6.25%.
- The MPC remains committed to aligning inflation with the 4% target within a band of +/- 2% while supporting the objective of growth.
What are the Reasons for Holding Interest Rates Unchanged?
- Food Inflation
- Higher food inflation keeps headline inflation elevated even though the Indian economy has witnessed broad-based moderation in inflation.
- The uncertainties in food prices continue to pose challenges, due to global uncertainties and the effect of El Nino.
- The arrival of rabi harvests in the market along with expectations of a normal monsoon, next year will also alleviate pressure on food prices.
- However, the food and beverages inflation remains elevated led by price pressures in vegetables, pulses and spices.
- Festival Season:
- The festive season will promote liquidity in the market due to inflated demand and increased consumption during festival days.
- Crude Oil Prices and Input Costs:
- Crude oil prices have eased, but the outlook remains uncertain, due to global uncertainty because of regional conflict and supply chain disruptions.
- Resilient Economic Activity:
- The Indian economy has displayed resilience despite the uncertainties and challenges posed by various factors.
- This has led to the decision to maintain benchmark rates, reflecting confidence in the economy's ability to withstand potential shocks.
- Previous Policy Repo Rate Hikes:
- The Monetary Policy Committee acknowledged that the previous policy repo rate hikes are still in the process of influencing the economy.
- Inflation Risk Management:
- Keeping rates unchanged might be a precautionary measure to closely monitor the situation and be ready to act promptly in case inflationary pressures escalate.
What is Inflation Targeting?
- About:
- Inflation targeting in India is a monetary policy framework that was adopted by the Reserve Bank of India in 2016.
- Under this framework, the RBI targets the inflation rate and uses monetary policy instruments to achieve it.
- Currently, RBI's primary objective is to achieve the 4% inflation target. The RBI has a comfort zone of +/- 2% within which inflation must remain. This means that the RBI aims to keep the inflation rate between 2% to 6%.
- Limitations:
- Structural Constraints: Inflation targeting may not be effective in addressing supply-side shocks or structural constraints that affect the economy, such as inadequate infrastructure, which can lead to higher inflation.
- Exchange Rate Volatility: Inflation targeting can lead to exchange rate volatility, particularly in countries with open economies, as changes in interest rates can affect capital flows and exchange rates.
- Socio-Economic Impacts: Inflation targeting can have social and economic impacts, particularly on vulnerable populations, as changes in interest rates can affect employment, income, and other macroeconomic variables.
- Data Availability: Inflation targeting requires accurate and timely data on inflation and other macroeconomic variables, which may not be available in all countries, including India.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Discuss the reasons for keeping the repo rate unchanged and the role of the Monetary Policy Committee in inflation targeting. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q1. Concerning the Indian economy, consider the following: (2015
- Bank rate
- Open market operations
- Public debt
- Public revenue
Which of the above is/are component/ components of Monetary Policy?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 1, 3 and 4
Ans: c
Q2. If the RBI decides to adopt an expansionist monetary policy, which of the following would it not do? (2020)
- Cut and optimize the Statutory Liquidity Ratio
- Increase the Marginal Standing Facility Rate
- Cut the Bank Rate and Repo Rate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q.1 Do you agree that the Indian economy has recently experienced V-shaped recovery? Give reasons in support of your answer. (2021)